Installing a home standby generator is one of the best measures you could adopt for your household during unexpected outages. Whether it is severe weather, grid failures, or other emergencies, a reliable standby generator will give you the peace of mind you need. However, where do you begin? This guide is designed to walk you through all the fundamental aspects of home generator installation. From selecting the model that best fits your needs to dealing with the complexities of installation and safety considerations, we hope to provide you with the information to bolster your household’s safety measures. Prepare yourself for boosting the resiliency of your home’s power system.
How Does a Standby Generator Work?
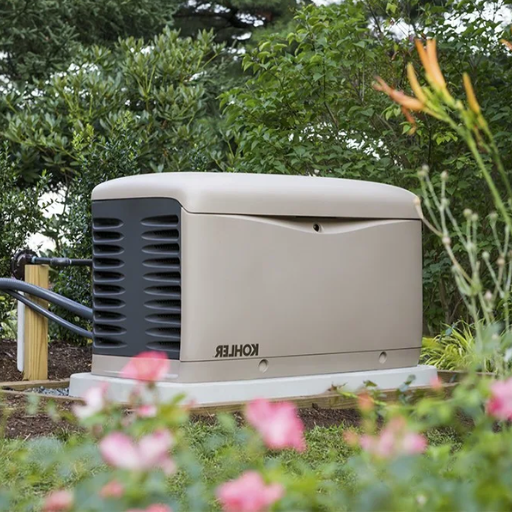

Standby generators are configured to detect and automatically supply power to your home during an outage. These generators are installed outside your home and are integrated into your electrical system. During power outages, the transfer switch detects the power interruption and commands the generator to start. The generator uses an external fuel source, such as propane or natural gas, to produce electricity. The system is designed to switch back to the utility grid once primary power is restored, and the generator will be shut down. This system provides your home with an uninterrupted power supply, which ensures a reliable backup solution.
Understanding the Basics of Generator Power
A backup power system consists of many parts, each integral in one way or another, that ensures reliability and steady flow of energy even when the primary energy source fails. These components consist of:
- Engine—Without the engine, there would be no structures like generators, and no companies would manufacture diesel-powered generators. This is because the engine is, in fact, the generator, and without a source of mechanical energy, there will be no output power generation. The generator engine runs using diesel, natural gas, and propane.
- Alternator—It helps convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The alternator contains a rotor that is very power hungry. Its partner constituent is the stator, which eventually yields this energy by generating induction electricity.
- Fuel System—A generator naturally comprises a fuel system used for daily work activities. If stationary, a fuel tank capable of storing a few gallons can be attached to portable generators, while standby models can use hundreds. Also, standby generators, most commonly used at homes, burn through 2 to 3 gallons every hour.
- Cooling and Exhaust System – Heat harms mechanical structures and must be eliminated immediately. Anything to do with cooling regulates temperature, while things to do with an engine remove toxic waste further down the line.
- Control Panel- The control panel acts as the brain for the generator. Users can track their performance, control settings, and check fuel levels. More sophisticated systems have features such as remote access through cellular devices.
- Transfer Switch—This device enables smooth switching from pure utility power to generator power and vice versa. Without this device, the generator would require manual operation, which would be very inconvenient during power failures.
Data on Generator Usage and Efficiency
More recent data shows the increasing dependence of generator systems in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. About some industry reports:
- As of 2022, the global generator market is valued at approximately $23 billion, and growth is expected to be at a CAGR of 5.1% from 20283 to 2030.
- Sales of standby generators for residential use are faster with 7% annual growth fueled by increasing power outages and extreme weather.
- Modern generators can achieve up to 90% fuel efficiency, minimizing carbon footprints and waste. Natural gas generators, for instance, are being touted as cleaner alternatives because they emit up to 40% less carbon than diesel-powered units.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Generators need routine work to function correctly. General maintenance consists of checking the bolts’ oil level, battery level, and air filter,s and periodically activating the generator to prevent it from idling. It is wise to have an expert conduct scheduled services to avoid complications and maximize device longevity.
Correctly foreshadowed, knowing the components, efficiency figures, and maintenance requirements completes the picture of generator systems’ character in contemporary power solutions.
The Role of the Transfer Switch in Generator Installation
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
|
Primary Function |
Switches power between the utility and the generator. |
|
Safety |
Prevents backfeeding to utility lines. |
|
Convenience |
Power circuits are directly from the generator. |
|
Compatibility |
Required for generators above 5,000 watts. |
|
Types |
Manual and automatic transfer switches are available. |
|
Installation |
Installed near the main circuit breaker panel. |
|
Operation |
Automatically or manually switches power sources. |
|
Cost |
Ranges from $300 to $1,500 including installation. |
|
Legal Requirement |
Often required by local building codes. |
|
Risk Without It |
Can cause surges, fires, or harm utility workers. |
What Are the Steps in the Generator Installation Process?

- Site Evaluation: The first step is to evaluate the generator’s placement regarding the site ventilation, distance from the transfer switch, and lcal governing rules.
- Generator Selection: Pick a generator that meets the operational power needs of the business or household while meeting the required safety and efficiency benchmarks.
- Site Preparation: Prepare the installation site at the generator’s location by clearing, leveling it, and considering local regulations regarding structures and ease of access.
- Transfer Switch Installation: Install the transfer switch next to the facility’s main electrical panel to easily be used for generator connections.
- Generator Installation: Connect the generator to the designated transfer switch with the proper electrical wires and connections, taking care to meet local codes.
- Testing Procedures: It is essential to run tests on both and confirm that the generator and transfer switch operate as expected. This includes powering the unit to test a smooth power sourcing change during outages.
- Routine Maintenance: Carry out routine checks on generator functions as part of the maintenance plan to sustain operational readiness and guard against operational malfunctions.
Site Preparation for Installing a Standby Generator
Correct site preparation enhances the ease with which standby generators are installed and their efficiency during operation. Careful steps such as planning and following set standards can reduce complications in the future and ensure compliance with jurisdictional laws. The following are crucial measures and components necessary for the planning phase of the generator installation:
- Selection of a Suitable Area
Choose a location that adheres to ventilation and safety restrictions. Basic building regulations recommend that generators be set back at least five feet from windows, doors, and vents, with an additional 18 inches from exterior walls to mitigate carbon monoxide poisoning. The chosen location should also be flat, dry, and above water potential flood levels whenever possible.
- Ensure Adequate Access and Controlled Air Flow
Controlled generator airflow prevents overheating and increases operational efficiency. Unrestricted airflow around the unit should be possible at the generator site. Moreover, adequate room around the generator to facilitate maintenance and repairs should be available. Manufacturer guidelines suggest a 36-inch clearance on all sides of the unit.
- Evaluate Ground Location
The generator’s base is critical for its equilibrium and vibration mitigation. Usually, a concrete pad is poured, or a prefabricated composite mounting pad is set in place. In frost-prone regions, use frost-resistant concrete to avoid cracking.
- Check Fuel And Electricity Connections
Fuel and electrical connections need to be easily accessible for the generator. Depending on the type of generator, this may mean a constant supply of natural gas, propane, or other approved fuels. A skilled contractor should be consulted regarding municipal code compliance and the proper configuration of these connections.
- Obtain Permits And Zoning Clearances
Most areas require installation permits and inspections for generators. Check with your area to avoid unwanted delays. There may also be noise regulations stating when a generator may be turned on, put into testing mode, or maintained.
- Install Adequate Drainage Systems
Excess water buildup around a generator site can cause rust that affects operation. Drainage systems should be installed to remove excess water, or the unit should be placed on a slope.
- Backup Proficiency Consideration
Look into the generator’s capability to determine if it meets future expansion needs. According to industry figures, standby generators allocated for residential use average between 7kW and 24kW, while commercial ones can go over 150kW. For standby generators, select a size based on your consumption requirements, but ensure there is additional capacity to cater for unforeseen demand.
By methodically resolving each of these checklists, proper compliance with local laws can be achieved while also guaranteeing optimal standby generator installation efficiency.
Connecting the Gas Line and Electrical System
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
|
Gas Line Sizing |
Use the appropriate pipe size for fuel flow. |
|
Gas Line Connection |
Connect upstream of other appliances. |
|
Gas Pressure |
Ensure 0.25–0.50 PSI for optimal performance. |
|
Distance from Home |
Use larger hoses for longer distances. |
|
Electrical Panel Connection |
Use a transfer switch for safe integration. |
|
Professional Installation |
Hire licensed plumbers and electricians. |
|
Permits and Codes |
Adhere to local regulations and fire codes. |
|
Testing |
Test connections for leaks and functionality. |
|
Backup Fuel Option |
Consider propane for consistent performance. |
|
Maintenance |
Regularly inspect gas and electrical systems. |
Testing and Finalizing the Installation
Once the generator has been installed, conduct a thorough functional test—simulate a power outage to check if the gas line and electrical connections provide continuous power.
How Much Does It Cost to Install a Standby Generator?

The cost to install a standby generator can range from 5,000 to 5,000 $ 10,000 on average; this figure includes the generator unit and installation. Generally, smaller generators cost less, but larger units capable of powering an entire home are more expensive. Other costs include permits from the area, preparing the location, and connecting the generator to the existing gas and electric systems, which are attributed to the overall cost. It helps to get several estimates from licensed contractors to make sure that the price, as well as the installation, meets expectations.
Breaking Down the Installation Costs
| Cost Component | Description |
|---|---|
|
Generator Unit |
$2,500–$10,000 depending on size and features. |
|
Labor Costs |
$500–$3,000 for installation services. |
|
Transfer Switch |
$500–$2,000 including installation. |
|
Site Preparation |
$500–$2,000 for concrete pads or adjustments. |
|
Permits and Inspections |
$50–$500 depending on local regulations. |
|
Wiring and Electrical Work |
$500–$1,500 for upgrades or additional wiring. |
|
Fuel System Setup |
$300–$1,000 for gas line or propane connection. |
|
Soundproofing (Optional) |
$200–$1,000 for noise reduction measures. |
|
Maintenance Plans |
$200–$500 annually for upkeep and servicing. |
|
Total Estimated Cost |
$5,000–$15,000 for complete installation. |
Factors Influencing the Cost of a Home Generator Installation
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
|
Generator Size |
Larger units cost more to purchase and install. |
|
Generator Type |
Standby costs more than portable or inverter types. |
|
Fuel Type |
Natural gas, propane, or diesel affects costs. |
|
Installation Complexity |
Difficult setups increase labor and material costs. |
|
Electrical Upgrades |
Older homes may need panel or wiring upgrades. |
|
Transfer Switch |
Essential for safe operation; adds to cost. |
|
Site Preparation |
Concrete pads or drainage may be required. |
|
Permits and Inspections |
Local regulations may require additional fees. |
|
Labor Costs |
Varies by region and installation difficulty. |
|
Maintenance Requirements |
Ongoing costs for servicing and repairs. |
Choosing the Right Installer for Your Budget
As I try to remain within my budget, I focus on getting an estimator with a good reputation and reviewing their case studies. I check several offers to get the best deal possible and validate all reviews and references regarding the service quality offered. In addition, I look for honesty regarding pricing and confirm that the practitioner knows the local regulations and ordinances to avoid surprises regarding fees or legal complications. With this in mind, I formulate strategies that help me decide without straining my finances.
Can a Portable Generator Meet My Needs?

If you need power for essential devices during outages or for activities like camping, a portable generator can significantly help. While they can supply adequate power for light appliances, small tools, and lights, they are not optimal for an entire home, running heavy equipment, or other demanding usages. As with any device, consider how frequently you will need the power and how much your appliances will use while connected to the generator.
Comparing Portable Generators vs. Whole House Generators
| Parameter | Portable Generators | Whole House Generators |
|---|---|---|
|
Power Output |
3,000 – 8,500 watts |
8,000 – 20,000+ watts |
|
Price Range |
$400 – $1,500 |
$2,000 – $5,000+ (installation extra) |
|
Fuel Type |
Gasoline, propane |
Natural gas, propane |
|
Fuel Consumption |
12-20 gallons/day |
13-48 gallons/day (propane) |
|
Installation |
No installation needed |
Requires professional installation |
|
Operation |
Manual setup and start |
Automatic start during outages |
|
Portability |
Easily movable |
Fixed, non-portable |
|
Noise Level |
Noisier |
Quieter |
|
Coverage |
Limited appliances |
Entire home |
|
Maintenance |
Frequent refueling, manual maintenance |
Minimal, automated maintenance |
|
Best For |
Short outages, budget-friendly |
Long outages, seamless power transition |
|
Safety |
Risk of CO poisoning if misused |
Safer, integrated into home system |
|
Lifespan |
Shorter lifespan |
Longer lifespan |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Portable Generators
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
|
Cost |
Affordable, $500–$3,000 |
Fuel costs add up over time. |
|
Portability |
Easy to move and transport |
Limited to small power needs. |
|
Setup |
Quick and user-friendly installation |
Requires manual start during outages. |
|
Fuel Options |
Runs on gas, diesel, or propane |
Fuel storage and refilling are needed. |
|
Power Supply |
Provides emergency backup for essentials |
Cannot power the entire home or large appliances. |
|
Noise Levels |
N/A |
Often noisy, may disturb neighbors. |
|
Safety |
N/A |
Carbon monoxide risk; needs ventilation. |
|
Maintenance |
Minimal for short-term use |
Regular upkeep and fuel management are required. |
|
Environmental Impact |
N/A |
Emits carbon emissions, not eco-friendly. |
When to Consider a Whole-Home Generator Instead
You may want to consider a whole-home generator if your power requirements exceed those of a portable generator, as it could better serve your needs. Below are five uses where whole-home generators are recommended:
- Persistent Power Supply
If you live in areas that frequently experience power outages due to storms and hurricanes, a whole-home generator is an absolute must to keep your household running.
- Heavy-duty appliances require whole-home Generators.
Whole-home generators can seamlessly power heavy-duty appliances like HVAC systems, water heaters, refrigerators, and ovens without overloading.
- Critical Medical Equipment
If the household relies on devices like ventilators, oxygen machines, or other life support equipment, a home generator provides reliable power that will help protect and ensure the safety of the household.
- Home Office or Business Needs
Whole-home generators are necessary if you run a business from home or telecommute because you need uninterrupted power for your work. Losses caused by outages are avoided altogether, alongside protected data, courtesy of whole-home generators.
- Long-Term Cost Efficiency
The initial price of a whole-home generator is undoubtedly a significant investment. However, families that consume a lot of energy find it more economical in the long run. Features such as automatic start and fuel efficiency make these generators practical for long-term use.
What Should You Know Before Installing a Whole-Home Generator?

| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
|
Generator Size |
Match size to home power needs |
|
Fuel Type |
Choose natural gas, propane, or diesel |
|
Installation Cost |
$8,000 – $16,000 (varies by complexity) |
|
Permits Required |
Electrical and plumbing permits often needed |
|
Placement Guidelines |
4 ft from walls, 3 ft from flammable materials |
|
Transfer Switch |
Required for safe power transition |
|
Site Preparation |
Level surface, concrete pad or gravel base |
|
Noise Level |
Check local noise regulations |
|
Maintenance |
Regular servicing for optimal performance |
|
Power Coverage |
Decide on full or partial home coverage |
|
Property Restrictions |
Check the HOA or local building codes |
|
Professional Installation |
Recommended for safety and compliance |
|
Backup Duration |
Depends on the fuel supply and generator capacity |
Evaluate Your Home’s Power Outage Needs
Estimating your home’s power outage needs is the first thing you must do before installing a whole-home generator. Focus on listing critical systems and appliances that should be kept running during an outage. These include refrigerators, HVAC systems, lights, and medical devices. Energy experts estimate that an American household consumes about 877 kWh of energy in a month, translating to approximately 30 kWh daily. It is safe to assume that most households will have lower essential power needs than they would ideally want to keep running.
Alternatively, you can list all necessary devices and their wattage that need to be powered during an outage. A refrigerator’s wattage draws between 600 and 800 watts, while central air conditioning can consume between 2,000 and 5,000 watts. Based on the results of your calculations, you may be able to ascertain the power capacity of the generator needed. Central heating and cooling systems are considered standard in most homes, and as such, many households are likely to have 22 kW generators available to power their critical appliances. On the other hand, if you live in a new house or have higher energy requirements, you will likely need to buy a generator with greater capacity.
Also, consider how often and for how long your area experiences outages. Reports indicate that weather-related outages are increasing in the U.S. due to hurricanes, severe storms, and wildfires. If you live in a region susceptible to prolonged and frequent outages, your investment in a reliable generator with high fuel capacity should be prioritized even further. A professional home energy audit can tailor a generator to your needs, ensuring your power options are efficient and available during crises.
Choosing Between Natural Gas and Propane for Your Generator
When evaluating your propane or natural gas options, especially in a generator, you need to consider availability, convenience, storage, environmental impact, and energy efficiency. Take into consideration this fundamental information that will assist you in making an educated decision:
- Availability
- Natural Gas: As a standard, natural gas is available in pipelines for direct delivery. In that case, it can be stored and supplied continuously without needing onsite storage. The only possible setback is in rural areas, far from town.
- Propane: Tank storage makes propane accessible in both urban and rural settings. Intake tanks, either above or underground, can reserve fuel on demand.
- Cost-Effectiveness
- Natural Gas: Natural gas is amongst the most competitively priced energy sources since it is offered via pipelines for a continuous supply with no additional fees.
- Propane: Compared to natural gas, propane is a bit less economical, especially with the additional costs incurred for delivery and refilling.
- Storage
- Natural Gas: There is no storage that propane poses, so instances of running out during prolonged use are not an issue. This means that it is convenient.
- Propane: The tanks must constantly undergo various safety checks, which poses the challenge of regularly inspecting and maintaining them.
- Environmental Impact
- Natural gas burns cleaner than other fossil fuels and contributes fewer greenhouse gases. This keeps the environment clean compared to emission levels.
- Propane is considered a cleaner fuel as it burns with fewer carbon emissions than natural gas.
- Energy Efficiency
- Natural Gas is less efficient than propane because of its convenience.
- Propane is more efficient than other fuels and provides greater energy output and heat. This makes it ideal for heavy-duty generators.
Considering all these factors, you can determine what fuel type best suits your area, finances, and ecological concerns. Both options have distinct strengths, and selecting the right one can guarantee efficiency when needed most.
Ensuring Peace of Mind with Proper Maintenance
Following proper maintenance practices is critical to ensuring optimal operation during an emergency. Generator failures are widespread, with up to 68% of generators failing simply due to a lack of regular maintenance and upkeep, including inspections. A thorough maintenance schedule minimizes the risk of potential failures and enhances the longevity of the equipment.
Here are some basic, yet essential, practices you should follow to help maintain your generator:
- Changing the Oil
Altering the oil for proper lubrication is essential as it helps ensure the longevity of the equipment. Different models and usage levels result in varied recommendations for oil changes every 50-200 hours, substituting with quality-grade oil and allowing free movement when used under extreme conditions.
- Checking the Air Filter
The air filter aids the smooth running of an engine and helps prevent deterioration. Cleaning the air filter every hundred hours and following the manufacturer’s recommendations helps ensure it is not strained due to dirt buildup.
- Inspecting The Health Of Batteries
Routine tests and changing them out every two to three years allow for peace of mind from issues regarding poor performance. Aged and faint batteries are widespread issues regarding performers, aided by generators that do not cater to issues such as performance problems.
- Caring For The Fuel System
Draining gas from the carburetor or installing stabilizers for gasoline-boosted generators has many perks. Gas and propane systems should be regularly checked for leaks and pressure aids to avoid potential detonations.
- Conduct Routine Checks
To properly check the generator’s longevity and reliability, you should perform routine load tests, which include running the generator under full load for 20-30 minutes at least once a month. This helps identify issues like wet stacking (increased fuel residue in the engine) or sludge (dirty oil) accumulation.
- Arranging Professional Maintenance
Having certified professionals review your generator at least once a year is crucial to identifying any potential issues with misaligned parts or disabled safety features. The generator should also have up-to-date servicing records, which increase its resale value.
Implementing these maintenance procedures will put you at ease, ensure that your generator will be operational when needed, and minimize the risk of any operational failure.
References
-
US installation, operation, and performance standards for microturbine generator sets – A detailed document on generator installation and performance standards.
-
Vortex-generator installation studies on steady-state and dynamic distortion – Research on installation techniques and their effects.
-
Technical experience during thermal and chemical recycling of a 23-year-old PV generator – Insights into generator recycling and installation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a home standby generator, and why should I consider installing one?
A: A home standby generator is a backup power system that automatically provides electricity to your home when the main power supply fails. It’s a reliable solution that ensures your home appliances and systems continue to function during power outages, protecting your home’s value and providing peace of mind.
Q: How do I determine the right size generator for my home?
A: Determining the right size generator depends on your home’s power needs. Consider the essential appliances and systems you want to run during a power outage, such as heating, cooling, refrigeration, and lighting. A professional generator installer can help assess your needs and help you choose the appropriate generator size for your home.
Q: Can a whole-house generator power my entire house?
A: Yes, a whole-house generator can be configured to power your entire house. It can provide electricity to essential systems and appliances, ensuring seamless operation during power outages. The specific capacity will depend on the generator installed and your household’s power requirements.
Q: Is hiring a professional electrician to install a standby generator necessary?
A: Hiring a professional electrician is crucial for installing a standby generator. Proper installation ensures safety, compliance with local codes, and optimal generator performance. A professional will have the expertise to connect the generator to your home’s electrical system correctly.
Q: What are the benefits of installing a whole home generator?
A: Installing a whole-home generator provides numerous benefits, including continuous power supply during outages, protection for your home appliances, increased home value, and convenience for your daily activities. It ensures that your home is resilient and prepared for unexpected power interruptions.
Q: How long does it take to install a home backup generator?
A: The installation time for a home backup generator varies depending on the complexity of the project and the specific generator model. Typically, it can take a few hours to a few days, including site preparation, electrical connections, and testing.
Q: What maintenance is required for a standby generator in your home?
A: Regular maintenance for a standby generator includes checking the oil and coolant levels, inspecting the battery, testing the system, and scheduling professional service annually. Proper maintenance ensures the generator runs efficiently and is ready when needed.
Q: Can I hook a generator to my home’s natural gas line?
A: Yes, many standby generators can be connected to your home’s natural gas line, providing a continuous fuel source. This setup offers the convenience of not needing to refuel and ensures the generator can run for extended periods without interruption.
Q: Are any products and services available to enhance the performance of a backup generator?
A: Yes, there are products and services available to enhance a backup generator’s performance, including automatic transfer switches, load management systems, remote monitoring, and periodic maintenance services. These enhancements ensure the generator operates optimally and reliably.
Q: Is a standby generator worth investing in my home?
A: A standby generator is worth the investment for homes in areas prone to power outages. It provides reliable backup power, protects your home appliances, maintains the value of your home, and ensures comfort and safety during emergencies. Its peace of mind makes it a valuable addition to your home.