Choosing the right components for your portable generator is critical to ensuring optimal performance, efficiency, and durability. Whether you’re setting up a reliable backup power source for emergencies or need a portable solution for powering equipment on the go, understanding the essential parts of a generator is key. This article will provide a comprehensive breakdown of the core components that make up a portable power system, explaining their roles, functions, and how they work together to deliver consistent energy output. From engines to control panels, we’ve got you covered with all the details you need to build or maintain a generator that meets your unique power needs. Let’s get started by exploring the fundamental building blocks of your power solution.
What are the most important generator parts I need to know about?
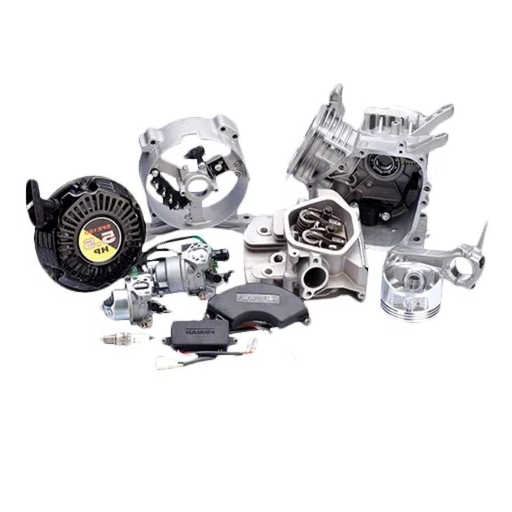

Essential engine components for generator operation
An engine is a generator’s heart, transforming fuel into usable energy mechanically. Important parts of an engine include:
- Cylinder with Piston: Turns the combustion process to drive the engine.
- Crankshaft: The rotating crank arm of the piston turns linear energy into rotational force.
- Fuel System: Supplies and controls the fuel, which is later burnt.
- Cooling System: Removes heat energy to cool down the engine and avoid overheating.
- Lubrication System: Minimizes friction between moving components, which ensures smooth motion.
The generator runs optimally and consistently if the fuel system, engine, cooling system, and lubrication system work together to produce energy while having their parts maintained for efficiency. All of these components guaranteed that energy is produced reliably while servicing these units was required to maintain the performance.
Electrical system parts that power your generator
The following are the primary components of the electrical system of a generator:
- Alternator: This piece transforms the mechanical power from the engine into electrical energy. It contains a rotor and stator which generate alternating current (AC) electricity.
- Voltage Regulator: Controls the level of the output to ensure value stasis irrespective of changes in load.
- Battery: Initiates powering up the generator, as well as controlling systems during operation.
- Control Panel: This device supervises and controls all activities of the generator, such as voltage, frequency, and all operating parameters.
These elements enable efficient and stable power generation. Collectively, they form the backbone of the generator’s electrical functionality.
Fuel system components for maintaining peak performance
The generator’s fuel system is responsible for providing fuel to the engine, which needs to operate at peak conditions. The primary components are listed below:
- Fuel Tank: The container for fuel needed during generator operation within a specific time frame. This usually determines the runtime of the generator.
- Fuel Pump: Moves the fuel to the engine at the necessary pressure for combustion from the tank.
- Fuel Filter: Prevents damage to the engine by capturing unnecessary particles and dirt from the fuel that can block and damage the engine.
- Fuel Injectors: Atomize the fuel in the combustion chamber of the engine to facilitate the ideal mixing of fuel and air for burning.
The aforementioned components require regular services that would preserve the generator’s dependability and effectiveness.
What maintenance kits and accessories extend my generator’s lifespan?
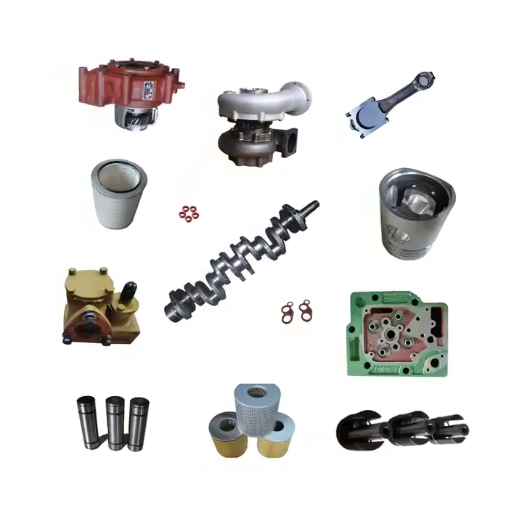

Essential maintenance kits for regular generator care
To keep a generator in its ideal working condition, it needs routine maintenance like oil changes, parts replacements, and symptom checks.
- Oil Filters: These are crucial in keeping the oil within the engine free of any dirt contaminants. Contaminated oil can lead to rough engine burnings and render the engine useless.
- Air Filters: Prevents reduction of an engine’s efficiency while increasing the life of a generator. Air filters trap dust, dirt, and airborne particles from entering it. To ensure the proper operation of a generator, these filters should be cleaned or changed every 100 to 200 hours of use.
- Spark Plugs: Required for igniting the mixture of petrol and dynamite within the combustion chamber of an engine, “spark plugs”, as the name suggests, spark the initial reaction that causes thrust. Regular checks and cleaning with some change ease prevent burnout misfires, which saves on cost and maintenance later down the road.
- Fuel Additives: Fuel stabilizers and conditioners which are of low quality greatly aid in the degradation of fuel, especially if the generator hasn’t been used for a prolonged duration. These stabilizers are fundamental in keeping the fuel and generator condition pristine.
- Motor Oil: Specific oils will guarantee compatibility and are provided in the kits. Maintenance won’t be an issue if the specified oil type is used, levels are checked regularly, and intervals between services are increased.
All components of the kits are designed around a particular engine, and these kits from the manufacturer improve reliability along with critical performance metrics such as fuel economy. Reliable maintenance schedules will improve generator lifespan while minimizing unplanned outages and costly repairs.
Filter and oil replacement components to maintain performance
To maximize the performance and efficiency of your generator, it is important to periodically change the filters as well as the oil. Air filters protect the engine from potentially damaging particles, while fuel filters minimize clogging and damage by ensuring that clean fuel is provided to the system. Oil filters capture impurities suspended in the engine oil (lubricating oil) in the system to ensure that its quality is maintained and the engine parts do not suffer from undue wear and tear.
Pleated synthetic filters outperform traditional cellulose filters with their enhanced dirt-holding capacity and extended service life. Furthermore, using appropriate engine oil like synthetic blends that withstand high temperature, thermal stress, and prolonged strain on the engine boosts overall engine performance over a wide range of operational conditions. Also, maintaining an uncompromising schedule of changing oil, usually recommended during specified operational hours on the engine, is crucial in avoiding excessive wear and tear while ensuring dependable operation.
Utilizing advanced diagnosis methods, like oil condition monitors, can provide valuable information related to contaminants, oil deterioration, and maintenance requirements. These maintenance strategies allow for selective action to be taken, which minimizes costs related to unexpected damages while increasing the life of the equipment.
Key accessories that protect and enhance your portable generator
Having the right accessories for your portable generator goes beyond convenience; it can enhance efficiency, safeguard critical components, and ensure safe operation. A weatherproof cover will shield the generator from dust and rain, as well as UV light, which, over time, can damage sensitive components. Heavy-duty extension cords, transfer switches, and other accessories ensure efficient power delivery while adhering to safety standards, greatly reducing the risk of electrical overload.
Other accessories, like a quality fuel stabilizer, ensure a portable generator can store fuel without losing efficiency during long gumming standstills, ensuring hassle-free start-up. Grounding rods minimize electrical risks through safe electrical discharge. Mobil Accessory Kits enhance the structural integrity and mobility of portable generators, allowing for simultaneous maneuvering across rough terrain, which greatly improves ease of transport without compromising structural sturdiness.
For improved supervision and other aspects of reliability, load monitors and wireless remote start systems help by giving real-time data about the generator’s performance, power output, and load balance. These tools improve management and allow users to take preemptive action to avoid overstraining the unit. Choosing these essentials allows users to sharpen the utility of their portable generators while also prolonging their lifespan.
How do transfer switches and connection accessories work with generators?

Manual vs. automatic transfer switch options
Transfer switches serve as a link between generators and power systems, providing safe power distribution during outages. With a manual transfer switch (MTS), the user must turn the switch, placing the electrical load on the generator and off the utility supply. MTSs are simpler and less costly than other transfer switches, making them a great fit for low interruption applications where utility outages are foreseen.
On the other side of the spectrum lies the automatic transfer switch (ATS). ATSs replace manual functions with machines that handle the workload. ATS power systems monitor the incoming electricity supply, switching over to generator power in case of a supply outage or voltage variation. Once stable electricity is detected, the ATS reverts the connection, bringing the load back to the grid. Automatic switch systems also bolster safety by limiting the need for manual operation, thus minimizing the chance for electrical backfeed.
From a budgetary standpoint, both options have merits dependent on one’s needs. Economical manual switches are ideal for smaller-scale applications, while ATSs are essential for environments with little tolerance for downtime, as they provide great reliability.
Installation components for connecting to your electrical panel
Careful attention is needed in choosing particular installation parts to establish a socket outlet to electrical panel connection that is both efficient and secure. Some of the primary components are:
- Transfer Switches: Power transfer between the main utility supply and a backup generator must be securely shifted by use of a transfer switch. To facilitate seamless power transitions during outages, the transfer switch must be automatic or manual, as it is pivotal in avoiding dangerous backfeeding of electricity.
- Circuit Breakers: Circuit breakers that are deemed acceptable for usage must be properly rated to control the electrical load in the system and avoid overcurrent situations that pose fire or damage risks.
- Conduit and Wiring: For Wiring, the proper type and gauge must be used. Conformance with local safety stipulations is more than optimised electric flow with correct gauges. Protecting the wiring from physical damage and environmental elements is best achieved with conduits.
- Grounding Equipment: From the perspective of electrical safety, properly directing fault current away from associated equipment and personnel in issue is necessary.
- Load Center: Distribution of power to other circuits is best achieved by the use of a Load Center, which acts as a control tower.
- Connectors and Terminals: Uploading a reasonable amount of thermal stress and preserving the integrity within the circuits can be achieved by applying rated connectors and terminals for tight and secure linkages.
Following the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines during installation is crucial for safety and compliance. It is advisable to consult a professional to evaluate the needs, considering the electrical panel’s capacity, load, and type of backup system used.
Safety accessories to prevent power outage issues
The implementation of safety accessories is crucial for minimizing risks from power outages while protecting the system and connected devices. The most important parts are:
- Surge Protectors: These devices protect from voltage spikes due to lightning bolts or during power restoration. Advanced surge protectors with high joule ratings and indicator lights are excellent for spotting exploitable weaknesses.
- Automatic Transfer Switches: An ATS automatically switches to backup power sources, such as generators. It automatically identifies outages and reroutes supply to ensure seamless operation without human effort.
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies: A UPS system helps sensitive electronics avoid damage from short-term power outages. An adjustable device provides a set time of energy allowance. When choosing a UPS, be mindful of output wattage, runtime, and battery charge rate.
- Circuit Breaker Interlock Kits: These kits close off power backfeeding through a generator command during operation, allowing only a single source of power feed, preventing fire or injury to utility workers.
- Energy Monitoring Systems: These systems can be fitted with smart sensors that aid in the constant monitoring of power usage. These systems are provided with advanced data, which helps in reducing work stress.
Correct installation and integration of these add-ons as per the NEC guidelines enhances safety and efficiency. It is recommended that accessories be customized depending on the building size, application, and load requirements to maximize performance.
What carburetor and fuel system parts commonly need replacement?
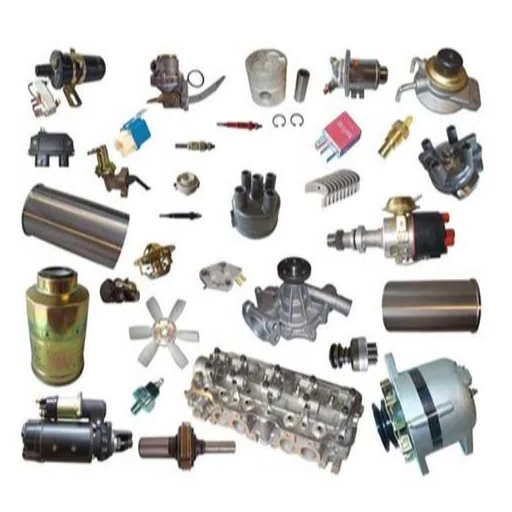

Carburetor gasket and component replacement guide
Replacing gaskets in carburetors and related parts is an important maintenance task to achieve the best engine response and fuel economy. Air leaks, maldistribution of fuel among components, and incomplete combustion occur due to overheating and fuel exposure, which deteriorates gaskets with time. These changes usually include the float valve, accelerator pump diaphragm, main carburetor gasket, and a few O-rings that serve to seal the entire fuel system, thus enabling its functionality.
- Disassemble the Carburetor: remove the carburetor from the engine and take it to an uncluttered workbench where it can be properly organized and cleaned. Doing so helps prevent contamination and makes reassembly easier.
- Inspect Gaskets and Seals: Check the gasket for tears, hard parts, or any other deformation that may prevent proper seating in the retaining grooves. Damaged parts should always be replaced.
- Clean All Surfaces: Mating surfaces should be scrubbed with a nonabrasive carb cleaner. Old gasket material or any leftover debris can lead to alte closures on proper sealing.
- Install New Components: Fuel should not steadily leak out from any gaps, which may come due to incorrect alignment.
- Reassemble and Test: After all the pieces are put together, the carburetor has to be put back on, and everything else attached so an operational check can be done on the engine. While running, looking for signs of fuel escaping or the engine turning erratically are prime indicators of poor installation.
Symptoms like sluggish throttle response, starting troubles, or even black smoke from the exhaust often suggest the gasket needs replacement or servicing of some carburetor parts. To get the most life out of the fuel system, regular checks and proactive part changes are best. The use of manufacturer-approved components is recommended as they are likely to endure longer and be compatible with the device.
Fuel pump and filter maintenance essentials
Ensure the efficient operation of an engine’s fuel system by properly maintaining the fuel pump and filter. The fuel pump, which supplies fuel to the engine at the proper pressure from the tank, must be checked very often to make sure that there is no sign of wear or malfunction. Some common signs of a failing fuel pump are poor fuel economy, problems with engine misfiring, or the car being difficult to start. By using the right equipment, periodic pressure testing with a fuel pressure gauge can help avoid potential issues as well as irreversible damage to the engine using incompatible fuel delivery.
The fuel filter is equally, if not more, important and serves the purpose of preventing dirt and other debris from going into the fuel injectors and the engine. To prevent clogged fuel filters, which may hamper fuel supply and hurt the fuel pump, the fuel filter must be changed as per the vehicle’s maintenance manual. Improvement of internal features within fuel filters allows even smaller particulates to be collected, which protects the entire fuel system, making the filtration system highly advanced.
In all maintenance works, particular care should be taken with replacing parts with ‘manufacturer-approved’ ones to ensure proper functionality and fit, as well as optimal performance. Besides, the filters are to be disposed of in a safe way whilst taking into account the environment to promote environmentally friendly maintenance practices. A properly devised operating plan regarding the inspections can greatly enhance the performance and durability of the fuel system.
How do I maintain my portable generator’s starter and battery system?
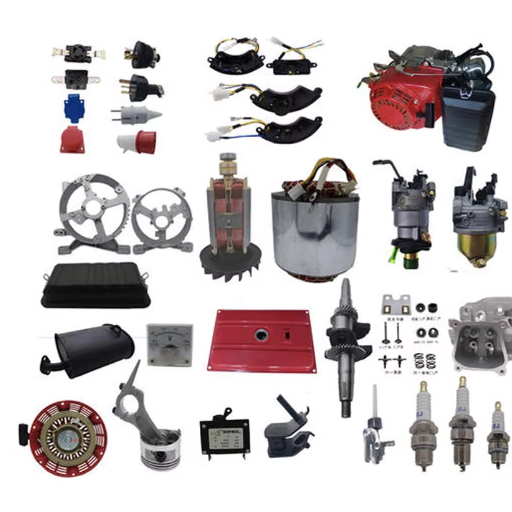

Key starter components and troubleshooting guide
The portable generator starter system, its motor and solenoid, ignition wiring, and the relevant switches are some of the most important components when considering its construction. All of this allows for the seamless operation of a portable generator from the moment it is started.
- Starter Motor: The motor starter provides the required rotation to get the engine of a generator running. Negative results can often be traced back to serious mechanical issues such as damaged bearings and brushes. An attempt to diagnose the problem has to check sequentially, starting from the electrical side and advancing mechanically. Check for continuity and voltage within the specified limits on the motor terminals with a multimeter.
- Solenoid: The solenoid serves as an interface, bringing together the battery and the starter motor. If the terminal is worn, one may hear a clicking noise when trying to start the vehicle and will have burned-out coils or oxidized terminals. Other than burnt terminals, the solenoid will also undergo voltage checks while the engine is being activated.
- Ignition Switch: The switch can turn on or off a flow of current to the starter circuitry. Signs of failure include the start system being totally dead or the engine unexpectedly firing up without any interactions. Having an active ignition switch means faulty contacts will be eliminated from the circuit and secure connections are guaranteed.
- Battery and Wiring: Good charging practices have to be met in order for the battery to run at maximum efficiency. Chronic over or under-charging due to faults within the alternator tends to damage the battery. Ensure complete attachment of wires and that there’s no corrosion growing on terminal connections as well as fraying where they connect to the battery.
Every single component working together is given better through routine testing and care. Refraining from repeated starter problems is achieved best by sticking to the prefabricated structure of suggestions for dealing with the parts. Incorporating tools like circuit testers and infrared thermometers aids in accurately pinpointing hidden faults. With such strategies, the dependability and lifespan of the portable generator are greatly enhanced.
Battery maintenance and replacement options
To maximize the reliability of a portable generator, battery maintenance must be conducted regularly. The first step for maintenance involves checking the battery contacts at regular intervals for corrosion or any other form of terminal blockage that could hinder effective electrical connection. Promising excellent electrical contact involves cleaning the terminals with baking soda and water or a dedicated cleaning agent. Moreover, proper usage entails monitoring the battery charge because both undercharging and overcharging can wear out the battery. Optimally, equip the battery with a smart charger, which safely disables when the set maximum threshold is reached, so your battery can be maintained without reaching excessive charging levels.
When it comes to replacement, choosing a battery that matches the specifications of the generator is critical. Different models of portable generators will most likely be supported with a lead-acid or AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) battery because of their reputation for reliability and effectiveness under diverse conditions. The manufacturer and the generator’s manual contain contact information for suitable replacement models, so make sure to check those as well. Other than that, newer developments in lithium-ion technology, while expensive, do provide a lighter and more energy-dense alternative.
No matter what type of battery you are dealing with, you should follow the replacement schedule given, which is typically every 3 to 5 years, based on battery usage. Lastly, in compliance with policies and to support renewable energy, obsolete batteries must be disposed of in an environmentally appropriate manner at certified recycling facilities.
Electrical component protection for peak performance
Protecting the reliability and functionality of electrical parts is crucial to the system’s peak underpin performance. Specialized enclosures for surpassing performance polymers, metals, or even high corrosion resistant alloys serve as the primary level of defense by safeguarding sharp components incased on towers from temperature changes, dust, or moisture. The material used in the making of these enclosures determines their durability and durability incased on physical abrasions or even chemical attacks.
Cooling aids such as thermal pads, active cooling systems, and even heat sinks guarantee a safe temperature range for the smooth running of components, which is an equally important juncture bound to incur deep sealed holes in the ground for shipping containers in case of removing the berthed vessel for incased gated di-less line rotary valve. Transition voltage spikes that can severely damage circuits and erode the operational liveness of equipment are neutralized by surge protection devices (SPDs).
Short circuits, moisture ingress, or corrosion greatly impact the reliability of a component, which can overall minimize their operational abilities. The extreme stress limits can be worked around the application of potting compounds incased along with conformal coatings, making them as primary face off strength, serving as an additional layer.
From modern technology, such as predictive maintenance systems and real-time monitoring sensors, critical information regarding the health or status of electric components is obtainable. These insights help in taking preventative measures, reducing system failures. By integrating physical protections with intelligent monitoring, critical electric components are not only comprehensively protected but also vital to system performance.
References
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What essential parts should be included in a complete generator product list for a portable power system?
A: A complete generator product list should include the engine, alternator, fuel system components (carburetor, fuel filter, gas lines), control panel with outlets, voltage regulator, air filter, ignition system, starting system (pull cord or electric start), exhaust system, and protective frame. For standby generators, you’ll also need transfer switches, mounting pads, and possibly sound-dampening enclosures for quieter operation. Always ensure you’re purchasing genuine replacement parts compatible with your specific model to maintain generator performance and warranty.
Q: How can I identify the correct replacement parts for my specific generator model?
A: To identify the correct replacement parts for your generator model, first locate the model and serial number typically found on a plate or label on the generator frame. Then, consult your owner’s manual, which contains a parts diagram and part numbers for your specific unit. Alternatively, visit the manufacturer’s website and use their parts lookup tool by entering your model information. When purchasing, always verify that the part number matches exactly to ensure compatibility, as many parts are not interchangeable between different models, even from the same manufacturer. OEM (original equipment manufacturer) parts are recommended for optimal performance and warranty protection.
Q: What are the most common portable generator parts that require regular replacement?
A: The most common portable generator parts requiring regular replacement include air filters (typically every 100 hours of operation), oil filters (every 100-200 hours), spark plugs (annually or every 100 hours), fuel filters (every 200-300 hours), and carburetor components. Engine oil needs changing every 50-100 hours of use. Other parts that may need occasional replacement include starter batteries for electric-start models, pull cords, voltage regulators, and fuel lines that can deteriorate over time, especially when exposed to ethanol-blended gas. Maintaining a small inventory of these essential replacement parts ensures your generator remains operational when you need it most, particularly during emergencies.
Q: What’s the difference between OEM and aftermarket replacement parts for generators?
A: OEM (original equipment manufacturer) parts are made by the same company that produced your generator and are identical to the components originally installed in your appliance. These genuine parts typically offer perfect fitment, reliable performance and maintain your warranty. Aftermarket parts are produced by third-party manufacturers and may be more affordable but can vary in quality. While some aftermarket parts match or exceed OEM specifications, others may offer less durability or slightly different specifications. For critical components like alternators or engine parts (pistons, piston rings), OEM is generally recommended, while maintenance items like filters or spark plugs may be safely sourced from quality aftermarket suppliers without compromising your portable generator’s performance.
Q: How do I determine the part number for generator components that need replacement?
A: To determine the correct part number for generator components, first consult your owner’s manual, which typically contains a parts diagram with corresponding part numbers. If unavailable, locate the model and serial number on your generator and visit the manufacturer’s website to access their parts lookup tool. Alternatively, contact the manufacturer’s customer service with your model information. For visible parts, check if the part number is stamped directly on the component. When purchasing replacement parts, always verify that the part number matches exactly, as similar-looking parts may not be interchangeable between different models.
Q: What energy output components should be maintained for optimal generator performance?
A: For optimal energy output, several key components require regular maintenance: the alternator (which converts mechanical energy to electrical energy), voltage regulator (maintaining stable output), capacitors, diodes, and the AVR (Automatic Voltage Regulator). The brushes in the alternator may need replacement after extended use. Additionally, the control panel components, including circuit breakers, outlets, and monitoring gauges, should be inspected for proper functioning. For portable generators specifically, ensuring clean fuel delivery through properly maintained fuel filters and carburetors directly impacts energy production efficiency. Regular testing under load will help identify any decrease in power output before it becomes critical, allowing you to replace or service components before complete failure occurs.
Q: What are the essential safety replacement parts to keep on hand for a portable generator?
A: Essential safety replacement parts to keep on hand include: GFCI outlets or components if your model uses them; circuit breakers that protect against overloads; carbon monoxide detectors if your model includes them; proper grounding components; heat shields and guards for hot surfaces; and spark arrestors for the exhaust system (especially important when using generators in dry conditions). Additionally, maintain spare fuses, emergency shut-off switches, and control panel components that monitor critical functions. These safety parts ensure your portable generator operates safely, protecting both the appliance and users from potential hazards. Always use genuine or qualified replacement parts for safety components rather than attempting repairs or modifications.
Q: How do environmental factors affect which generator parts need more frequent replacement?
A: Environmental factors significantly impact generator part longevity. In coastal areas with high humidity and salt air, metal components like mounting brackets, fasteners, and exposed electrical connections corrode faster, requiring more frequent replacement. In dusty environments, air filters need more regular changing to prevent engine damage. Extreme heat accelerates the deterioration of rubber and plastic components like fuel lines, gaskets, and seals. Cold climates affect battery performance and may stress starting components. High-altitude operation requires specific carburetor adjustments or jets. If your generator is exposed to frequent rain or moisture, weather-protective components wear faster. For generators used in construction sites or rough terrain, vibration dampeners and mounting components experience greater stress. Maintaining an inventory of environment-specific replacement parts ensures your portable power system remains operational regardless of conditions.