Power outages can disrupt daily life, compromise home security, and lead to costly damages. A standby generator offers a reliable solution by providing an automatic backup power source, ensuring your home remains functional during emergencies. This guide will walk you through the essential steps and considerations involved in installing a standby generator, from assessing your power needs to ensuring compliance with local regulations. By understanding the technical requirements and processes, you can make informed decisions to safeguard your home and maintain peace of mind in the face of unexpected blackouts.
What Size Generator Do You Need for Your Home?
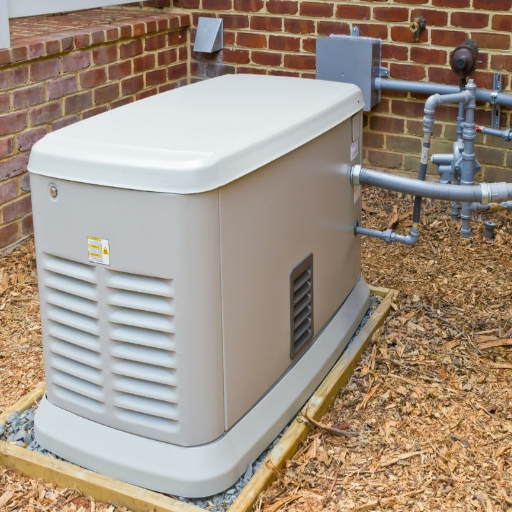

Calculating Your Home’s Power Requirements
To estimate the power needs for my home, I first have to undertake identifying critical appliances and system that I would like to power during an outage.
- Lighting: Wattage for every bulb times the quantity of required bulbs.
- Refrigerator: Running wattage (~300W) and starting wattage (~800W).
- HVAC System: Central air systems usually take on average from 3,000 to 5,000W or even more.
- Medical Equipment: Usage varies; consult device specifications.
- Rest of Music Devices: include but not limited to: laptops (60-100W), tv (200W), and microwave (1,000W).
Incorporating a safety margin of 20-25% allows the generator to accommodate deviations or extra loads that may be temporarily placed on it. To illustrate, if my calculated wattage comes to 5,000W, I would use a generator that has a minimum rating of 6,250W. That way, I can be sure that the standby generator will function optimally and dependably.
Whole House Generator vs. Essential Circuits Backup
Whole house generators power an entire home as a unit. This means that all appliances including HVAC systems, refrigerators, and water heaters can be used during an outage. Such generators usually come with a higher capacity, mostly exceeding 22kW and reaching up to 48kW or more, depending on the size of the home as well as the total wattage of the appliances.
On the opposing side, an essential circuits backup generator only powers selected essential circuits like lighting and needed appliances such as fridges. This means that the capacity needed to power essential circuits is much lower than 5kW and 10 kW. I make sure that the total wattage is within the margin that can be maximally handled along with a 20-25% margin.
The final decision boils down to one’s budget, power requirement, and what is deemed most important to them during an outage. When it comes to backup essential circuits, they prove to be far more affordable while whole house generators are more time complex and expensive to install.
Matching Generator Size to Your Electrical System
Initially, I sum up the wattage of the machinery and systems that are essential for me during an outage. For instance, many people prioritize their sump pump, furnace, refrigerator, as well as lighting circuits. The average watt consumption is usually 600 watts for a fridge, 1500 for a sump pump, 700 for a furnace blower and around 300-500 for general lighting depending on the particular configuration.
When I determine the total wattage for the appliances in use, I increase the number by 20- 25% for the starting surcharges that are common with various appliances like air conditioners and refrigerators. In the case where I want to power an entire house, I look at the service panel’s connected load which could be anywhere between 20kW and 30kW or more depending on the size of the house and electrical load demand.
Finally, I select a generator whose capacity is equal to or slightly above the estimated need. For critical circuits, a 5 to 10-kW portable generator is often adequate and cost-effective. However, I opt for a standby generator greater than twenty kW for full-house coverage, making sure it meets the maximum load rating and local electrical code stipulations. That way, I can ensure effective, dependable power at minimal expense associated with excess capacity.
What’s Involved in the Standby Generator Installation Process?
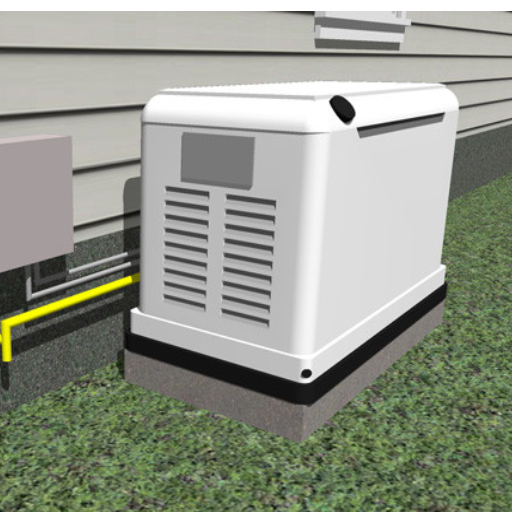
Site Preparation and Permit Requirements
Suitable site planning starts with choosing a site that satisfies both production requirements and regional regulations. To reduce the amount of vibration the generator experiences as well as boost longevity, the generator has to be set on a solid and flat area such as a reinforced concrete pad. There must be sufficient clear space around the unit for air circulation, maintenance work, and other safety measures such as a minimum of 5 feet around windows and doors, as required by the NFPA 37 regulations regarding open flame and electricity safety.
- Transfer Switch Compliance: This is the automatic disconnection switch that must be installed as per the National Electric Code requirement during the working of the generator.
- Exhaust System Placement: These must not be pointed to the contested regions and are subject to the Noise Absorption Policy for designated emission levels.
- Electrical Load Consideration: Compliance of the wiring to the electrical capacity of the generator in relation to the sized wires AWG are the distance and strength of amperage the self-powered generator wire will need.
- Fuel Source Connections: All fuel lines (natural gas or propane) must comply with local and state fuel codes for pressure regulation and installation safety.
- Inspection Requirements: In many jurisdictions, visual inspections of electrical fittings, transfer switches, and fuel systems are mandatory following installation before final sign-off.
Fulfilling these technical requirements and acquiring the relevant permits facilitate the installation process, thereby mitigating the possibility of compliance or functional problems.
Transfer Switch Installation and Electrical Connections
Adhering to safety protocols whilst ensuring reliable operation hinges on the proper configuration of a transfer switch. It all begins with finding the relevant switch type appropriate to load requirements: These include manual or automatic transfer switches.
The transfer switch must be firmly mounted next to the primary electrical panel. Additionally, conductor wires must be sized according to National Electrical Code (NEC) requirements which guarantees an appropriate wire gauge for current allocation. As an example, a 100A transfer switch usually needs a copper conductor sized to 4 AWG for a 75°C terminal rating.
To secure utility input, generator input, and load output terminals, all connections must be adequately torqued as per specifications so overheating is avoided. It is necessary to ground the switch, from then on, all metallic enclosures must be bonded whilst meeting the guidelines of NEC Article 250.
To ensure a smooth transition from utility to generator power, the testing of the transfer switch post-installation must be completed. A load test should be done to check specific operational limits: voltages, time for transfer (which is usually 3-10 seconds for ATS), and the integrity of the system as a whole. Performing these tests and collecting local inspection checklists will certainly improve the likelihood of compliance and durability in the long run.
Natural Gas or Propane Line Installation
Natural gas or propane lines have to be installed by local safety rules and industry standards for them to be usable and safe.
- Pipe Material: Approved materials for construction include steel, copper, and polyethylene. Each type has a specific application as well as corresponding rules that govern its selection. Durability, ability to withstand pressure, and rust resistance are considerations in selecting the material.
- Pressure Ratings: Lines are rated for the intended gas pressure. Residential customers normally utilize low-pressure systems operating at 6-7 inches of water column (approximately 0.25 psi), while some systems with higher required pressures may be configured.
- Size Calculations: The installation of pipe has to be computed according to the BTUs that each of the appliances will be connected to and so, the appropriate sizes for the pipes are selected to minimize any chances of gas pressure being reduced.
- Leak Detection: Once the system is fitted, it is subjected to leak detection tests through approved procedures like testing with a soap solution or electronic leak detectors, and only after these tests do I pressurize the system for use.
- Distance and Routing: I design the routing for their lines so that it will be as short as possible while also making sure that any acute angle that can result in high levels of vibration is avoided to help reduce strain on the line.
I can guarantee the safety, effectiveness, and legal compliance of the installation within these criterions. If there are more parameters in the systems’ engineering, I am ready to explain them in more details.
Should You Hire a Professional for Home Generator Installation?

DIY vs. Professional Installation Considerations
In deciding whether to self-install a home generator or hire a contractor, one has to evaluate numerous technical and safety aspects of the task.
- Power Requirement Evaluation: Estimating your generator should cater all your power requirements accurately is important. It includes estimating total wattage for all crucial appliances and systems so that the generator can service peak loads without getting damaged.
- Compliance With Electrical Codes: Local and state electrical codes should always be followed to ensure that the installation is not only safe but also legal. Most DIY installations try to skip this part, which can lead to penalties or dangerous situations.
- Discharge Ventilation: Generators create carbon monoxide and their placement should take this into account. Experts determine and rule out the distance from windows, doors and vents based on the manufacturer’s guidelines to make sure the users will not die or get poisoned with carbon monoxide.
- Fuel System Connections: In all cases, whether using natural gas, propane, or diesel, adequate fuel line connections along with the valve setting require attention to prevent leaks or fire. Such specialists use pressure regulators and connectors that have been certified for specific fuels and approved flow rates and types.
- System testing and pre-commissioning procedures: After the installation, leak checking, load transfer efficiency check and functional testing, as well as power failure operation testing is conducted to ensure everything is functioning properly and seamlessly.
The potential cost-savings associated with a DIY installation can be enticing, however, the consequences of improper installation that can lead to damaged equipment, safety risks, or legal issues far exceed the benefits. The peace of mind associated with a certified professional guarantees proper installation, all relevant details will be incorporated in the design, together with the desired life span, and completely meet all defined legal and technical requirements.
What to Expect During Professional Installation
With professional generator installation, you will receive a methodical approach that ensures all appropriate technical and legal elements are met. Initially, the installation team will conduct a site survey to optimize the positioning of the generator with respect to ventilation, fuel source accessibility, and local requirements. They will also assess the electrical load requirements to match the generator capacity appropriately. For instance, residential generators tend to fall between 7kW to 20kW, whereas commercial units surpassing 150kW are commonplace due to specific use cases.
After this, the professionals install the unit on an adequately reinforced base or platform for safe and stable positioning of the generator. Then, it has to be integrated into the electrical system of the home or building using a transfer switch, almost always ATS for automatic switches during outages. This part of the work is very sensitive since it can result in backfeeding the electricity grid, which is dangerous.
As a final step, we will perform a comprehensive validation of the installation which entails load bank testing to verify the generator’s performance in meeting the required conditions of power, voltage, frequency, and load servicing. The technician is anticipated to deliver a comprehensive maintenance strategy alongside the test results to ensure the generator is fully functional throughout its usage.
What Type of Generator Is Best for Backup Power?
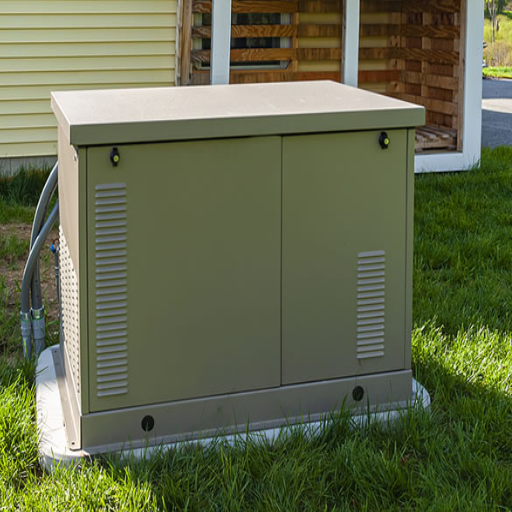

Comparing Portable Generators vs. Home Standby Systems
The primary considerations in my case when comparing home standby systems and portable generators rest on specific needs, power requirements, and budget.
Portable generators are cheaper and more versatile, but they shove out limited pug power. They are most suitable for short-duration outages. For example, a portable generator rated at 5000 to 7500 watts can support limited loads like refrigerators, lights, and small power devices. They do need a manual setup and, and periodic refueling (in most cases propane or gas) and do not come powered up during outages.
On the other hand, home standby systems are often intended to be permanently mounted and aid in automatic power backups. Primarily, these are integrated directly into the electrical system through an ATS and utilize natural gas or propane as fuel sources. Home standby systems are mostly advisable for long term usage as they are convenient and reliable. The only disadvantage is the cost since they come with more expensive professional installation needs.
Some preliminary considerations for my case would be the estimated wattage needs, fuel and maintenance availability, and whether uninterrupted service during outages is necessary.
Natural Gas vs. Propane Standby Generators
Availability, efficiency, cost, and environmental concerns are some of the essential factors that need to be considered while evaluating the use of natural gas (NG) and propane (LPG) generators. During prolonged outages, the fuel supply for natural gas generators remains uninterrupted as they are connected directly to a utility supply line. This provides automatic ignition and eliminates the need for manual refueling, making NG systems highly convenient where the infrastructure exists. In addition, they also tend to emit comparatively lower greenhouse gas emissions than propane, thus making them a better choice environmentally.
On the other hand, propane generators rely on stored fuel in dedicated tanks, which is easier in regions where there are no access to natural gas pipelines. Under certain conditions, propane has a greater energy content per unit than natural gas which can lead to better fuel efficiency. Also, propane has indefinite shelf life, which is great for emergency preparedness where storage is an issue.
Each fuel type has its advantages depending on the situation, where natural gas is superior in gas-rich urban centers, whereas propane is best suited for rural and remote areas.
How Long Does Home Standby Generator Installation Take?
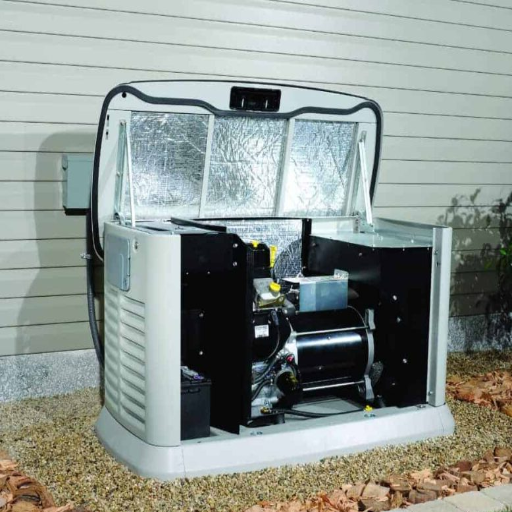

Factors That Can Delay Your Generator Installation
There are several reasons which may elongate the time estimate provided for the installation of a home standby generator. First and foremost, most local authorities have different policies when it comes to issuing permits. It may take you a significant amount of time to obtain permits which can vary depending on your area, so I suggest wasting no time and instead immediately consult your local building department for their guidelines.
The site for the installation also needs to be prepared, which comes with its challenges. Leveling the site, ensuring adequate drainage, and setting a base to limit operational problems are some of the tasks that need to be performed. Depending on how complex these tasks are, it can alter the timeframe estimate that is expected. Additionally, if your site requires landscaping or grading, those factors also need to be added to the estimate.
- Electrical system requirements: To ensure that my standby generator is properly integrated into the electrical system of the house, I need to verify the load capacity by checking the amperage on the main panel and the transfer switch. This is usually done when the generator is upgraded as the new unit can be provided with a separate transfer switch. This rearrangement does increase the time required for installation.
- Gas line: When working with a gas standby generator, I need to confirm the size and pressure rating of the gas line to make sure it meshes with the generators specifications. Natural gas systems operate with pressure ranging from 3 to 5 psi and propane usually sits around 10 to 11 inches of water column.
Lastly, unexpected weather or logistical issues may impact the schedule. Hiring a certified installer who knows how to manage these issues will ensure that delays are kept to a minimum and the entire process is smooth.
Post-Installation Testing and Verification
Effective generator systems require careful and well-planned post-installation tests to ensure they operate safely and efficiently.
- Load Testing: When performing load testing, I check that the generator can handle the load within ‘throttling’ boundaries. I then proceed to start the generator not lower than 50 and not greater than 100 percent of full throttle and sustain the voltage and frequency (120/240V and 60Hz ±1 respectively) for residential units.
- Voltage and Frequency Calibration: While using a multimeter or power quality analyzer, I adjust and gauge the voltage that the generator’s output should be and is expected to be with that of the building’s electrical level. For voltage, this region encompasses ± 5% of the nominal levels expected. As for the frequency, it should maintain a stable level within range.
- Transfer Switch Validation: Checking the seamless operation of Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) requires simulating a power outage. As I evaluate the transfer time, I keep an eye out for the ATS typically completing the transfer within 10 to 30 seconds range, to minimize the service stop time.
- Fuel System Check: While testing the fuel supply line, I check the connectivity for leaks and pressure differences that may arise. For gas piping systems, the pressure should not ease below or surpass the ranges of 3-5 psi. For propane-supplied systems, an adequate pressure of 10-11 inches of water column is required for proper combustion.
- Performance Metrics: I evaluate the generator’s performance in terms of extended operation and its affective steady-state performance. Important metrics are maintained temperature, noise levels (in decibels), and engine oil pressure stability.
These steps provide confidence that the generator system has been installed according to design conditions and will operate dependably for a long time.
Reference sources
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How do I install a standby generator for my home?
A: Installing a standby generator involves several steps: site preparation, placing the generator on a proper foundation, connecting to your fuel source (natural gas or propane), installing a transfer switch, and connecting electrical wiring. While some homeowners with advanced DIY skills might handle parts of this process, most installations require professional expertise. For safety and reliability, hire a certified electrician to install your standby generator and ensure it meets local codes.
Q: What is the average cost to install a whole home standby generator?
A: The cost to install a standby generator typically ranges from $5,000 to $15,000, depending on several factors. The generator size (which determines how much of your home it can power), brand, and fuel type affect the equipment cost. Installation costs include the transfer switch, wiring, permits, and labor. A basic 7kW system might start at around $4,000 installed, while a 20-25kW generator capable of whole home backup could exceed $12,000. Additional expenses may include a concrete pad, gas line upgrades, or electrical panel modifications.
Q: What should I consider when buying a generator for my home?
A: When buying a generator for your home, consider these key factors: power requirements (calculate the wattage needed for essential appliances), fuel type (natural gas, propane, or diesel), runtime (how long it can operate without refueling), noise level (especially important in residential areas), automatic operation capabilities, maintenance requirements, and warranty terms. You’ll also need to decide between a portable generator, an inverter generator, or a permanent standby system. For permanent installations, evaluate available space, proximity to your utility power connections, and whether you need whole home coverage or just essential circuits.
Q: How can I determine which generator is the best for my specific needs?
A: To determine which generator is the best for your needs, first list all appliances and systems you want to power during an outage. Calculate their combined wattage requirements, including startup surges for motors. Consider your climate (heating/cooling needs), duration of typical outages in your area, and budget.
Q: How long does it take to install a standby generator in a house?
A: Installing a standby generator to a house typically takes 1-3 days, depending on complexity. The process includes placing the generator on a prepared pad (usually concrete), connecting it to your fuel source, installing a transfer switch, and wiring it to your electrical panel. Simple installations might be completed in a single day, while more complex setups or those requiring extensive modifications to gas lines or electrical systems could take longer. Weather, permit approvals, and scheduling inspections can also extend the timeline. Working with experienced professionals can streamline the process and ensure that your home receives proper installation.
Q: Can you connect a generator to a house without a transfer switch?
A: No, you should never connect a generator to a house without a transfer switch. This is extremely dangerous and illegal in most jurisdictions. A transfer switch is essential safety equipment that prevents “backfeeding,” which could electrocute utility workers or damage your electrical system. The transfer switch ensures your home is completely disconnected from the utility grid before the generator begins to supply power to your home. For standby generators, automatic transfer switches detect power outages and seamlessly transition your home to generator power. If you’re considering a generator installation, the transfer switch should be considered a mandatory component, not an optional add-on.
Q: What maintenance does a standby generator require for reliable performance?
A: For reliable performance, a standby generator requires regular maintenance including oil and filter changes (typically every 100-200 operating hours or annually), air filter inspection and replacement, spark plug checks, battery testing, fuel system inspection, and testing the automatic transfer switch.
Q: Do I need permits to install a standby generator at my home?
A: Yes, permits are typically required to install a standby generator at your home. Most jurisdictions require electrical permits, and depending on your location, you may also need building, mechanical, and/or gas permits. These ensure your installation meets safety codes and standards. The permitting process often includes plan reviews and multiple inspections during installation. Working with a professional electrician to install your standby generator helps navigate this process, as they’re familiar with local requirements.








