Overview of Power Outages in Guadalupe
The Guadalupe Outage is chiefly attributed to harsh weather conditions, worn-out equipment, and a rise in power demand. Storms and strong winds result in power lines falling, while very high or long-lasting temperatures overload the system, causing blackouts. Additionally, in some localities, services may be disrupted from time to time due to routine repairs or unexpected equipment breakdowns. There are plans to tackle the problems mentioned above through technological solutions of upgrading the infrastructure, as well as investing more in grid mitigation, so that the outages experienced by the people can be lessened.
Definition of Power Outages
Interruptions in power supply in a region are the power outages caused by reasons like harsh weather, malfunctioning of equipment, or excessive load on the grid resulting in the affectation of residential premises, business, and even vital services.
Importance of Staying Informed
Being aware of the situation to ensure people’s safety during power outages is crucial. This is because it helps reduce the suffering, and supplies or resources are used or put into studies prudently. Good information, and on time, allows people and societies to prepare well, engage actively, and recover more quickly. The following paragraphs explain five reasons that explain the need to be in the know of what’s happening around/how others are doing during the GUADALUPE OUTAGE:
Weather Forecasts
This includes weather conditions, such as hurricanes and downed power lines. People should stay away from such dangers and be on the lookout for any risks that may endanger their lives. However, many injuries occur during an outage because people are unaware of the risks present, as is often the case during a hurricane.
Outage Updates
This is important because the amount of time without power affects the measures to be taken; for instance, whether to book a place to stay or one can simply wait for the time to pass without electricity.
Conservation of Resources
La información relacionada con los cortes de luz ayuda a gestionar mejor los diversos recursos como los alimentos o el agua. This means the meal will include perishable foodstuffs that have been stored in fridges or freezers before the expiry date.
Health Services Utilization
Keeping abreast with the availability of service centers, for instance, shelters, medical resources, or warm regions in occasional much cooler temperatures plays a key role in the preparedness of people.
Communities’ Effort
Even amid outages, community members talk to each other to help one another, whether by sharing generators or other resources, or by assisting their weaker neighbors. The National Academies of Sciences also refers in their research on the role that social networks play in power outage resilience strategies among long-term cases.
Rather than face these adversities passively and helplessly, people become active participants and try to facilitate security, making effective attempts to cope with power cut problems.
Current Status of Outages in Guadalupe
More recent statistics indicate that the Guadalupe Outage has been ongoing for days in the areas experiencing heavy rain. More than 3,500 families, based on the records of electric companies, will not switch on their power while teams are on the ground trying to rectify the situation. The blackouts are in the western and central parts of Guadalupe, preventing them from reconnecting due to fallen trees on the lines and flooding.
The authorities have since issued statements indicating that teams are working relentlessly, especially in areas such as hospitals and other key response sectors. There is no definite estimated recovery period, as some sections will be reenergized within 24 hours, while others, especially the worst-hit areas, may take as long as 72 hours without power.
Safety Advisory: It is wise for residents to check for the status of the situation through relevant official information; avoid any fallen electricity cables; and be aware during nighttime as visibility is poor. People who need a refuge, to freshen up, or just to charge their gadgets are welcome to the emergency shelters established at Guadalupe Civic Center and Lone Star High School. The public should immediately notify the authorities of any danger caused by the Guadalupe Outage.
Outage Map and Reporting

To view the most recent outage map, visit the official utility site and click on “Outage Map.” This map is cited as interactive because it displays the impacted area, the anticipated restoration timelines without any changes, and updates them accordingly. If you are reporting an outage, please contact us at 1-800-OUTAGES or report online using the reporting tool on our website. Remember to include the exact location where assistance is being rendered to enhance response time.
How to Access the Outage Map
There’s always the option to be notified regarding any disruptions to the service in the Guadalupe area. Here’s what you need to do.
- Access the Website: To visit the utility website, type in the address http://www.utilitywebsite.com/outagemap in a new tab on your browser.
- Look for the Outage Map Section: After landing on the homepage, find the ‘Outage Map’ tab either within the menu or as a link on the front page.
- Some Advanced Options: The graphic within the outage map features zoom capabilities, allowing you to view the perspective of a particular movement. As such, all the affected territories can be seen, highlighted using several shades of colors that depict the level or the extent of damage.
- Capabilities Search and Filters: Enter your address and your area into the search box to bring information relevant to you. You can also use filters to view specific information, such as active outages or expected recovery times.
- Access through Mobile Devices: A majority of utility companies have simplified versions of their maps for mobile devices or have developed exclusive mobile apps. Find the official utility application through your app store if you choose to access it while on the move.
The latest Google searches indicate that newer versions of outage maps, available for most regions, now feature weather overlays, power restoration progress bars, indications of power restoration in areas already restored, and, when applicable, power restoration forecasts. Some outage maps display even forecasted restoration periods, utilizing artificial intelligence and historical data. Without a doubt, these features come in handy when outages and repairs are concerned, allowing you to easily carry out notifications and field services swiftly.
Steps to Report an Outage
| Step | Details |
|---|---|
| 1. Identify the Issue | Determine if it’s a full outage, flickering lights, or downed power lines. |
| 2. Stay Safe | Stay 30 feet away from downed lines; call 911 for emergencies. |
| 3. Choose Reporting Method | Options: phone, text, online, or mobile app. |
| 4. Provide Location | Enter the affected address or service area. |
| 5. Use Text Commands | Text “OUT” to the utility’s designated number. |
| 6. Call Utility Hotline | Dial the utility’s outage reporting number (e.g., 1-888-LIGHTS). |
| 7. Check Outage Status | Use online tools or apps to track restoration updates. |
| 8. Sign Up for Alerts | Register for text or email outage notifications. |
Understanding the Outage Map Features
Unfortunately, customers may experience an impact during any utility interruption due to the presence of information accessible on outage maps. These tools not only indicate which zones are impacted by the utility interruption but also help customers understand the extent and degree of recovery from the disruption. Below, some of the most common features on the outage maps are described.
- Weather Overlays- Shows real-time weather conditions such as storms or high winds that are causing or contributing to power outages within an area.
- Outage Detection Scale – Colored bands, depicting various degrees of an outage, ranging from minimal service disruption to comprehensive and severe challenges.
- Estimated Recovery Time – Provides an expected start time, enabling users to make necessary arrangements.
- Customer Reporting Tools – Ensures that individuals can interact with the system and report outages, allowing these issues to be captured and corrected at the local level.
- Prediction Utilising AI – Employs past facts from experience, limiting itself to predicting within time frames. Possible cases of gloves’ retraction in interpreters out of operation may be examined too.
The advantages provided by the described functions can assist people during such instances (Guadalupe Outage).
Causes of Electric Outages in Guadalupe

Guadalupe Outage can occur due to:
- Adverse Weather – Thunderstorms, powerful gusts, and heavy downpours of rain are common causes of damage to electrical infrastructure and resulting outages.
- Trees – Disruptions in electric supply during times of winds or storms are caused mainly by trees that touch overhead lines or bring them down.
- Equipment Breakdown – The power grid may experience failure due to the breakdown of machines that have been in use for an extended period.
- Road Accidents – Several incidents, especially vehicular accidents that involve the power utility, cause power outages, but only in areas where the lines have been cut or destroyed by electric poles.
- Maintenance – Repairs and improvements are made to the networks, and the power is temporarily turned off.
- Animals – Forest creatures, such as birds and squirrels, may inadvertently cause damage to appliances, resulting in inefficient service delivery.
Understanding the aforementioned factors enhances community preparedness and mitigates irregular power outages.
Natural Disasters and Weather Impact
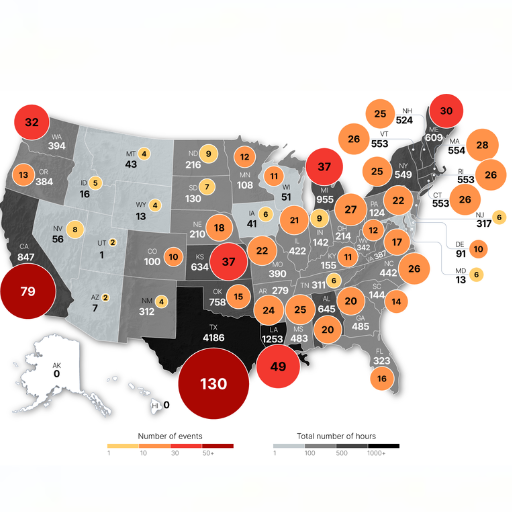
Power outages are primarily caused by natural disasters and, in some cases, by catastrophic weather conditions. These phenomena pose a significant challenge to the available infrastructure, often causing disconnection from power, and restoring those affected may take days, if not weeks, based on the level of damage sustained. The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) states that more than 70% of the major outages in the period 2018-2022 in the USA were weather–related, for instance, hurricanes, thunderstorms, snow, and wildfires.
Storms such as Hurricanes and Tropical cyclones:
Excessive hurricane winds and rainfall can bring down trees and power poles, causing power cables to be damaged or severed. For instance, during 2022 Hurricane Ian, more than 4 million Florida residents experienced a power outage.
Thunderstorm and tornado:
Some violent storms are accompanied by loud thundering, high-velocity winds, blinding light, and knocking ice on the ground, which can cause structural damage to power systems. Transformers may split apart, causing an outage due to a lightning strike or a tornado may level the strong mettle of the high voltage transmission towers. In one case noted in June 2023, a series of storms and outages resulted in power blackouts affecting more than 500,000 people in the Midwest region of the United States.
Winter Weather:
As the fall of freezing rain, snow, and ice adds undue weight on the wires, it is noticed that they break. Additionally, ice-covered roads are hazardous to drive on and can cause severe damage to structures containing utilities. For example, during the Great Texas Freeze of 2021, millions were powerless as the cold weather suppressed the demand, and electricity was in short supply.
Wildfires:
In areas with a high likelihood of drought or extreme dryness, it is common for transmission lines and substations to be damaged by fires. Utilities typically carry out public safety power shutoffs (PSPS) to remove factors that could easily lead to another bushfire. For example, California sought to avert the likelihood of fire damage during the 2020 wildfire season, which contributed to a significant number of controlled blackout incidents across the State.
The need to anticipate extreme weather events and their consequences on electricity supplies has been crucial. Modernized grids, renewable energy, and resilient infrastructure are being considered by communities and the government to mitigate damage and expedite recovery after such events occur.
Infrastructure Issues
Old Power Grids
There are numerous electrical power grids in existence today that have been constructed for many years, even decades ago. But most of them were not prepared for current electricity consumption levels. Take, for example, the 2019 report of the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), which gave America’s energy infrastructure a grade of C-. This indicates that the necessary up-gradation and supercussed modernization are long overdue.
Lack of Integration of New Sources of Energy
Another challenge hindering the shift to green energy, such as solar and wind energy, is the scarcity of infrastructure for efficient dispersal and storage of such energy forms. The available battery storage and transmission grids lag the expansion of wind and solar energy.
Susceptibility to Extreme Climatic Conditions
Today, power grids fail even in cases where extreme weather, such as hurricanes, wildfires, and snowstorms, occurs. A case in point is the February 2021 winter storm in Texas, which disrupted power supply in many parts of the state; more than 4.5 million customers were affected, an incident which exposed the frailty of the state’s grid system.
Cybersecurity Concerns
Grid systems are now more interlinked than on past occasions, which in turn makes it easier for cyber threats to occur and to affect or compromise the grid. Cases of computer break-ins are said to have increased, and therefore most systems urgently need cybersecurity processes that avert dangers that may arise from outside.
Insufficient Availability of Electricity in Rural Areas
There are several reasons that make it difficult for rural populations to access electricity, one of which is that most of the electric grids in these areas are very old, and some do not exist at all. Such discrimination leads to an increase in poverty levels, as the conducive environment necessary for recovery from this challenge is less likely to be present in these regions.
Addressing these flaws will require multi-sectoral efforts and the deployment of advanced technologies on a large scale, as well as substantial financial assistance, to increase energy security and respond to dynamic energy requirements.
Human Factors and Accidents
Human error is a causal factor in the majority of accidents, regardless of the segment of activity – whether it is transportation, construction, power generation, or similar. Such accidents are often attributed to people’s actions, behaviors, or the way things are structured. The following are some of the reasons why accidents occur, together with brief descriptions and data where relevant:
Fatigue
Tolerance of fatigue undermines the effectiveness of reasoning and rationality, resulting in failures and mishaps. Reports from the National Safety Council state that for every 100 safety incidents in which one worker is involved, 70 workers will experience the effects of fatigue, and their performance will be compromised. In the case of transport, for instance, arduous long-distance travel tires drivers and makes them very prone to causing accidents.
Attentive Dotting
Dotting or dotting caveats concerning the use of mobile phones, as well as smoke interference and the like, are the leading causes of accidents. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) acknowledges that people losing their attention while driving caused more than 3 thousand fatal incidents in the USA in 2022.
Inadequate Training
A lack of proper training on safety measures or equipment among workers is likely to lead to accidents and related errors. Moreover, construction is one of the sectors that also cites the lack of training as a significant factor contributing to work-related injuries. At the same time, OSHA, on the other hand, lists it as a sector that needs improvement.
Stress and Mental Health Aspects
Excessive stress or uncontrolled mental illnesses increase the chances of making mistakes, having poor decision-making skills, and being less effective at work. Various research studies have shown that errors resulting from stress significantly contribute to the majority of workplace accidents, particularly in high-stress fields such as medicine and aviation.
Disregard of Safety Measures
Failure to adhere to the laid-down safety measures can be disastrous. An example is the Center for Construction Research and Training reported that as much as 60% of deaths in construction are a result of failure to adhere to safety regulations such as fall protection and hazard assessment.
These human factors can be managed at a manageable level by introducing proper interventions, which may involve improving competence/skills through training, undertaking scheduled time-outs, offering support to improve mental health, and adhering to existing safety principles, among other measures.
Impacts of Power Outages

When power goes out, it has an impact on routine activities and even the most critical functions in various aspects. It results in a loss of income for many companies due to delays in their activities, requests, and even the deterioration of products when they are interrupted. Power cuts are unpleasant even when they do not disable heating or cooling equipment or communication gadgets in a household, as the people are still able to communicate inside. Longer term, extended blackouts could also compromise crucial services – such as hospitals, emergency interventions, or even water installations – thereby putting people’s safety at risk. Additionally, the economic and social repercussions underscore the need for adequate infrastructure and emergency planning to prevent such consequences from occurring.
Impact on Residents and Businesses
Disruption of Daily Life
Power outages can significantly disrupt day-to-day routines for residents, rendering basic appliances and devices unusable. For example, refrigerators stop preserving food, leading to spoilage, and individuals lose access to lighting, making evenings inconvenient and unsafe.
Economic Losses for Businesses
Businesses often suffer financial repercussions due to halts in operations. According to a U.S. Department of Energy report, power outages cost the economy an estimated $150 billion annually, with small businesses being particularly vulnerable.
Educational Interruptions
Remote learning and digital classrooms rely on electricity and internet access. Outages can hinder educational activities, leaving students disconnected from their studies and educators unable to deliver lessons.
Health and Safety Concerns
Individuals who rely on electronic medical equipment are often highly vulnerable to power outages. Moreover, heating and air-conditioning services become unavailable, subjecting individuals to adverse temperatures which may pose a threat to their well–being.
Ramifications on Public Services
Certain critical services, such as water treatment and transportation systems, can be affected, potentially causing problems for the community at large. There can be long delays in services, and health safety measures may be violated if public transportation or safe water supply is disrupted.
Emergency Preparedness During Outages
Anticipatory action for power interruptions has been widely accepted as a matter of safety concern. Here we will go through the central respective interventions with consideration of both existing practices and benchmarks:
Prepare Basic Emergency Essentials
Get ready and pack a well-thought-through emergency kit made up of, among other things, flashlights and spare batteries, water – at least a gallon for each person for 3 days, foods that do not go bad quickly, a can opener – this one doesn’t run on energy 🙂, and a First Aid kit. It is reported in The Federal Emergency Management Agency–FEMA that 48% the of American population is not completely stocked with any emergency supplies, therefore stressing the more that it’s wise to have them ready.
Keep Abreast
NOAA Weather Radio and other mobile alert services from government agencies should be used to stay informed about adverse weather conditions and any alerts within or nearby areas. To highlight the connection between storms and power cuts, the U.S. Department of Energy also provides information indicating that as much as 70 percent of power outages are attributed to storms, making it prudent to follow the Guangzhou weather forecast.
Having a Backup Source of Energy
Purchase a back-up in case of an outage, that is a portable generator, or even a battery packs for a few of the essential appliances and gadgets. Studies have shown that approximately 30% of the population in the United States contends with a power outage annually, hence making backup plans for day-to-day operations quite essential.
Consider Health Requests
In the case where someone in a household is a member who uses any medical equipment, such as oxygen support that requires power, prepare a means by which power can be restored. Reach out to the local power producer and apply for the reservation of restoration services, if this option is available.
Communication guideline
Outline how family members or neighbors shall communicate with each other, as well, as cell towers might have been affected by the blackout. Ensure that everyone in the group knows who to contact in an emergency and where to meet in case of separation.
Communities that prepare ahead for emergencies not only minimize the danger but also withstand the impact of any possible disaster. With the frequency and intensity of severe zero-events increasing over time due to climate change, it has never been more important to adopt these preventive tactics.
Long-term Consequences of Frequent Outages
Recurrent disruptions could prove quite adverse and catastrophic for individuals and nations in the long run. Underneath are the five primary long-term causes and consequences of continuous blackouts:
Economic Losses
Time and time again, an interruption in the supply of electric power results in a loss to the economy due to various factors. Businesses that rely on electricity for their processes may miss production time or revenue. In some cases, businesses may also incur additional costs when purchasing generators or other energy-saving mechanisms. A U.S. energy department report points out that power interruptions in the US result in economic losses to the tune of up to $150 billion annually.
Essentials of the Raiding Age
Storms and treacheries on the battleground are frequent interruptions that can cause systems essential to national security, such as those that provide energy or accelerate degradation. They make systems, especially the old ones, work harder, or worse, they cause premature aging of all systems as they try to restart all over again after every disruption, leading to high maintenance costs or the need to replace them.
Public Health Risks
Power blackouts often interrupt the delivery of health-mitigating and restorative healthcare services, including maintaining the safety of medications and providing air conditioning during extreme weather conditions. The very old and those suffering from any illness are particularly at risk. Research indicates that ailments stemming from heat tend to increase during heat waves over the summer, particularly when there is a Guadalupe Outage.
Interference in Learning
Long Guadalupe Outages may affect the use of technology meant to facilitate learning both in schools and at home. Learners are often equipped with inadequate resources to meet their learning goals in areas like these, where a scarcity of resources already exists.
Effects on the Environment
Many energy-saving devices are relied on in power due to, which increases emissions of these pollutants. As the use of these devices increases, emission levels rise, and thus the environment suffers significantly as a result. If this continues unabated, the air and the environment will be heavily affected as a result of using these chemicals.
These effects underscore the importance of investing in energy systems and climate resilience to avoid other effects, such as frequent blackouts and power failures of all infrastructures. Additionally, no action beginning with ‘José Guadalupe Outage’ may go beyond this point, since all pieces will be invaded by religion in its entirety.
Solutions and Preventive Measures

Contribute to Green Energy Development
A shift to renewable sources, such as solar, wind, or hydro power, would significantly reduce dependency on traditional power grids. Such renewable energy technologies are, therefore, more stable and less vulnerable to external impacts.
Improve Existing Grid Energy Infrastructure
Implementing modern techniques to enhance power grids would improve dependability and reduce the risk of blackouts. The examples include smart grids, which have enhanced systems that allow much easier and faster fault location and restoration.
Support Bush-Energy Voltage Dong Wallet located in the Treatment Facility 4
The use of large batteries that can charge and discharge power as needed would eliminate power interruptions and allow for the storage of power during off-peak hours.
Increase by conserving energy
Consequently, the energy consumption of demand and savings appliances, as well as habits that do not enhance consumption and, therefore, reduce outages, is significantly reduced.
Bolster Institutional Development
Governments should, as a matter of urgency, develop and promote infrastructure geared towards sustainable energy sources and climate-friendly investments, in the form of subsidies and other mechanisms, to encourage uptake in these endeavors.
Natural calamities are, as a rule, beyond an individual’s control and hence stress their infrastructure instead of relying on a predictable weather condition like a tornado, an appropriate strategy would involve knowing the ways to lessen the impact of such weather conditions as a tornado. Dams also predispose occupants to water shortages and flooding, as was experienced during the Guadalupe Outage in 1993 in Texas.
Improving Electric Infrastructure
Electricity infrastructure improvement is significant for the provision of a reliable, secure, and sustainable energy supply in light of these two facts, but also hard facts of the climate. This was recently confirmed by recent research, which states that the growth in energy demand over the next few decades will be approximately 3% per year, driven by increased electrification, as well as the surge in population and the adoption of electric cars. In response to this need, there are several significant measures that may be put in place:
Upgrading of the Transmission and Distribution System
Many of the electric grids around the world are very old and some need to be overhauled quickly due to many reasons, including the need to integrate higher capacities and more renewables. The reliability and efficiency of the grid can be significantly improved with smart grids that utilize sophisticated communication and sensor technologies. For instance, the US Department of Energy thinks that the use of smart grid technology can reduce power outages and interruptions. This study suggests that it is possible to save billions of dollars a year from the loss of economic activities.
Incorporating Renewableness
To shift to more conventional forms of energy, such as all the clean forms of energy, including solar, wind, and hydro power, the existing transmission has to undergo at least some changes, there is need for investment in energy storage technologies such as big batteries, to mitigate the problem of renewable energy desert areas. IRENA’s analysis and predictions show that global capacity of batteries for storage is going to increase by more than 40% every year till 2030, which will definitely enhance energy management capabilities.
Strength to Withstand Climate Change
As natural disasters have become more frequent and intensified, it is also essential to increase the electric system’s capability to perform under conditions of a hurricane, flood, or fire. It could be achieved through underground wires, weatherproof materials, and distribution micro grids. A recent study states that every dollar spent on resilient energy infrastructures’ construction and maintenance is able to save up to four dollars on the costs of reconstruction following disasters.
Reduction of Energy Usage and Control of Its Use
Of course, when innovative energy management technologies are deployed, they help to alleviate the pressure on the grid. For example, by using smart meters and demand response programs, customers can adjust their electricity consumption according to the actual state of the grid, thereby avoiding shortages during peak periods.
Such upgrades of infrastructure structures provide not only reliability in the energy sector but also help fight the climate change battle internationally and create jobs in the renewable energy industry. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), investments in clean energy and infrastructure enhancement are expected to attract $50 trillion and generate 14 million jobs worldwide. Proactive actions are necessary to bolster current and new infrastructure, as the grid of the future cannot be built with a ‘business as usual’ mindset. It must be resilient, environmentally friendly, and adaptable.
Community Preparedness Programs
Community preparedness programs play a vital role in ensuring our collective safety and resilience. I believe these programs provide individuals with the knowledge and resources needed to respond effectively to emergencies. By participating in these initiatives, we can foster a sense of unity and readiness, making our communities stronger in the face of challenges.
How to Stay Updated on Outages
The awareness strategy for dealing with an outage as it occurs is helpful for any citizen to mitigate specific risks and avoid the unnecessary inconveniences that come with the blackout. Below are simple but effective ways of staying alert:
Utility Provider Websites or Apps
Many utility companies have made it their business to offer more information in real-time regarding outages, expected outage duration, and safety issues. For example, companies like PG&E and Duke Energy provide maps showing where the outages occurred and the progress made. Search for your provider’s website and mobile application for a faster response time.
emergency notification systems
Sign up in your area for any alert systems set up by the disaster management agency, such as the Federal Emergency Management Agency in the US, which has a system called IPAWS, the Integrated Public Alert and Warning System. The alert systems enable issuing power warnings and INTERRUPTION warnings caused by disasters directly to the phone.
Social Networks
Keep an eye on your utility corporation and the municipality through their social media accounts, such as Facebook and Twitter. These platforms are used to perform several operations, including quick information dissemination and customer care. An example could be provided in a report of 2023, in which participants confirmed that almost 43% of them use Twitter to get updates whenever there is an emergency and people lose power.
Google Search
Google is a good way to learn about power outages in a particular area. For example, enter search phrases like “power cut near me” or enter the brand name of the power retailer. Google provides graphs, links to individual sites with maps, and also news. Typing “ComEd outages,” for example, links directly to their outage page and any active interruptions.
Weather and News Apps
Applications such as AccuWeather, or media organizations based in the regions, habitually share vestiges of oncoming storms or disaster reports, which may imply possibilities of power interruptions. Some even offer notifications regarding your geographical location, so you can receive all the relevant updates.
These resources can be utilized simultaneously or separately to inform and prepare individuals within the context of any unexpected outages, thereby minimizing panic and unpreparedness, and ensuring appropriate action is taken during available time gaps.
References
- Quick Response Research on the September 8, 2011, San Diego Blackout
This report provides insights into power outages and their impacts, which could offer relevant context or methodologies for analyzing outages like the Guadalupe Outage.
Read the report here - Disaster Planning in New Mexico
This document discusses disaster preparedness and response strategies, which might include relevant frameworks applicable to power outages.
Access the document here - Outage Effects on the TCP-Wireless Integration for Data/Voice Services in CDMA Systems
While this is more technical, it discusses the effects of outages on communication systems, which could provide a unique perspective on the technological impacts of outages.
View the publication here
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Guadalupe County is prone to outages; however, the causes may differ depending on whether it is stormy, there is an equipment breakdown, or a maintenance operation is underway. Regularly updating the local news and checking for announcements from the utility providers is needed for her current situation.
To view the blackout map for your area allocation, visit the local utility provider’s website, such as the SRP website for Guadalupe. Several providers also offer real-time information on power outages, allowing you to see which areas are affected and when power is expected to be restored.
Your utility company will have a procedure that you need to follow to report an outage in Guadalupe Valley, either by using their custom service phone number directly or by going online. Outlining the precise location and consumption patterns will help them address the electric power failure issue more effectively.
In a situation when blackouts occur, it is best to go for safety rather than risk approaching fallen electricity cables and also avoid burning candles, which would ignite fire. It is, however, advisable that the freezer and refrigerator doors be left closed and that a portable radio be carried for local government broadcasts in case of a power loss.
Such information is obtained through internet searches on utility companies’ websites or from the respective customer support departments. They might have information that describes the problem and how long it would take to solve it.
Indeed, interruptions in service can be reported to GVEC by calling their toll-free helpline or by logging onto their website. In most cases, separate areas are available for reporting outages and checking for updates, allowing you to stay informed about the situation.
The geographical location of a blackout affects the period of blackout restoration; for instance, rural centers or other remote areas may be a challenging region, thus taking longer to fix the problem than when located in urban areas. Power Restoration for Utility Companies is done according to the number of standby customers affected, as well as the short- or long-term damage caused by the issue.
For such incidents, try reporting every problem with consistency that happens in your municipality to the supplier. By doing so, they can conduct investigations into the issue, such as obsolete apparatus and the lack of capacity to handle a large area, which can result in poor service reliability.
To avoid being caught up in future outages in Guadalupe County, you are encouraged to subscribe to your utility service provider’s alert system. Most of these companies offer the option to send their customers texts or emails with information about basic repair work scheduled, potential power interruptions, and updates on restoration progress. Hence, you will not be left out of any development.