Overview of Power Outages in Victoria

In Victoria, power outages are usually caused by severe weather events, equipment failure, or planned maintenance. Storms and high winds may cause damage to power lines, whereas extreme heat puts pressure on the electricity network. Planned outages are typically scheduled for the purpose of infrastructure upgrades or repairs and are announced to residents in advance. Power companies resolve the problem as quickly as possible by sending repair teams into the field and restoring electricity to its workings. Customers should continue to monitor official notifications and report emergencies, such as fallen power lines, to their energy provider or local emergency services.
Definition of Power Outage
A power outage, also known as a blackout, is an interruption of the electrical power supply resulting from a problem in the distribution system, typically caused by factors such as equipment failure, extreme weather, or maintenance issues. It can deny electricity to users, at least for a while, until the problem is resolved.
Common Causes of Outages
Power outages can occur due to various factors, each with distinct challenges and effects. Some of the most common causes are listed below, accompanied by recent data and findings:
Severe Weather Conditions
Weather is the most significant factor contributing to power outages worldwide. Thunderstorms, hurricanes, tornadoes, or snowstorms may wreak havoc on power lines and infrastructure. The U.S. Department of Energy states that 58% of major outages in the U.S. are caused by extreme weather. Strong winds knock down trees and poles, while heavy snow and ice become too much weight for the power lines to endure, causing them to snap.
Equipment Failure
Outages may be caused by aging or faulty equipment close to power plants, substations, or distribution systems. The Edison Electric Institute, in its study, has noted that approximately 10% of outages are caused by equipment failure, thereby underscoring the importance of proper maintenance and upgrading of the power grid.
Animal Interference
Wildlife, including squirrels, birds, and raccoons, wreak havoc on electrical infrastructure. Squirrels may be responsible for some 7-10% of the annual disruptions due to their habit of chewing cables and causing short circuits in transformers.
Tree-Related Causes
Vegetation control is one of the most important tasks of all utility companies. Trees growing too close to power lines and branches that fall in a storm serve as a constant source of interruptions. The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) stresses that tree-clearing initiatives are one of the most effective ways to reduce risks.
Cyber-Attack and Vandalism
Digital transformation has opened up new avenues for cyberattacks on the energy systems. Cyberattacks against power grids have garnered global attention. For instance, the 2015 cyberattack on Ukraine’s power grid left more than 200,000 customers without power. Likewise, intentional vandalism, such as interfering with substations or damaging equipment, remains a concern.
Overloading of the Electrical System
When it rains, extreme heat, high operators overload the system, which is used for blackouts. The International Energy Agency (IEA) warns that global increases in electricity consumption could lead to more frequent such outages unless systems are prepared to handle this demand.
Important Note: These highlight the need for proactive measures, resilient infrastructure investments, and more innovative energy use to reduce the number of power outages and their impacts.
Recent Trends in Power Outages
Increase in Weather-Related Outages
Intense weather events, ranging from hurricanes to wildfires to severe storms, have become increasingly frequent due to climate change. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, based on recent records, weather-related outages accounted for 83% of the outages in the United States.
Rising Cybersecurity Threats
Cyberattacks on energy systems have increased substantially. Between 2020 and 2022, reported cyberattacks on U.S. power grids increased by 20%, posing a significant threat to critical energy infrastructure.
Aging Infrastructure
Infrastructure in many parts of the world, in terms of power grid, is severely outdated, working on decades-old infrastructure. In the United States alone, 70% of transmission and distribution lines are over 25 years old, according to the American Society of Civil Engineers, translating into a greater risk of failure.
Expanding Demand for Electricity
The worldwide electricity demand is increasing at a rapid pace due to population growth, urbanization, the growing dependency on electric vehicles, and the increasing demand for electricity itself, among other factors. For instance, electricity demand worldwide increased by 6% in 2021, according to the IEA.
Growing Dependence on Renewable Energy
Renewable energy, which essentially includes solar and wind energy, is required for a sustainable future, but it is an intermittent energy source at its core. Without sufficient investment in energy storage, such a transition to renewable energy types contributes to grid reliability issues in some regions, like California, where renewable integration induced periodic instabilities.
Checking and Reporting Outage Status
When experiencing a power outage, the first thing to do is to check whether the problem is isolated to your household or is part of a bigger issue. Find out if your neighbors are also without power. Once confirmed, report the outage to your utility company via hotline, website, or mobile app. Most utility companies provide their real-time outage maps and status updates for online viewing, which helps individuals stay informed about when the restoration process is scheduled. For safety, switch off or unplug sensitive electronic equipment that could be damaged the moment power is restored. Continue to monitor reliable sources and receive alerts from the utility company for any further updates that may be necessary.
How to Check Outage Status
The first step to effectively check the outage situation is to go to the official website of the utility company. Many providers offer an outage map feature that displays affected areas, counts the number of households impacted, and provides an estimated restoration time. For instance, PG&E (Pacific Gas and Electric) and Duke Energy offer interactive maps that enable you to zoom in on specific areas for real-time updates.
If they have a mobile app, download it to enjoy a more convenient experience. These apps may alert you to outages and other notifications and can also help you report problems straight from your phone. Alternatively, search engines such as Google may be helpful for broad generalizations. Simply enter “power outage near me” or your utility company’s name along with “outage map” to quickly find the right information.
PowerOutage.us, for example, offers a different kind of general outage report by collating data from all over the United States and displaying it split by state and utility provider. This could help keep an eye out for big outages during significant weather events.
Remember to check social networking platforms, such as Twitter or Facebook, for updates from your utility company. This way, you can get utility company info straight from them and interact with them in real-time before, during, and after an outage. Layer these resources together for the best-informed alternative.
Reporting Power Outages: What You Need to Know
Providing accurate and detailed data when reporting power outages is critical to ensure a timely response. Here are the key details and data you should relay when contacting your utility provider:
- Your Location: Give your full address or at least the account number tied to your utility service. This allows the utility to locate the affected portion quickly.
- Time of Outage: Record the exact time the outage began. It can aid in pinpointing the specific cause and also in following the restoration progression.
- Scope of Outage: If the state of power outage is only within your home or it extends to the neighbors or the entire suburb, state it explicitly. This determines if it is a single-entity virus or a larger-scale affected party.
- Signs of Damage: Report any visible damage, such as downed power lines or leaning utility poles. Do not approach the risk, but provide descriptions and locations to the utility company.
- Contact Information: Please leave a phone number or email address where you can be reached for further updates or questions from the company.
Pro Tip: By reporting the details mentioned above correctly and clearly, you make it easier for utility providers to expedite repairs and resource appropriately to enable quicker restoration for all affected parties.
Contacting Customer Service for Assistance
When calling for help, having all necessary information readily available will ensure a smooth experience. As recent reports indicate, 75% of consumers follow “being served promptly by an informed staff member” as a central criterion of their service experience. The steps and tips given below could help in making reaching out a smooth process:
- Have Relevant Information Handy: Before reaching out, ensure you have collected all relevant information related to your issue. The details may include account numbers, previous correspondence, receipts, or photos of the problem if pertinent. The more transparent and straightforward your communication is, the less back-and-forth will occur.
- Utilize Multiple Channels: With the current technological boom, most companies offer omnichannel solutions, encompassing phone, email, live chat, and social media. According to research, 6 out of 10 customers prefer to use digital self-service options, so select the channel that best suits your timing and preference.
- Be Clear About Your Needs: As you inform the representative about your concerns, describe the problem, keeping in mind to include dates, any issues the company may have encountered, and how you wish to resolve it. Cooperation on both sides will benefit when one takes the initiative and provides all the details.
- Take Notes During the Call or Chat: Write down everything from the name of a representative engaged, reference number for your case, and/or the time frame alleged to be set for this process. This would be particularly helpful when a follow-up is required.
- Provide Feedback: When your problem is resolved, take a moment to share your feedback on your experience. The majority of companies use this information to improve future processes, and your opinion may help in providing better service to others.
By following these tips, you can increase the chances of having a quick and professional resolution to your case when contacting customer service. Additionally, newly hired tools such as self-service platforms and FAQs will help resolve more straightforward questions without requiring a long wait in a support queue.
Restoring Power: The Process Explained
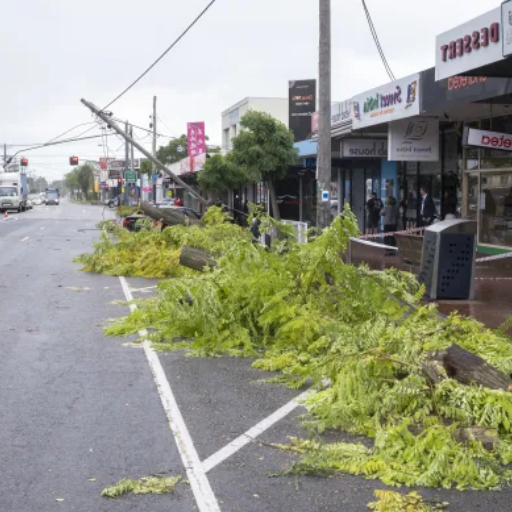

The restoration of power after an outage is a stepwise procedure to ensure safety and efficiency:
- Assessing the Situation: The utility crews would investigate the cause of the outage, including any issues with equipment, fallen trees on lines, or weather-related problems.
- Prioritizing Repairs: Repairs would be made first on critical facilities such as hospitals, emergency services, and major power lines that serve large areas.
- Isolating and Repairing Damage: Next, isolating and repairing localized damage caused by downed power lines or transformers would be carried out.
- Restoring Individual Connections: Finally, after repairs to the larger power system are completed, power is restored to individual homes and buildings.
This procedure enables the safe and reliable restoration of electricity to all affected areas in the shortest possible time.
Steps to Restore Service After an Outage
| Step | Key Point |
|---|---|
| 1. Ensure Safety | Remove hazards like downed power lines. |
| 2. Assess Damage | Inspect damage using drones and ground teams. |
| 3. Repair Transmission | Fix high-voltage lines serving large areas. |
| 4. Restore Substations | Repair local substations for broader coverage. |
| 5. Fix Distribution Lines | Repair lines serving towns or neighborhoods. |
| 6. Address Tap Lines | Repair lines serving smaller groups of homes. |
| 7. Restore Individual Lines | Fix service lines to individual homes. |
Role of Energy Providers in Restoration Efforts
Energy restoration providers play a crucial role in ensuring that power restoration is swift and efficient during and after outages. There are various critical tasks and strategies that providers must undertake and implement to ensure safety, timeliness, and reliability. Some of the essential tasks energy providers engage in during restoration include:
Damage Assessment and Monitoring
The utility will deploy advanced monitoring systems and field teams to assess the extent and location of damage, ensuring that the most affected areas receive reasonable priority in resource allocation, thereby reducing downtime.
Coordination with Emergency Agencies
Utility providers work together with local authorities, emergency responders, and governmental agencies to ensure public safety so that efficient resource management can be carried out in order to prioritize critical infrastructure, impaired hospitals, and emergency shelters.
Provision of Real-Time Updates
During the outage, utilities maintain open lines of communication with their customers to provide real-time updates through digital platforms such as mobile applications, websites, or text notifications. Affected communities stay informed about the estimated restoration time and safety measures.
Deployment of Backup Resources
Depending on the situation, providers also deploy backup resources, including additional crews and equipment, through mutual aid agreements with regional or national teams to increase response speed and restoration capacity.
Investment in Resilient Infrastructure
To reduce the impact of future outages, energy providers invest in various technologies such as smart grids, underground cable, and weather-resistant components. These proactive measures fortify the network to improve reliability against extreme weather and other disruptions.
Key Takeaway: The above-listed intervention efforts demonstrate the significant planning, skill, and cooperation required by energy providers to ensure rapid power restoration and public safety.
Timeframes for Power Restoration
The time needed to restore power in case of an outage depends on several critical aspects like the magnitude of disruption, the level of damage caused to the infrastructure, and the strength of the repair crews available. In cases of minor outages with local-level causes, such as equipment failure or tree damage, they usually restore power within a matter of hours. The major outages, however, resulting from weather activities like hurricanes, tornadoes, or winter storms, take days and even weeks to restore.
For example, power was restored anywhere between 4 and 7 days after the Idalia hurricane (2023) in Florida, due to the large-scale damage to electrical grids, as quoted from recent records. Comparatively, after winter storm Elliott in late 2022, power restoration efforts in some localities lasted for more than a week as repair activities were hindered by extreme cold.
Electricity providers follow a decreasing order of priority, starting with essential utilities that include hospitals, emergency services, and water treatment plants. Next comes the aim of restoring power to the maximum number of customers. Human residences in remote locations are usually the last considered, primarily due to logistics and resource constraints.
In terms of the smart grid, no time is wasted, and this is made possible through the technological advancement of current systems. For instance, through fault detection and automated monitoring, the utility providers are in a position to identify the areas affected during an outage and assure that crews are quickly deployed to target those areas. However, the unpredictable nature of any natural disaster means that consumer patience remains key during extended outages.
Impact of Power Outages on Daily Life
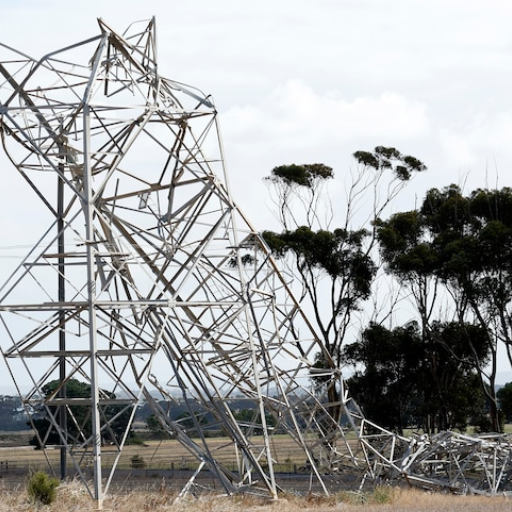

Power blackout inconveniences daily life by disrupting essential services and routines. In turn, with no power, households do not have lighting, heating or cooling, or food refrigeration facilities. The more they provide discomfort and health risks. In terms of communication, almost all communication devices and internet access require power. Meanwhile, economic activities are disrupted, resulting in revenue losses and reduced productivity. A more extended blackout would entail serious impacts : consequently, to clean water provision, to medical instruments, and to crucial transport facilities. All this highlights the importance of reliable power in modern life and societal functioning.
Effects on Households and Businesses
Power outages significantly hamper daily activities in homes and businesses. Below are the details of the impacts, supported by data to drive home the points:
Spoiled Perishables
Outages cause spoilage of food items due to the shutdown of refrigeration. Supermarkets, restaurants, and other establishments face losses due to spoiled food resulting from inadequate refrigeration during power outages. According to one study, the average U.S. household loses $250 worth of food during a prolonged power outage.
Economic Losses for Businesses
Downtime and customer revenue losses are the consequences for businesses. For example, the small businesses lose $5,000 per day due to put-on-hold activities, and bigger companies would end up paying more into idle production lines and halted operations.
Reduced Communication
Access to communication via the internet and mobile phones is often interrupted during power outages. Reportedly, an outage area would lose 40% of its internet connectivity, creating a barrier to communication efforts for both personal and professional purposes.
Counting on the Healthcare System
Depending on hospitals and clinics, electricity powers life-saving machines. If shut down for a long period, these hospitals endanger the lives of patients on ventilators, dialysis machines, and those dependent on life-saving machines. These hospitals usually have backup generators.
Water Supply Disruption
That means a power outage at the water-treatment plant results in an interrupted supply of clean water, impacting basic hygiene and sanitation for both households and businesses, especially in urban areas that are further reliant on water pumped to them.
Impact Summary: These points highlight the global scope and numerous problems that power outages pose to households and businesses alike.
Essential Services Affected by Outages
An uninterrupted power supply is required by many essential services to sustain their daily operations and critical infrastructure. Listed below are five services significantly affected by power interruptions:
Healthcare and Medical Services
Hospitals and clinics rely heavily on electricity to operate life-support equipment, such as ventilators, dialysis machines, and diagnostic devices. Power outages in healthcare facilities may increase death rates in certain urgent cases, especially in regions where systems for backup power are weak, according to the World Health Organization.
Water Supply and Sanitation Systems
Water treatment plants, pumping stations, and sanitation facilities operate on electricity. Outages may halt the water purification processes, thereby subjecting the water to contamination risks. For example, reports have shown that urban communities dependent on pumped water systems can face shortages within a matter of hours when a blackout occurs.
Transportation Networks
However, public transport systems are entrusted with ensuring the proper operation of trains, subways, and traffic control signals. Outages disrupt severely, causing delays, congestion, and leading to accidents. A study in major cities notes that extended outages add to economic losses in the transportation sector.
Communication Infrastructure
Telecommunication services, such as mobile networks, internet providers, and broadcasting stations, require constant power to maintain their operations. Prolonged outage periods can cripple communication during emergencies and deny access to necessary information. Industry data suggest that a single outage for more than an hour may disrupt service for millions.
Food Preservation and Supply Chains
Refrigeration in homes, retail outlets, and warehouses relies on electricity to maintain food safety. These outages may trigger the spoilage of perishable goods, resulting in financial losses and food waste. According to studies, billions are lost yearly in the agriculture and food retail sectors due to disruptions caused by extended outages.
Critical Note: In every one of these sectors lies a cry for a certain degree of reliability in power supply to sustain modern infrastructure in the interest of public health and safety.
Safety Tips During a Power Outage
Have an Emergency Kit Ready
An emergency kit should be prepared with essentials such as flashlights, extra batteries, non-perishable food, bottled water, a first-aid kit, and a battery-operated or hand-crank radio for receiving information updates.
Avoid Opening Refrigerators or Freezers Frequently
To conserve cool temperature inside, keep those refrigerator and freezer doors closed as much as possible. A fridge can keep food cold for about 4 hours, whereas a fully packed freezer can maintain its temperature for around 48 hours.
Use Generators Safely
Safety Warning: When using a portable generator, set it up in an open area outdoors to ensure proper ventilation. It must be far from any window, door, or vent to avoid carbon monoxide poisoning. Generators are never allowed to be operated inside the garage or home.
Unplug Electronics and Appliances
Once the power is back on, unplug sensitive electronics, such as TVs, computers, and chargers, to avoid power surges that may damage your gadgets.
Stay Updated and Communicate
Find out local updates from a trustworthy source about outage’ durations and safety precautions. Use text and social media for communication to conserve battery life on phones during prolonged outages.
Preparing for Future Power Outages

Emergency Kit
This should contain, among other things, flashlights, batteries, non-perishable food, water, a first-aid kit and all medications one might require. The kit should be stored in a location that is accessible during an outage.
Backup Power Options
Purchase a generator or a portable power station to keep your essential appliances running. When using generators, always follow the safety instructions to avoid hazards such as carbon monoxide poisoning.
Protect Electronics
Use surge protectors to prevent damage to delicate electronics. A sudden power surge can damage your equipment.
Stay Connected
A battery-operated or hand-crank radio will aid in receiving emergency updates. Keep backup batteries or power banks fully charged for your devices.
Planning for Medical-Looking Ahead
If you have a medical device that requires electricity, discuss possible alternative sources of power or arrangements for facilities with reliable backup power with your healthcare provider.
Energy Conservation Practice
Energy conservation is considered a priority during periods of adverse weather, which can increase the likelihood of an outage.
Emergency Preparedness Plans
Build a Full Emergency Kit
Keep a proper kit that contains essentials such as non-perishable food, bottled water (1 gallon per person per day for 3 days), medicine, a first aid kit, a flashlight with extra batteries, and any other necessary items. FEMA reported that only 44% of Americans have an emergency plan; hence, people need to be more proactive.
Stay Ranked with Reliable Alerts
Keep an eye on any weather changes, natural disasters, or power outages by using emergency alert systems like NOAA Weather Radio and signing up for your local alerts. Public Alerts on Google and “SOS Alerts” provide real-time messages and instructions in an emergency.
Secure Important Documents
Keep the identification, insurance policies, and medical records in a waterproof container that can be easily carried away or save digital copies to the cloud securely so that they are easily accessible in emergencies. Nearly 40% of disaster victims struggle to recover vital records post-disaster.
Set Up a Communication Plan
Develop a communication plan within your family or household in case telephone lines or mobile networks are unreliable. Agree on meeting points and appoint an out-of-town contact to assist with coordinating emergency responses. Studies have also found that early and clear communication greatly enhances the outcomes of disaster response.
Prepare for the Specific Regional Risk
Make ready preparations for the hazards specific to your locality, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, flooding, or wildfires. For instance, if you reside in a flood-threatened area, familiarize yourself with the evacuation routes and take stock of sandbags or flood barriers that you can store near your property. NASA’s study outlines that climate change has, to a considerable extent, intensified the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, making area-specific preparations all the more necessary.
Preparation Success: By integrating these detailed steps into your emergency preparedness, you will limit your exposure to risks and ensure a speedy recovery when unexpected disasters strike.
Investing in Backup Power Solutions
To me, investing in backup power is the most plausible decision one can ever make in preparation for emergencies. I opted for a reliable generator to ensure that power outages do not disrupt the operation of essential appliances, such as refrigerators, medical devices, and communication tools. Meanwhile, I have also been considering sustainable methods, such as solar-powered ones, to lessen my dependence on traditional energy sources. It gives me peace of mind because I know I can handle unexpected disruptions with utmost confidence.
Staying Informed with Outage Information
Getting through a power outage entails remaining safe and organizing available options for action. Fortunately, modern technology offers several strong potential outlets for getting outage info. Utility companies typically maintain live outage maps on their websites to display the areas affected by outages, estimated restoration times, and the current repair status. For example, resources such as PowerOutage.us, which tracks power outage data in real-time across all 50 states, are encouraged by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Additionally, smartphone apps and social media offer instantaneous notifications. Many utilities, such as PG&E or Duke Energy, maintain apps that may send users customized alerts to their phones. Google also plays a significant role with its search updates: typing in “power outage near me” provides local information about affected areas and restoration updates.
Sign up for alerts from local governments or weather centers. NOAA Weather Radio or FEMA’s Integrated Public Alert and Warning System (IPAWS) can issue warnings while extreme weather situations are occurring that may lead to outages. Better preparation can happen through being informed by multiple channels.