It can be very annoying and potentially expensive if the generator does not work as intended for any reason or malfunction. A generator used for domestic, commercial, or site use must be replaced immediately. The power of the generator to operate electrical devices during a power failure or as a power supply can cause various problems, such as generator starting issues and fluctuating voltages. This is why this guide exists, and its aim is to help you develop the skills to tackle various generator problems on your own. Whether you’re a resourceful technician or a first-time client, this complete manual will guide you through the problem identification process, which will be easy on your end and, based on that, bring the machine back into operation.
Understanding Common Generator Issues

Battery Malfunction
Depending on the context, a non-operational or near-dead battery is often the culprit behind the startup problem. The battery’s voltage and connections should be tested regularly to ensure optimal operation.
Fuel Supply Problems
Low fuel levels, bad fuel, or a clogged fuel line, among others, are among the biggest enemies of a generator’s smooth startup. Fuel should not be the problem; hence, thoroughly check the entire fuel system to rule out any blockages and ensure the fuel is fresh.
Blocked Air Filters
The Generator unit fails to start properly when the engine doesn’t get enough air due to dirty or clogged air filters. Another smart way to keep the Generator unit running smoothly is to clean or replace air filters as part of the maintenance routine.
Faulty Spark Plugs
Spark plugs play a significant role in the ignition process, and if they are worn out or faulty, then the process is disrupted. Just use an engine manual to check for signs of wear or corrosion, and then, if needed, change the spark plugs accordingly.
Low Oil Levels or Oil Sensor Faults
A low oil level or an oil sensor that is not functioning correctly can trigger the safety mechanism, which prevents the Generator from starting. All are advised first to undergo oil checking and ensure the sensor is functioning.
Overview of Generator Problems
Battery Failure
One prevalent reason a generator won’t start is a battery that is either discharged or broken. This situation can occur if the battery hasn’t been used for a long time, if it’s been charged insufficiently, or if the terminals are corroded. Taking care of the battery, such as regular testing and cleaning of connectors, can significantly reduce the frequency of battery-related failures.
Fuel System Issues
Contaminated or stale fuel can block the fuel lines and filters, which may lead to engine performance issues or the engine just stopping all of a sudden. Another problem is that air may be trapped in the fuel lines, which can cause improper fuel flow. The proper operation of the fuel system should be checked regularly, and this action will also provide equipment maintenance.
Overloading
If a generator is used with a connected load exceeding its rated wattage capacity, the device’s internal components can get too hot, causing it to shut down as a security precaution. The first thing operators must constantly monitor is the total load to avoid overloading the generator, and this is also necessary when distributing power to various locations.
Control Panel Errors
The central observatory for checking the generator’s state is the control panel. In the event of hardware or software problems with the control unit, the machine may not start or run as intended. Firmware updates and diagnostic equipment are usually enough to resolve the issue.
Environmental Factors
Unfriendly environments can degrade the machine’s performance. The machine, for example, might be seriously affected by the large amount of moisture, which could cause corrosion of electrical parts, while the airflow and cooling system could be blocked by dust and dirt.
Signs Your Generator Needs Attention
Difficulty Starting
A generator that has trouble starting and requires multiple attempts to succeed could indicate several issues, such as a run-down battery, clogged fuel lines, or a defective starter motor. The point is that regular maintenance checks can prevent such problems from occurring or even more costly repairs later on.
Unusual Noises or Vibrations
If a car or a motorcycle emits loud or spooky sounds, like “knock,” “grind,” or “rattle,” chances are there is mechanical damage that must be fixed, e.g., a bearing within the engine that is worn out, some parts being loose, or the misalignment of the engine. Theoretically, the excessive vibrations are traced to unbalanced equipment or a faulty mounting.
Irregular Power Output
Spikes or inconsistent voltage levels can challenge the power supply. And this can be due to issues with the alternator, the voltage regulator, or the electrical circuit connections. This will affect the reliability of the devices and systems connected.
Excessive Exhaust Smoke
Fuel combustion or engine efficiency problems are marked by thick black, blue, or white smoke emanating from the exhaust. This can be caused by clogged air filters, faulty injectors, or oil leaks, among other things, and should be dealt with urgently to prevent further damage to the engine.
Fuel or Oil Leaks
Leaking fluids, such as gas or oil, from your power generator is another indicator that something is not right with the equipment. In a worst-case scenario, what was a simple leak can escalate into a severe performance problem that may exceed the safety limits.
Overheating
When the generator is running hot, it may indicate a malfunctioning cooling system, e.g., a low coolant level, a defective radiator, or an airflow cutoff. And the engine’s life can be ruined by prolonged overheating.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide for the Generator
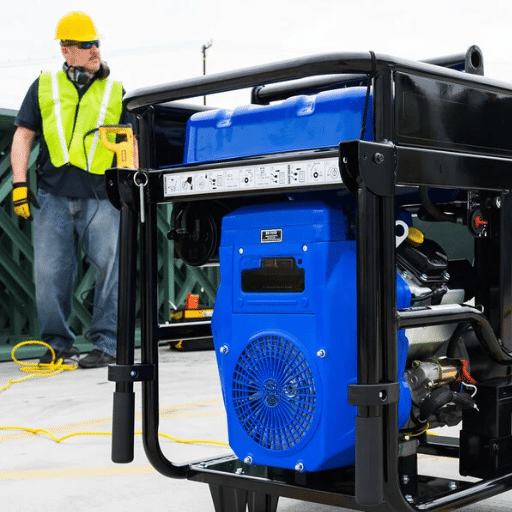
1Inspect for Visible Damage
The first step is to check for cracks, wear, or leaks in the visible exterior components, such as hoses, gaskets, seals, and so on. If any part is damaged, it must be replaced immediately to prevent further complications.
2Check Coolant Levels
Generator overheating can cause a cool-down or a no-start condition. Check the coolant reservoir and make sure it is filled to the proper level. Without manufacturing engineering print, add the described amount of water or a new coolant can.
3Clean the Radiator and Air Vents
Regular air supply is necessary for the efficient working of the vehicle cooler, so the cooling system and air vents must stay clean. A smooth brush or compressed air will do the cleaning and restore the airflow properly.
4Test Hoses and Connections
Check the tightness and integrity of all connections. Any loose or worn connections should be either repaired or replaced with new ones to prevent leakage or airflow interruption.
5Monitor Operational Performance
Following the step-by-step instructions to resolve the problem, start the generator and check the feedback. Record the process; the application must do so. Signal any strange noises, vibrations, or temperature changes, and continue with the necessary procedures if required.
Troubleshooting Generator Starting Difficulties
When dealing with the generator’s power-up issue, it must methodically identify the problems. Here are the most common sources of the problem that can interrupt the regular generator operation, as a result of which the generator won’t be able to start:
Insufficient Battery Power
One of the most common reasons the generator won’t start is a weak or dead battery. This can be caused by not using the generator for a long time, incorrect charging, or corrosion on the battery terminals. One of the maintenance procedures you must follow is to check the battery’s voltage and charge it to the manufacturer’s specifications, and clean any corroded terminals.
Fuel System Blockages
Blockages, such as in the fuel filter, lines, or even the carburetor, can prevent fuel from reaching the engine. One should look for any obstructions in the fuel lines and clean clogged or dirty areas. Use fuel that is stable and, most importantly, clean. Furthermore, the user must confirm that the fuel pump is functioning correctly and that it is delivering the required pressure into the system.
Faulty Spark Plug or Ignition System
If the spark plug is not as it should be (i.e., damaged) or is fouled, there will be no ignition, so the engine will have a hard time starting. One needs to remove the spark plug and inspect it closely for damage, cracks, or deposits. Replace it if it’s necessary, and then check the ignition coil to see if spark is being generated correctly.
Air Intake Issues
The entire air supply is cut off due to a jammed air filter or a slightly obstructed intake. The air-fuel mix might not be perfectly done when it enters the engine cylinders. Regular inspection and replacement of air filters are essential for ensuring optimal engine performance and clean air intake.
Oil or Coolant Configuration Problems
Low-oil sensors are part of nearly all current generators and are responsible for preventing starting in the event of improper oil quality or level. Likewise, even the small amount of coolant lost from the liquid-cooled series is enough to cause overheating and startup failures. Ensure that oil viscosity and coolant levels are as specified in the user manual.
Once these issues are addressed in a structured manner, almost all generator-starting problems can be solved quickly. If, however, equipment problems persist, a qualified source must perform the certification and repair work to identify and fix the main mechanical or electrical issues.
Diagnosing Fuel System Failures
It’s the generator’s malfunctions that often lead to fuel system failures. To determine these matters precisely, it is of utmost importance that the fuel delivery process be studied systematically, step by step. To kick off this process, the fuel supply needs to be checked for any signs of poor quality: stale fuel, water, and debris can impede fuel flow, and the combustion efficiency can be compromised. On top of that, the fuel filter should be the following item on the list to check for possible clogging; filters that are really badly plugged may cause the fuel pressure to drop quite a bit and severely affect proper operation.
Next, to ensure the vehicle will be functional, the gas pump must be checked to confirm it is producing the proper pressure as specified by the manufacturer. An ineffective petrol pump could mean that the engine is not getting enough fuel, which may cause it to perform erratically or not to start at all. Moreover, inspect the fuel lines for damage, and replacement of any damaged lines can be a factor that prevents the gas from being supplied to the engine correctly and consistently.
Always check the air vent and gas burner, depending on the gasoline system you have. Limitations developed in those portions can cause uneven fuel delivery and poor engine performance. Make sure all electronic devices are functioning correctly and are at the correct voltage.
Resolving Battery Malfunctions
Dealing with flat batteries is very sensitive, and it is of utmost importance to always first determine the cause. Testing the battery’s voltage with a calibrated multimeter will tell you whether it is within the manufacturer’s specifications, which are typically 12.6V for a fully charged car battery. Also, examine the battery posts and cable connections for any visible dirt, rust, or mechanical damage, as these may be the reason there is no electrical flow. The dirt is cleaned with a water-and-baking-soda mix, and then the connection is agitated in place.
To make a more accurate diagnosis, one needs to assess the battery’s cold-cranking amps (CCA) using a dedicated load tester. A significant difference between the CCA value and the rating may be a sign of plates’ internal degradation or sulfation; at the same time, evaluate the alternator output voltage under load conditions—since low charging voltage, i.e., generally under 13.5V, can be seen as an indicator of a faulty alternator or voltage regulator. It is also necessary to ensure that auxiliary systems do not disable the battery’s ability to retain its charge, as these systems may drain it when the ignition is switched off. The complete review of these parameters, identification of functional components’ wear and tear, and repair or replacement as necessary will undoubtedly lead to achieving the battery’s peak functional ability.
Repairing and Maintaining Your Generator

Inspect the Oil Level and Quality
Checking the oil level should be done, as it is one of the most critical components of the lubrication system, to maintain the oil at an adequate level. The oil should be changed every 50-100 hours or according to the manufacturer’s recommendation. Make sure you use the specified oil type as indicated in the generator’s manual.
Clean or Replace the Air Filter
A clogged air filter is one of the reasons for the engine’s inefficiency. Fry to observe the filter every 25 hours or after extensive use in a contaminated environment. If damaged, clean the filter or replace it.
<h3style=”color: #1976d2; font-size: 1.5em; margin-top: 0; margin-bottom: 15px;”>Test the Spark Plug
Remove the spark plug and inspect it for signs of aging, carbon deposits, or breakage. Substitute it if it’s not fresh or worn, and position the gap within the manufacturer’s prescribed limits.
Inspect and Tighten Connections
Inspect all electrical system connectors, cables, and terminals for slackness or rust. If there is any slack, make it taut again and, if that is insufficient, treat the affected areas with the appropriate remedy or tools.
Check the Fuel System
Drain and replace with new fuel, or replace with contaminated fuel as necessary. Clean the carburetor and check the fuel line and filters for any blockages or wear. Stabilized fuel should always be used to avoid gum build-up.
Test the Generator Under Load
Devote the time and effort to keeping the generator running smoothly and in good health, ensuring it produces the necessary output voltage. Study the manual and see what it says about load conditions if you are not sure about the loads.
Essential Generator Maintenance Tips
Regularly check the oil levels and quality of the generator to ensure they are in good condition, supporting maximum output and the unit’s lifespan. Many generators are programmed for an oil change every 50 to 100 hours of operation, which is again dependent on the manufacturer and model. Only the grade of oil mentioned explicitly in the owner’s manual shall be used; the oil shall be checked for any impurities or loss of properties, e.g., it may smell burnt or appear cloudy. One of the most important aspects of keeping the oil system in good condition is preventing internal wear and overheating; thus, the operation remains stable under challenging situations and is not interrupted.
If air filters are dirty or blocked, this can lead to a significant decrease in a generator’s efficiency due to reduced airflow to the engine. Make sure to check closely for dust, debris, and damage. Replace the air filters as recommended in the manual, and as needed. The generator’s combustion process and power output depend on adequate airflow, and it is essential to prevent overheating and potential internal component damage.
Generators with electric starters must have a working battery to ensure the starters work properly. Use a multimeter to test the battery regularly to be sure it has the required voltage. For corrosion, clean the terminals with a terminal cleaner or a mix of baking soda and water. If the battery is old or its function is failing, replace it immediately to avoid problems during emergencies.
Common Repairs for Generator Issues
Fuel System Maintenance
A clogged fuel filter or old fuel can cause starting or performance problems. A solution is to check the fuel filter regularly and change it when trash builds up. On top of this, fuel lines should be inspected for cracks or leaks, as these can inhibit fuel delivery. The practice of fuel storage should always follow recommended methods, such as using stabilizers to prevent degradation.
Carburetor Cleaning and Adjustment
Over time, carburetor jets can clog with various types of deposits, leading to misfires or engine stalling. However, the right cleaner and proper cleaning of the carburetor may restore the engine’s operation to normal. For it to work correctly, the air-fuel ratio must be set according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Spark Plug Replacement
Dirty spark plugs may cause engine problems that need fixing. The spark plug must be removed for inspection, checked for wear, carbon, or damage, and, without further delay, replaced with the correct one described in the user manual and gapped adequately so the ignition performs at its best.
Voltage Regulator Repair
An erratic voltage regulator may cause erratic power output or eventual equipment damage. With a multimeter, check the voltage to remain steady regardless of the load to determine how troublesome the voltage regulator is. If applicable, the voltage droop test is a reliable way to test and certify the regulator, though it’s not precise, so a better test is needed for proper electrical function.
Cooling System Inspection
A robust cooling system is required to prevent overheating in liquid-cooled generators. It is necessary to check and fill the coolant more often than usual, following the manufacturer’s guidelines. Besides that, it is essential to inspect the radiator and hoses, ensure they are not obstructed or leaking, and that all connections are tight.
Circuit Breaker and Wiring Troubleshooting
The power operation can be interrupted by overloaded or faulty circuit breakers. Resetting breakers is the first step; do this when necessary. If the problem persists, check them for damage or wear. Also, wiring has to be checked for fraying, corrosion, or loose connections, and whatever is necessary to prevent the electrical hazards, replace or repair the wiring.
Generator Repair Services and When to Seek Help

Recognizing the right time to turn to professionals for generator repair solutions is the key to reliable, safe operation. You should get help right away if you notice frequent power interruptions, hearing noises that are not regular, or seeing components that are damaged, such as wires, fuel lines, or moving parts. Also, if there are many engine stalls, you know a lot of smoke, or the generator does not start, the symptoms indicate that a pro should come in and diagnose the system. Simple checks and maintenance tasks can often be enough for minor problems, but when things get tough, the issues have to be solved by trained staff; otherwise, jobs would not be done right, safety would be at risk, and parts would get damaged. Firstly, ask for help with problems related to power systems, fuel leaks from the generator, or sudden/major mechanical failures, as these are safety or troubleshooting issues.
DIY Repairs vs. Professional Services
| Parameter | DIY Repairs | Professional Services |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Generally low, only material expenses | Higher, includes labor and expertise |
| Tools Required | Basic tools essential | Specialized, advanced tools used |
| Skill Level | Requires basic to intermediate mechanical knowledge | Handled by certified, skilled professionals |
| Time Investment | Often time-consuming | Usually quicker diagnosis and resolution |
| Complexity | Ideal for simple or minor issues | Recommended for advanced or complex problems |
| Safety Risks | Increased risk without proper training | Reduced risk, follows industry standards |
| Diagnostics Accuracy | May rely on trial and error | Utilizes advanced diagnostic technology |
| Warranty Coverage | Often voids equipment warranties | Typically retains or extends warranty |
| Long-Term Reliability | May lead to recurring issues | Ensures comprehensive, lasting repairs |
| Recommended Use | Minor fixes like oil changes | Major issues like engine or brake repair |
Finding Reliable Generator Repair Services
It is highly critical to keep several factors in mind when looking for trustworthy generator repair services. Probably the first thing to consider is the person who will perform the job. So the next step would be to check the service company’s qualifications, which will likely include certificates, training, and experience with your particular generator brand. Contractors of top brands are more likely to have the means, such as special tools and the ability to use only genuine parts, for providing the best service and at the same time prolonging the life of the machine.
Also, read customer reviews and the company’s reputation in the sector to assess the service’s dependability and quality. In most cases, the high scores and happy users will be proof of the company’s reliability. Yet, it is essential to verify that the provider meets industry standards, as only then will the probability of inadequate repairs be lowest and the conditions be the safest for everyone. Moreover, ask about the warranty and service guarantee, which protect the investment and provide peace of mind against future problems.
Optimizing Generator Performance

To ensure the generator operates optimally, perform regular maintenance, use it efficiently, and monitor it. First, follow the manufacturer’s maintenance program. This should include regular time-based oil changes, filter replacements, and coolant use, which should also be checked regularly. Second, always run the generator with a load within the manufacturer’s limits to avoid overstraining it and reducing efficiency. Third, use only quality fuel and store it so it does not become contaminated, as contamination will decrease the machine’s efficiency. Lastly, you should conduct inspections regularly to detect and rectify problems at an early stage. The overall outcome of these measures is that the machine becomes more reliable, lasts longer, and experiences fewer shutdowns, among other benefits.
Improving Generator Running Efficiency
Unleashing efficient generator capacity does not come from simply keeping and using modern technologies and methods effectively. The integration of real-time monitoring systems is a highly preferred option. These systems use sensors and IoT technology to monitor aspects such as fuel consumption, engine temperature, and load fluctuations, enabling operators to make necessary adjustments based on data. It is also a good idea to use load management strategies, such as load shedding or peak shaving, to ensure the generator operates at its maximum capacity without being overloaded. The improvement of fuel technology is also a significant factor; for example, the use of synthetic or specially formulated fuels can enhance combustion efficiency and reduce residue buildup. Besides, connecting generator operations to renewable energy sources in a hybrid manner can boost generator efficiency and make the system much more environmentally friendly. By all means, these are the latest ways to achieve operational excellence, which, in turn, reduce costs and the plants’ environmental impact.
Expert Advice on Long-Term Generator Care
For the best possible operational longevity and effectiveness of generators, all environmental and usage considerations must be addressed. It is of grave importance to evaluate the installation’s location and ensure sufficient ventilation to allow heat to disperse and avoid overheating. The presence of high moisture levels, dust, or particles must be addressed through protective housings or enclosures. In fact, these elements can degrade the quality of critical components and negatively affect the generator’s performance. What is more, regularly scheduled load testing is another essential aspect; putting the generator into service under different loads determines its capacity and readiness, thereby simulating real-world demand.
Furthermore, the future of generator operation lies, in a great measure, with the fuel technology innovators. Specifically, for diesel generators, you can achieve a longer fuel shelf life and protection against contamination with the aid of stabilizing agents, while the issue prompts a natural gas unit to comply with gas composition standards to avoid residue formation that can damage the engine. Keeping abreast of emission regulations is also a good idea if you want your generator to always be in line with environmental and legal standards.
Reference Sources
-
Elements of Generators Selection, Sizing, and Maintenance in Nigerian Industries
Key Findings: This study emphasizes the importance of proper generator sizing and maintenance to ensure reliability and cost efficiency.
-
Design of Multiple Signal Generators Based on DDS
Key Findings: This paper focuses on the design and testing of a signal generator using Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS) technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why won’t my generator start when I try troubleshooting it?
If the generator does not turn on, the first step is to test the battery and gas supply, since a weak battery and stale gas are the most common causes. Check the engine’s spark plugs and the ignition system for any mechanical wear, fouling, or corrosion, as they can disrupt the combustion process. Make sure the fuel filter and carburetor are in good working order, and that the fuel valve is fully open so there is a perfect fuel supply. Also, pay attention to the oil level and the oil sensor safety switches, which could prevent the system from starting due to low oil. In the end, check the choke position and the starter connections; you can also consider load testing the battery if there is slow cranking.
How do I diagnose low or fluctuating output during generator troubleshooting?
Voltage that is either too low all the time or changes too fast is more often an issue with the voltage regulator or the brushes and bearings on the alternator; visually inspect these parts for damage and correct the connections. Do the math between the loads’ demand and the generator’s capacity to avoid overloading the generator; additionally, check it with a load bank if available. Intermittent output may be caused by the wrong wire size, a loose conductor, or a connection that has lost its clean contact; check these and either remove the cause of trouble or reestablish the connection.
What should I check if my portable generator stalls under load during troubleshooting?
If the portable generator stops working under load, it might be because the fuel filter or carburetor is blocked, reducing fuel flow when demand is high. Go through the air filter and the intake to be sure that the engine is getting enough air and, at the same time, that the fuel system is connected without any kinks or collapse. Look at the ignition system and spark plug through the lenses for fouling or a weak spark that will not survive the increasing load, and check their condition. Make sure the fuel pump (if fitted) is O. K. and also be sure that the regulator is not the cause of the fluctuating engine speed. Moreover, check if the generator is not using an inappropriate fuel/air mixture due to a defective choke or governor linkage.
How can I troubleshoot unusual noises or vibrations when troubleshooting a generator?
The majority of shaking, vibrating, and other unusual sound types are generated by mechanical issues, the most frequent of them bear on loose mounts, bad bearings, or out-of-alignment couplings; always tighten engine and alternator mounts. Check the separations between the rotor and stator, and look for any foreign matter that may be touching the moving parts and causing the noise. Look for exhaust system leaks or loose parts that cause noise, as they will also have a further adverse impact on the system. Make sure correspondents are dispatched to the correct location to avoid overloading. Also, noise can be caused by the system’s electrical oscillation, which is why you need a properly secured generator.







