Every so often, you might experience an unforeseen power outage. As you rearrange previously set activities, this can create a parasitic drain on your daily life. Severe weather or natural disasters can lead to interruptions in your daily schedule. Purchasing standby generators removes this worry, providing peace of mind and allowing you to continue your daily routine when the power goes out. There’s no need to worry about safety when investing in a fluid power system. This article will walk you through all the parts that make up a power generator and how to install them to create a self-sustaining and uninterrupted system. Prepare yourself for a future where you’ll feel less worried about the resiliency of your home and the reliability of energy sources.
What is a Standby Generator and How Does it Work?

A standby generator automatically provides power to your home during an outage. It’s usually installed outside your house like a window air conditioning unit and connects to your home’s electrical system. Standby generators use fuel sources such as natural gas or propane, allowing the generator to run reliably unattended. During the outage, crucial systems like lights, heating, cooling, and smart appliances, are powered seamlessly. The generator powers down once utility power is restored and switches back to featuring regular energy when available.
Understanding the Basics of a Standby Generator
A standby generator is a powerful backup power solution that automatically provides power to homes and businesses during power outages. These generators are installed outside the house and connected to an existing fuel supply, such as natural gas or propane. Modern standby generators are more efficient with technological advancements and can, depending on their capacity, power an entire household.
Key Features and Specifications:
- Power Output: Standby generators vary in capacity, typically from 7 kW to 150+ KW. Smaller residential units may provide enough power for essential systems, while larger units can serve full-house backup or commercial operations.
- Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS): The ATS is an integral part of the system that monitorsthe power supply and identifies any interruptions. Automatic generators turn on within seconds of a blackout and switch to standby power, creating an almost unnoticeable transition.
- Fuel Efficiency:
- Natural Gas: An inexpensive and clean fuel source for urban areas.
- Propane: Commonly used in rural areas where natural gas is not accessible. A 500-gallon propane tank can fuel a 20 kW generator for 5 -6 days under full load.
- Noise Levels: Newer standby generators are designed to be quieter than older ones, averaging around 60-80 decibels, which is equivalent to a conversation or a running dishwasher.
- Durability:
- Many models stand up to severe environmental conditions due to their weather-resistant enclosures.
- Advanced systems have corrosion-proof aluminum or steel casings, extending the generator’s lifespan.
Benefits of a Standby Generator:
- Reliability: With automatic activation, the generator does not need to be manually started in case of an emergency.
- Convenience: Unlike portable generators, standby generators usually do not require manual refueling.
- Safety: Standby generators avoid issues caused by power outages, such as sump pump failure, pipes freezing, or security systems shutting down.
Industry Trends and Data:
- Market Growth: A 2023 industry report stated that the standby generator market is set to grow at a 6.7% CAGR globally between 2023 and 2030 due to an increase in weather-related power outages and an elevated need for uninterrupted power supply in residential and commercial buildings.
- Power Outages: A study conducted in the U.S. showed that the number of power outages has increased by 64% over the last decade, supporting the need for reliable backup power solutions.
- Green Energy Integration: Many manufacturers are working towards creating renewable energy-powered standby generators that align with eco-sustainability goals.
Follow these basic details and keep yourself updated with the latest information. You can make the right choice in selecting and using a standby generator for your requirements.
How a Standby Generator Provides Backup Power
Standby generators automatically start during a power outage and ensure the uninterrupted flow of power and Electricity in standby for critical systems and appliances. These are a few of the many benefits of using standby generators. Here is a five-key overview of how standby generators work.
- Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS): The smart automatic switch monitors the utility power supply and instantly switches to generator power on standby whenever there is a system outage, minimizing downtime.
- Sustained Fuel Reserve Supply: Standby generators are usually mounted onto a gas pipeline or a propane container. This allows them to operate without changing fuel boxes.
- Voltage Regulation: Sensitive electronic and devices risk permanent damage to their inner workings due to slight changes in power fluctuations. Advanced standby generators, modern model pre-orders, modifications, and can protect such devices with enhanced voltage output controlling tech.
- Load Management: Limiting the overworking of fuel-powered generators allows for several different options. This aids in directing power to the most needed areas.
- Remote Monitoring: The Gen Z operator side of devices is well ahead of the users, with modern fuel powering shift generators. The users are now in control of the overall Gen settings on shift to mobile theorem and user interfaces.
Every one of these modernized things works together for a broad range of standby fuel-powered turbines. They cannot only shift the user over to a new fuel rather than standby; they also provide disable modes to the user enabling unlimited power while disabling the charger, which then gives a constant flow of fuel aid in case of outages, powerful changes while ensuring smooth sail with uninterrupted, highly responsive degree of convenience.
Choosing Between a Portable Generator and a Standby Generator
| Key Point | Portable Generator | Standby Generator |
|---|---|---|
|
Power Output |
3,000–8,500 watts |
8,000–20,000+ watts |
|
Price Range |
$400–$1,500 |
$2,000–$5,000+ (installation extra) |
|
Fuel Type |
Gasoline, propane, diesel |
Natural gas, propane |
|
Operation |
Manual start, requires setup |
Automatic start, seamless operation |
|
Mobility |
Portable, easy to move |
Fixed, permanently installed |
|
Installation |
No installation needed |
Professional installation required |
|
Noise Level |
Louder operation |
Quieter operation |
|
Maintenance |
Regular refueling, manual upkeep |
Minimal, professional servicing |
|
Best For |
Short outages, budget-friendly |
Long outages, whole-home power |
|
Safety |
Requires outdoor use, CO risk |
Safer, integrated with home systems |
How to Install a Standby Generator in Your Home

- Pick the Right Generator
Evaluate the power capacity based on the appliances and systems you want operating during the downtime.
- Choose a Correct Position
Mount the generator outside on a stable and level surface, ensuring it is a safe distance away from windows, doors, physical structures, or air vents where carbon monoxide does not pose a risk.
- Secure Permits
Before doing anything, ensure you review the local laws and acquire any permits needed to follow the building codes.
- Prepare the Location
Make sure that the region you are setting up the generator is tidy, and then set up an appropriate platform—ideally a concrete pad—for it to sit on.
- Install the Transfer Switch
Get a licensed electrician to set up an automatic transfer switch to increase efficiency by seamlessly shifting power mid-use of the generator.
- Connect to Fuel Line
Safely attach the generator to a dependable fuel line, such as natural gas or propane. However, this should be dealt with by a professional.
- System Testing
Once the transfer switch and the generator have been connected, check and see if they function effectively and manage the load effectively if enabled.
- Schedule Periodic Inspections
Follow up with the generator and have it inspected at intervals to keep it in good condition.
Hiring a certified electrician or technician for the installation is highly recommended to ensure safety and proper functionality.
Steps in the Installation Process
- Plan the Installation Site
Find an appropriate site for the generator that will ensure compliance with the local safety limitations and guarantee adequate ventilation. Based on recent industry trends, generators need to be located 5 feet from all doors, windows, and vents due to the risk of Carbon monoxide exposure. Furthermore, the location should also be level and have sufficient space for maintenance.
- Secure Permits
Obtain all the permits from the relevant authorities and local bodies to install the generator. Permits vary from regions where some may need documents for inspection to check for compliance with building codes and safety standards.
- Install The Transfer Switch
The transfer switch is extremely important as it ensures seamless and safe switching from utility power to generator and vice versa. According to the latest recommendations, this step should only be done by a licensed electrician to avoid backfeeding, which is hazardous for people working on electric lines.
- Prepare the Foundation
Design a solid and reliable base that can withstand the weight of the generator unit. Concrete pads or prefabricated generator pads are usually best for reliability. For example, residential generators, typically 10-20 kW, tend to weigh around 300-500 pounds, thus requiring a robust base.
- Connect the Generator to the Fuel Source
Install a fuel line with sufficient capacity to a fuel source such as natural gas, diesel, or propane. Recent recommendations propose using more corrosion-resistant materials and ensuring the fuel line’s capacity adequately supplies the generator’s power needs.
- Wire the Electrical System
Connect the generator to the home or building’s electrical system via the transfer switch.. Generator wiring should include a connection to the electrical system of the home or building using a transfer switch. All wiring must comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC) for functionality and safety.
- Conduct System Testing
After installation, check the system to verify that all connections operate as intended. Suggested practices include load testing or other checkups that validate the generator’s capacity against its operational requirements. Reports say the testing should incorporate realistic scenarios, including power outages, to verify reliability.
- Establish Maintenance Protocols
Implement a maintenance schedule for tasks such as oil changes, air filter inspections, and battery checks. More recent insights suggest standby generators require servicing every 6–12 months or after 200 hours of use for optimal performance.
As outlined, attention to detail, adherence to guidelines, and employing the latest safety recommendations ensure efficient and secure installation. Generator setup and ongoing professional support should always accompany expert assistance.
Connecting to the Electrical System: What You Need to Know
While connecting to the electrical system, I detach all power sources before commencing work. Transfer switches serve to safely connect generators and electrical panels, which cancels backfeeding while safeguarding utility workers. Within the guidelines of the manufacturer’s specifications, I check all connections to make sure there are no loose ends. Whenever in doubt, hiring a licensed electrician serves as the safest way to guarantee everything is executed appropriately.
What is the Cost to Install a Home Standby Generator?

The cost of installing a home generator system may vary greatly based on the type of generator and installation. On average, the installation of generators will cost between $5,000 and $15,000.
- Generator Costs: Depending on wattage and features, a generator can cost between $2,000 and $6,000. Smaller generators that power essential circuits will be more affordable, while larger units that power the entire house will be more expensive.
- Installation Expenses: The installation is likely to cost between $3,000 and $10,000. Other additional expenses related to the installation will be hiring an electrician, site preparation, pouring concrete/composite pads, and gas line connection. The general complexity of the electrical work also influences pricing.
- Permits: An additional required expense will be the permit. Local jurisdictions often require a permit for generator installation, which costs between $50 and $200.
- Transfer Switches: Activate switches, critical in installing an electric system will on average cost $400-2000 even after labor.
- Maintenance Contracts: Some homeowners prefer subscription plans, which average about 200 to 500 a year, to keep the generator in peak condition.
Regional labor rates and the accessibility of gas lines can still influence the overall cost. It is crucial to get estimates from different contractors, considering all expense possibilities like site preparation and fuel source connections. Although the standby generator might seem costly initially, it assures peace of mind for homeowners facing unpredictable or prolonged power outages.
Factors Affecting the Installation Cost
The installation cost for a home generator depends on permits and the unit’s power capacity. Local labor prices, the type of fuel, and the complexity of the site preparation are also main components.
How Much Does It Cost to Install the Generator?
| Key Point | Portable Generator | Standby Generator |
|---|---|---|
|
Unit Cost |
$500–$2,500 |
$3,000–$6,000 |
|
Installation Cost |
$400–$1,300 (optional) |
$3,000–$5,000 |
|
Total Installed Cost |
$900–$3,800 |
$6,000–$11,000 |
|
Fuel Connection |
Manual refueling |
Connected to gas line |
|
Transfer Switch |
Optional, $400–$850 |
Required, $600–$2,500 |
|
Concrete Pad |
Not required |
$150–$400 |
|
Permits |
Not required |
$50–$200 |
|
Labor Cost |
Minimal or DIY |
$40–$100/hour |
|
Best For |
Temporary, small-scale use |
Long-term, whole-home power |
How to Determine the Right Size Generator for Your Home?
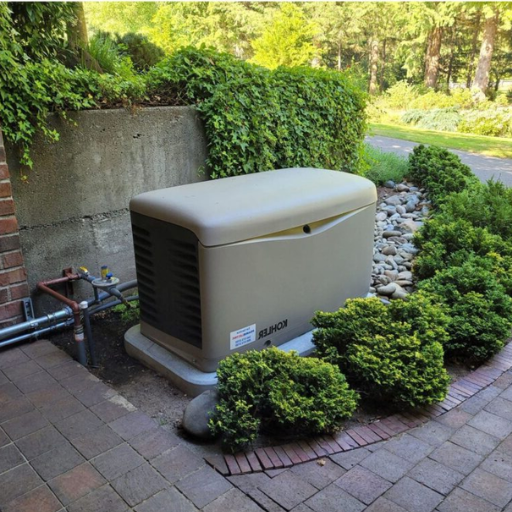

When purchasing a generator, decide what appliances and systems are essential to power during an outage. Medical equipment, heating and cooling appliances, refrigeration, and even lights are often priorities. Carefully calculate the total wattage needed by summing the wattages of all the items to be powered. Typically, this information is available on the device’s nameplate or instruction booklet. Furthermore, for the major appliances such as air conditioners and refrigerators, don’t forget to add the starting wattage, which is generally much higher than the operating wattage, to the total. After calculating the total, selecting a generator that can deliver power slightly above the total calculated needs is best. In case of doubts, one can always turn to professional electricians to make informed decisions.
Calculating the Power Your Home Needs
Understanding how much power is used in your home will first require you to calculate the energy consumption of appliances you consider as essential. The following is a calculation with rounded estimates that you can follow unconventionally to estimate your power needs effortlessly:
- Register Your Essential Appliances
In this first section, you must state all devices and appliances you consider essential or that require power supply. Refrigerators, televisions, air conditioners, lights, and other devices may also be included. In case any medical device or any other item that is critical for your daily life exists, do not forget about them as well.
- Estimating Appliance Energy Consumption
Appliance charging elements and user manuals offer handy suggestions about the wattage estimate, and so do average powered devices. Here are a couple of reasonable estimates for a few standard devices for your reference:
- Charger for laptops: 50 – 100 watts
- Screw microwave: 800 – 1200 watts
- Washing device: 500 – 1500 watts
In the average range of:
- Refrigerator: 100 – 800 watts
- CA (Central Air Condition): 2000 – 4000 watts (2,000 – 5,000 BTU)
- LED light bulb: 10 – 20 watts
It is worth noting that some appliances need a significant startup wattage compared to their active wattage. This overheating effect is very noticeable in refrigerators and air conditioners, often going 2 to 3 times their active consumption.
- Adding all the Power Appliances Get Together.
Calculate the wattage of the appliances you intend to use at one time. Utilize the requirements for a refrigerator (800 watts), LED light bulbs (60 watts), and a microwave (1,200 watts). In this case, the total wattage would add approximately 2060 watts.
- Account For Safety Margins When Choosing Generators.
To ensure proper functioning without hindrance, it’s a good idea to go for a generator or energy source that is notably higher than the total you calculated – an additional 20-30% ought to do the trick. To further illustrate, if your total usage is 2060 watts, your preferred power source should have 2500 watts.
- Preparing In Advance Is Always The Best Idea.
Tablets, smart gadgets, vehicles, and air conditioning units are key appliances that require further upgrades. Therefore, anticipate adding newer devices as time passes. Adding these changes in the calculation works wonders.
Use them in conjunction with tracked data to determine your household’s power needs and subsequently figure out which generator or backup system is best suited. Through precise calculations, overloading equipment becomes a concern of the past. It is ideal to always start with a professional electrician for expert advice.
Understanding the Whole-House Generator Capacity
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
|
Typical Capacity Range |
10,000–60,000 watts |
|
Small Home (Under 2,000 sq ft) |
10,000–15,000 watts |
|
Medium Home (2,000–3,000 sq ft) |
15,000–22,000 watts |
|
Large Home (3,000–5,000 sq ft) |
22,000–32,000 watts |
|
Extra-Large Home (5,000+ sq ft) |
36,000–50,000+ watts |
|
Essential Appliances |
Fridge, lights, medical devices |
|
High-Demand Appliances |
AC, heaters, electric stoves |
|
Starting vs Running Power |
Consider higher starting wattage |
|
Future Needs |
Plan for additional appliances |
|
Professional Assessment |
Recommended for accurate sizing |
What are the Benefits of a Home Standby Generator Installation?

Apart from these, installing a generator in one’s home provides many advantages by providing complete backup power to ensure all systems, such as cooling, heating, and refrigeration, continue operating during a power outage. Standby generators enhance a person’s family’s safety and security by preventing food spoilage, maintaining communication, and powering medical devices if needed. Without a doubt, standby generators increase convenience, and with their effortless functionality, they are one of the best investments to help sustain daily routines during sudden power cuts.
Ensuring Peace of Mind During a Power Outage
Because my essential appliances and systems continue running without a hitch, having a home standby generator gives me peace of mind during power outages. This allows my family to stay comfortable, our food to remain fresh, and crucial devices like communication tools or medical equipment always to be operational. Regardless of the circumstances, this reliability makes me feel secure and prepared.
Automatic Power Backup with Generac Power Systems
Generac Power Systems has backup generators designed to provide power automatically during outages for homeowners’ and businesses’ needs. Here are five key details and features about Generac’s generators:
- Seamless Automatic Operation
Generac standby generators come with an automatic transfer switch that starts the generator a few seconds after the outage is detected. Your home and/or business will continue operating even when there are outages, with no manual work needed.
- Multiple Fuel Options and Fuel Efficiency
With Generac, you can get generators with dual-fuel options, which means you can use natural gas (NG) or liquid propane (LP). This provides dependability and optimized fuel consumption depending on your level of supply.
- Mobile Monitoring Technology
With a smartphone, tablet, or PC, you can check the status of your generator using Generac’s Mobile Link™ Remote Monitoring. You can set alerts, maintain, and confirm your generator remotely to ensure it works when needed.
- Powerful and Durable Engines
Purpose-built G-Force engines are mounted on Generac generators specifically built to withstand prolonged use. They are costlier than traditional generators, but for good reason, providing performance you can depend on in day-to-day life with longer lifespans.
- Generac provides extensive warranty terms and after-sales service guarantees.
They have unparalleled customer service, standing face-to-face 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
Generac’s automatic standby power systems are custom-tailored to suit your power requirements across multi-day outages.
Long-Term Savings and Reliability
As noted in the essay ‘A Portable Generator – What Are The Benefits’ by Ryan Williams, investing in a Generac automatic backup generator harnesses incredible savings and unrivaled reliability. Therefore, these generators are built to be energy efficient, ensuring optimal fuel use and steadily reducing operating costs. To add value, according to some market analysis, standby generators like those of Generac enhance a property’s value by 5 percent, showcasing the investment advantage offered to homeowners.
Furthermore, Generac’s generators have advanced load-managing capabilities to control the use of power and, in turn, reduce the cost of electricity bills. They are also built to endure extreme weather and rough usage. When properly maintained, these generators can last 25 years. In addition, the natural gas models do not require constant refueling, making them more dependable and cheaper than diesel-powered generators.
Apart from the savings Generac offers, its accuracy is unmatched. Power cuts have proven 70 percent customer satisfaction with the seamless performance of its system during outages. Customers cite systems switching and the inability to halt the power supply as the centerpiece of its systems. Along with comprehensive guarantees, those using Generac’s generators are assured of worry-free reliability, reducing long-term operational costs.
Common Generator FAQs and Troubleshooting Tips

|
FAQ/Troubleshooting Tip |
Details |
|---|---|
|
What size generator do I need? |
Depends on power needs during outages. |
|
How much does installation cost? |
Varies by generator size, fuel, and setup. |
|
How loud is the generator? |
Typically around 66 dB at 20 feet distance. |
|
What fuels can generators use? |
Gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or propane. |
|
What is the difference between generator types? |
Standby is permanent; portable is movable. |
|
How do I start a generator? |
Follow the manufacturer’s guide; manual/automatic methods are available. |
|
Why won’t the generator start? |
Check fuel, oil, spark plugs, and carburetor. |
|
How often does maintenance need to be conducted? |
Regularly check oil, filters, and battery. |
|
How do I reset a generator? |
Turn off, disconnect the battery, reset the wiring, and reconnect. |
|
What is an automatic transfer switch? |
Switches power between the generator and the grid automatically. |
|
What does the yellow light on the generator mean? |
Maintenance reminder for battery, oil, and filters. |
|
How long does a generator run? |
It depends on fuel type and load; it will last 24-72 hours or more. |
|
Can I install a generator myself? |
Professionals should do the installation. |
|
How do I fix generator stalling? |
Replace spark plugs, clean filters, and ensure sufficient fuel. |
|
What do I do with clogged fuel lines? |
Clean lines, avoid old fuel, and check the carburetor. |
|
How heavy are home generators? |
Commonly 350- 550 lbs for air-cooled models. |
|
Why won’t the generator produce power? |
May need spark plug, connection, or voltage check. |
|
What happens if the generator is overloaded? |
Circuit breaker trips, reduces load, and resets. |
|
How big of a fuel supply do I need? |
Depends on the generator type and expected runtime. |
|
Can a generator get wet? |
Outdoor use is safe with proper enclosures. |
How Often Should a Standby Generator be Serviced?
Currently, most manufacturers recommend servicing standby generators yearly, regardless of use, to maintain performance and extend their lifespan. Nonetheless, depending on the model and environmental conditions, some may require more or less frequent servicing. Here’s a breakdown of the most overlooked guidelines:
- Routine Maintenance: For frequently used machines or those in harsh regions, maintenance needs to be done after every 100-200 hours of operation or six months. It encompasses ensuring adequate oil levels, changing oil, and replacing filters.
- Monthly Checks: Advanced machines come with self-check features. However, to avoid issues like low oil or cooling fluids that impede performance, manual checks need to be done once a month.
- Load Testing: Professional load bank testing should be done once every fiscal year for optimal performance. This guarantees sufficient power is available when needed and prevents wet stacking resulting from prolonged low-load conditions.
- Professional Servicing: To maintain optimal performance, have a skilled technician perform thorough inspections twice yearly. This should include checking the battery, connections, spark plugs, fuel lines, and air filters to ensure they are in good condition. Servicing every six months is particularly important in regions with constant outages.
- Consult the owner’s manual for maintenance needs and equipment schedules. For instance, Generac recommends an inspection every 6 months or 200 hours of run time for their standby generators.
Following these maintenance schedules, along with the proper check-ups, will enhance a standby generator’s efficiency, dependability, and service life. Ensure that maintenance records are kept to monitor service intervals and retain the warranty.
What to Do if Your Generator Fails to Start?
|
Step |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Check fuel level |
Refill with fresh, non-ethanol gasoline if empty. |
|
Inspect fuel system |
Look for bad mixes, clogs, or impurities. |
|
Replace stale gas |
Drain old fuel and refill with stabilized fresh gasoline. |
|
Inspect oil levels |
Add or replace oil if levels are low or old. |
|
Check battery |
Recharge or replace if dead or the connections are loose. |
|
Unplug all devices |
Ensure nothing is plugged into the generator. |
|
Adjust choke |
Adjust to closed or half-open position based on engine temperature. |
|
Clean air filter |
Replace if clogged to improve airflow in the carburetor. |
|
Clean carburetor |
Remove debris or clogs using a carburetor cleaner. |
|
Replace the spark plug |
Clean or replace if dirty, worn, or faulty. |
|
Check the coolant level |
Add coolant if deficient to prevent engine overheating. |
|
Inspect the control panel |
Ensure the generator is in “Auto” mode for automated start. |
|
Test the electrical system |
Check wiring and spark to confirm functionality. |
|
Position on the surface |
Ensure the generator is level to avoid sensor malfunctions. |
References
- Getting serious about safety and loss prevention emergency power and standby generators – Texas A&M University repository.
- Ways of Going About Determining Backup Power Options for Homes in California – California Polytechnic State University digital commons.
- Emergency-power substation PCM system- PV backup system – Youngstown State University repository.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a home generator, and why do I need one?
A: A home generator, also known as a standby or backup generator, is a device that provides power to your home during utility power outages. It is essential to ensure that your home appliances and systems continue functioning when the main power supply is interrupted.
Q: How do I determine the generator size I need for my home?
A: To determine the generator size, you must calculate your power needs by adding up the wattage of all essential home appliances and systems you want to power during an outage. A whole house generator can power your entire house, but you might also consider a smaller unit if you only need standby power for critical appliances.
Q: Where should a generator be installed?
A: A generator should be installed outside your home, typically on a concrete pad. It should be placed away from windows, doors, and vents to prevent exhaust fumes from entering your home. The location should also allow easy maintenance access and comply with local building codes.
Q: How does a whole-house generator work?
A: An automatic transfer switch connects a whole-house generator to your home’s electrical system. When the generator detects a power outage, it automatically starts and transfers the electrical load to provide power to your home. The generator will return to standby mode once utility power is restored.
Q: What are the fuel options for a home backup generator?
A: Home backup generators typically run on natural gas, propane, or diesel. Natural gas is often preferred because it connects directly to your home’s gas line, providing a continuous fuel supply. Propane is another standard option; it can be stored in tanks on your property.
Q: Can I install my standby generator myself?
A: For home generator installation, it is recommended that you hire a professional installer or one of the authorized Generac dealers. They will ensure the generator is installed correctly, safely, and in compliance with all local codes and regulations.
Q: How long does the standby generator installation process take?
A: The installation process for a standby generator typically takes one to two days, depending on the complexity of the installation and any additional work needed, such as gas line connection or electrical upgrades.
Q: What maintenance does a home generator require?
A: Regular maintenance is critical for ensuring the reliability of your home generator. This includes checking the oil and filters, testing the battery, and running the generator periodically to ensure it operates smoothly. Many authorized Generac dealers offer maintenance services.
Q: Will a generator power my home automatically during an outage?
A: If your generator is equipped with an automatic transfer switch, it will automatically start and power your home during an outage. Once the utility power is restored, it will return to standby mode without any manual intervention.