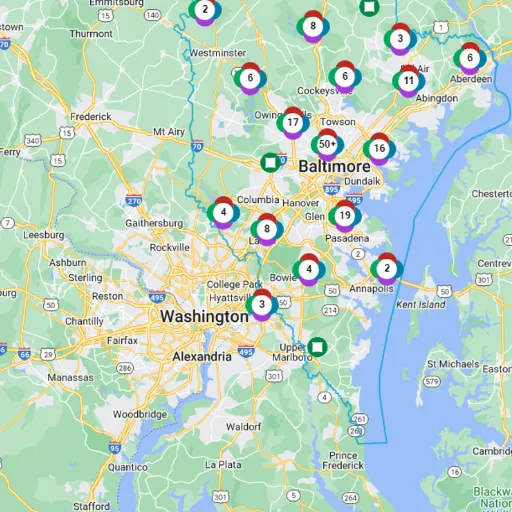
Power outages do not just merely inconvenience residents; they disrupt daily lives, local businesses, and may even be dangerous. Hence, knowing the scale and cause of outages in Washington, D.C., bears special significance for both residents and businesses. This small piece guides you through the D.C. Power Outage Map, a powerful outage tool that tracks updates in real-time and provides outage analysis throughout the district. Whether you want to learn about the leading causes of outages, understand the interpretation of the outage map, or prepare for unexpected power outages, this blog will equip you with the knowledge you need to become a knowledgeable entity in all things related to outages.
Overview of Power Outage Map in D.C.
Severe weather conditions, equipment failure, or grid maintenance are the most common causes of power outages in D.C. High winds, heavy rains, and ice storms damage power lines, while infrastructure-related uncertainties and load management issues increase disruptions. Planned outages are two prevalent situations in which such services are interrupted to complete one or another aspect of electrical maintenance. The areas affected by these outages may vary from small pockets to large sections of the district. Knowledge of the essential causes of outages allows residents and businesses to be better prepared to limit potential disruptions.
What Causes Power Outages?
Disturbances in electric power exist in three major categories: transient, sustained, and brownouts. Transient outages—momentary interruptions, for instance—are mostly caused by temporary disruptions, such as a tree branch making temporary contact with a power line. Sustained outages indefinitely cut off the electricity supply through damage to infrastructure by severe weather events such as hurricanes, thunderstorms, or ice storms. Brownouts, meanwhile, are characterized by the lowering of voltage in the electrical system, typically associated with demand exceeding supply during peak periods.
External factors like extreme weather conditions, downings of trees, animals climbing and bridging between phases – common causes of power outages – lightning strikes overload systems, while winds blow down power lines. Human activities, including incidental damage caused by construction works or other factors, can collide with utility poles and significantly contribute to the situation. Potential cyber-attacks on grid systems represent additional modern-day hurdles, besides having equipment failure linked with grid aging or inadequate maintenance, to the reliable delivery of electrical energy across grids.
Recent Trends in D.C. Power Outages
Recent records point to a marked increase in power outages in the District of Columbia due to the interplay of several factors. Climate change has intensified the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, such as storms and heatwaves, placing a greater strain on electrical infrastructure. For example, during the summer months, severe thunderstorms have been increasingly causing more extended outages owing to the extensive damage they inflict upon overhead power lines. On the other hand, with rising urban development, there has been an increasing demand on the electrical grid, thus putting its capacity and resilience to the test.
Another sore contributor is aging infrastructure. Most parts of the D.C. grid were installed decades ago and now desperately need modernization to carry the modern loads efficiently. The utilities, however, have been upgrading parts of their system to more resilient ones, such as underground cables, but these take years and a lot of money. The design and enhancement of robust cybersecurity measures for physical infrastructure have become a concern, especially against emerging cyber threats that target critical infrastructure systems. The challenges discussed underscore the urgency of grid modernization to ensure an uninterrupted energy supply in the current circumstances.
Impact of Weather on Power Supply
Extreme weather patterns and conditions hamper the very essence of existence, from good reliability and efficiency in services needed by power supply systems considered. They can record numerous power outages, downed transmission lines, and impediments in energy distribution processes. Such ice storms, for instance, are essentially considered hazards that put undue strain on power lines and equipment, thereby distorting them. In contrast, the high temperatures of a heatwave lead to increased electricity use from the widespread use of air conditioning. Data show how discrepancies against weather disturbances have been growing over recent years due to climate change. This immediately highlights the need for climate-resilient designs, i.e., weather-resistant materials and distributed energy systems that can evolve into a safe and reliable energy source, regardless of adverse weather conditions.
How to Access the D.C. Power Outage Map?
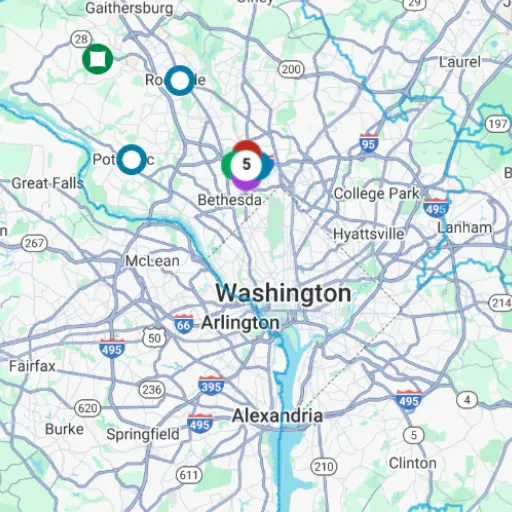
The following steps will guide you in using the D.C. Power Outage Map:
- Visit the Official Website: Open up a browser and head to the official website of your local utility company, such as Pepco.
- Locate the Outage Map Section: Thereon, locate the link or tab named “Outage Map” or “Power Outages.” It is usually present in the main menu or under a “Customer Resources” section.
- View Outage Details: Head over to the outage map page to find severe weather reporter updates on the status of power outages, including affected area data, estimated restoration durations, and the number of customers affected by the outages.
For the most up-to-date information, it is essential to visit the utility provider’s official platform.
Official Sources for Outage Maps
Official outage maps provided by utility companies should be relied upon most for complete and accurate information regarding power outages. These maps are typically kept up-to-date with information on affected zones, estimated restoration times, and an outline of the extent of disruption. Secondary analysis based on verified data available through other online portals provides a more detailed picture of the context. For example, such supplementary information might identify adjacent issues with infrastructure or locate alternative service providers. Using both will supply the most reliable and actionable insights without relying on either alone. Always cross-check any information from secondary sources against that given on the official platform of the utility provider for verification.
Third-Party Resources and Apps
Analysis of third-party data sources and software thus becomes necessary when attempting to present a synthesis of accurate data stemming from many verified sources. The software collects information from official databases, company reports, and public records, and is updated with the latest information. When faced with search algorithms, they highlight emerging trends and inconsistencies, which in turn enhance the decision-making process. This complementary use of platforms provides an extensive and secure data-based analytic foundation that users can use to resolve their problems effectively.
Interpreting the Outage Map Data
Outage map data interpretation requires a multilateral approach, utilizing in-depth visualization tools and advanced search engine-based integrations. In this concept, a graphical overlay is combined with relevant, up-to-date information retrieved from trustworthy online platforms, thereby enhancing the depth of insights. Such integration is capable of spotting emerging patterns and assisting with determining and understanding the problematic infrastructure zones, scale, and possible sources. Exploiting dynamic data streams makes it possible for each user to engage in an assessment process of their own, forecasting interrupts with precision from which they will navigate intervention decisions to ensure resources get assigned to where they matter most.
What to Do During a Power Outage?

Stay Safe and Alert
- Check for any immediate hazards – are there down wires or erratic electrical equipment that could pose a risk to your safety?
- Switch on flashlights or battery-powered lanterns; avoid using candles as a fire hazard.
Contact Your Utility Provider
Notify the electricity provider if the outage has not yet been announced. Most providers have posted maps and updates on outages via their mobile apps or websites.
Preserve Food and Water
- Keep the doors of your fridge and that of the freezer shut to retain the cool temperature for the longest time possible, as perishable items usually remain good for about 4 hours in a closed fridge.
- If need be, use coolers and ice to store crucial goods.
Unplug Electrical Devices
Unplug appliances and electronic equipment to protect them against power surges upon power restoration.
Follow Emergency Updates
Stay informed about weather conditions, safety instructions, and information about restoration from a battery-powered or hand-crank radio.
Avoid Overloading Generators
If you plan to use the portable generator, ensure it is placed outside and at a distance from any windows or doors to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
Prepare for Extended Outages
- Save your phone battery using power saver mode and use it only for essential calls.
- Grab your power bank; if medically necessary, look for activation of emergency generators.
Safety Precautions to Take
Stay Aware of Carbon Monoxide Risks
Using carbon-monoxide generators like portable generators must always be done outdoors in an open-air setup, a space at least 20 feet remote from any home for safety. Also, ensure that your homes are fitted with working carbon monoxide detectors so that they can warn you when there is any accumulation.
Safeguard Against Electrical Hazards
Avoid touching any fallen power lines, for they may actually be live and dangerous. Threatened lines should immediately be reported to any power company concerned. When using power restoration equipment such as generators, make sure all connections respect electrical safety measures to prevent backfeeding that can put utility workers at risk.
Ensure Proper Food and Water Safety
Minimizing the number of times your fridge and freezer are opened during a power outage is required to maintain food temperatures. Consume or discard perishable foods after four hours of no refrigeration. Also, ensure you can access clean water; if it is not available, be sure to boil or use purification tablets.
Maintain Communication Systems
Keep a battery-operated or crank-powered radio with you so you can always be informed of any updates from your local authorities. For digital communications, get surge protectors and a wall charger with an inverter built in so that you can protect your devices and stay connected through the outage.
Plan for Emergency Lighting
Go for LED flashlights and lanterns for efficient lighting during an outage, alternatively. Avoid candles whenever possible, as they pose a fire hazard, especially in areas where they will not be supervised or where there is high activity. Stock extra batteries so you can retain lights for a long time.
Prioritize Health Precautions
If you or anyone uses power-dependent medical devices, seek assistance in your local outage management program ahead of time to locate those providers who will assist you with backup power or to shelter you temporarily. Store your first aid kit well for easy access in case of a minor injury or emergency.
How to Report an Outage
A customer should report a power outage as soon as possible to enable the utility to respond in a timely manner. To report an outage, first, try to check if the outage is just affecting your own location by viewing a few properties around or contacting some neighbors. Next, if it appears that the outage covers a wider area, follow the steps below:
- Contact Your Utility Provider: Locate your local electricity provider’s phone number or website, typically listed on your utility bill or available on their official website. Most providers have a hotline for reporting outages or a web form for faster processing.
- Utilize Mobile Apps: Many utilities offer mobile applications that allow you to report outages directly. Mobile applications often contain tracking options to follow up on repairs in real-time.
- Leverage Social Media or Alerts: Monitor your utility company’s official social media pages. Updates are frequently posted regarding ongoing outages and restoration times. Some companies also respond to reports concerning outages via these platforms.
- Verify Safety Conditions: When reporting the outage, describe visible faults, such as power lines down or damaged transformers. Do not approach those faults and notify the relevant authorities if necessary to limit risks.
- Sign Up for Notifications: Subscribe to outage alerts offered by your power utility. These alerts usually provide updates on restoration, repair status, and, in high-risk weather events, preventative measures.
Being very detailed within the report, including but not limited to the time of the outage and any observed damages, will help the repair team quickly identify and fix the issue. Have all information related to your account ready when placing the report, as this will speed up the process.
Staying Informed During an Outage
During an outage, reliable sources of information should be prioritized. Seek official updates from your utility provider’s website, mobile apps, and social media channels since they will provide the most accurate and up-to-date information. Local news agencies and weather-related reporting will also be of help. Emergency radio broadcasts could provide you with great updates if available. Do not listen to unverified sources; to ensure the information you receive is reliable and up to date.
Utilizing Social Media for Updates
Consider social media platforms as a corroborating source of information, presenting live updating and community insights. By following verified emergency service, utility, or local authority-related accounts, users can gain quick access to the most urgent updates relevant to their area of concern. Additionally, these experienced search tools can identify authoritative sources while verifying information disseminated on social media. This synthesis method ensures a high degree of accuracy with wide coverage, ultimately enabling an informed decision-making process in the event of an outage or critical event.
Local News and Alerts
Local news and real-time alert systems form the backbone behind sourcing pinpointed and localized information during emergencies or critical events. By also littering those updates in advanced search engines, individuals would be assured of getting timely information on disruptions, hazards, and recovery efforts from verified sources. These sources compile data from credible sources, such as municipal websites, emergency broadcast channels, and community organizations, to provide excellent insight into rapidly changing situations. This enhances situational awareness and facilitates instant, well-informed decisions regarding the phenomenon that a given community is currently facing.
Community Resources and Support
Integrating community resources with advanced information-gathering tools makes the information flow seamless in situations. By referencing local aid networks, volunteer organizations, and verified public initiatives, one can identify key support avenues that are targeted towards their needs. These resources, in tandem with modern information systems, will map out the specifics of ad hoc aid, including the location of shelter sites, medical services, and logistical support centers. Thus, the data from this integration is both local and actionable, which facilitates strong teamwork, rapid decision-making to mitigate the impact, and accelerates recovery.
Post-Outage Considerations

After an outage is declared, the restoration of communications becomes paramount in order to enable the dissemination of critical information and facilitate coordination. An assessment of the status of local cellular networks and Internet Service Providers should begin immediately. Where they are offline ,establish connectivity through alternative means such as satellite phones or radio networks. Collaborate with local authorities and service providers to establish restoration timelines and interim solutions. In cases of massive outages, emergency communication hubs should be established to keep the public informed and provide assistance. Document and account for all actions taken, keeping all stakeholders informed to maintain transparency and trust throughout the recovery period.
Restoration Process Explained
The restoration process is essentially a service approach that methodically identifies, addresses, and resolves service disruptions. The first step involves a thorough assessment of the disturbance to determine the scope of the issue, including the construction of affected areas and the implementation of preemptive measures for critical systems to minimize their impact. Advanced diagnostic tools, combined with real-time monitoring and data analysis, facilitate actionable insights into fault locations and causes with precision in resolution.
Further, mobilize teams to repair where necessary and equip the teams with all tools and resources required while adhering to industry best practices and safety standards. Further, enforce redundancy to maintain partial functionality while full service is being restored. An example would be dynamic rerouting of traffic through unimpacted networks to preserve essential functions during repair operations.
Throughout fault management, communication with stakeholders should be maintained at all times, employing automated updates to provide accurate and timely information via email, SMS, or even through public dashboards. Alongside restorations, regular system tests and performance validation guarantee that all services are operational and capable of withstanding any further disruption. Continuous improvement strategies, including a post-incident review and feedback integration, round out the framework and make it ready for restoration at an enhanced speed and with greater reliability.
Assessing Damage and Claims
An equitable truce will be established to resolve disputes over damage and claims, which entails a step-by-step valuation of the affected parties to determine the magnitude of loss and the resources required to effect recovery thereof. Advanced data analytics and geospatial tools play a crucial role in gathering situational insights, including high-resolution imagery and weather pattern analysis. These technologies, along with historical damage patterns and predictive modeling, pinpoint the impacted sectors with precision.
Besides, the claims verification processes are streamlined through digitized records, real-time data validation, and blockchain-based systems to preserve the integrity of the process with accuracy. In contrast, these structured approaches serve stakeholders by providing final evidence-based decisions with less ambiguity in decision-making. Employing such advanced procedures minimizes delays in processing while ensuring efficient resource allocation and further speeding the actual restoration processes.
Long-Term Improvements to Power Infrastructure
Technological enhancement backed by strategic planning must be considered for the sustained resilience and efficient power infrastructure. The installation of smart grid systems is at the crux of real-time monitoring, fault detection, and activation to disruptions. Incorporating renewable energy, especially wind, solar, and hydro, fosters legitimacy issues in fossil fuel reduction and provides for the global sustainability agenda. Energy storage, facilitated by innovations in battery technology, such as lithium-ion batteries and the soon-to-emerge lithium solid-state storage, is crucial for mitigating supply disruptions to renewable energy.
Modernization of transmission and distribution networks will, in turn, enhance efficiency and reduce power losses through the use of advanced conductor materials and the application of high-voltage direct current (HVDC) technology. System defense mechanisms must be deeply entrenched in cybersecurity protocols as the digitalization of the infrastructure develops, in order to protect against possible cyberattacks. Supporting R&D and policy interventions that promote collaboration between private and public sectors will ensure that power systems not only curb demands at present but can also address expected challenges in the coming days, such as rapid urbanization and greater electrification of sectors, including transport. It is through this that power infrastructure can then be made more reliable, sustainable, and resilient.
Reference Sources
-
- Key Findings: This study explores how cognitive service technology can enhance the monitoring and identification of issues in DC power systems. It highlights the use of convolution maps as a critical tool for identifying potential disruptions and improving system reliability.
-
- Key Findings: This paper examines how data science and machine learning can optimize electricity management policies, focusing on reducing costs and improving power quality. It includes an analysis of power outage statistics to identify patterns and propose solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How can I check for a power outage in my area?
A: To see if there is an outage in your area, visit the D.C. Power Atlas online. Most utility companies offer such a service, and their services get updated every minute or so to reflect the current conditions. You want to keep your browser updated to the latest versions of Firefox, Chrome, or Safari while browsing outage information for optimal performance. You may also report outages to your utility company so that you get the most accurate information. Tracking the outage map will help you get an idea of the severity of the power disruptions.
Q: What should I do during a power outage?
A: During a power outage, remain calm and safe. First, check if the area is affected using the D.C. Power Outage Map. If so, try not to light candles; use flashlights instead. Unplug all sensitive gadgets to prevent them from getting damaged once power returns. Keep abreast of news updates and outage maps, armed with your mobile data. Eventually, when you face a long outage, you have to food-saver-mode for your refrigerator and freezer.
Q: How often is the D.C. power outage map updated?
A: The D.C. power outage map is updated either in real-time or at block intervals whenever new outage information becomes available. The utilities tend to keep the map at maximum levels of accuracy regarding the information on current outages and estimated restoration times. This is necessary so that residents can plan ahead in the event of outages. If you experience a prolonged outage, you may want to check it frequently or set up alerts from your provider. Additionally, having a reliable internet browser is helpful when viewing the map.
Q: Can I report a power outage through the outage map?
A: Yes, most D.C. power outage maps allow their users to report those outages directly from the platform. This enables utility companies to respond quickly to issues that arise in the area. When reporting, always provide as accurate information as possible regarding your location, the nature of the outage, and other relevant details. This is sometimes useful in assisting the Exelon Company and other local utilities to prioritize their response efficiently. Excellent way to provide for the cumulative safety and service restoration efforts.