Power generators are of very lucrative use in cases of power outages, as well as in areas where electricity is merely an unthinkable luxury. Nonetheless, even so, not every generator is the same. Whereas home generators are mainly designated for a certain set of requirements, that is, towards several power requirements, particular operational needs, and competitive pricing, commercial generators are clearly performance-oriented, aiming for robust power companionships. This article, therefore, reveals the basic differences between a home generator and a commercial generator so that its readers should be imparted with much insight of value to ascertain from which point of view to make their decision. This criterion would be essential to making the right choice, essentially to anyone, for the homeowner requiring a standby power supplement for essential household appliances, or to the business owner needing a robust system to weather a serious challenge like a power interruption.
Overview of Generator
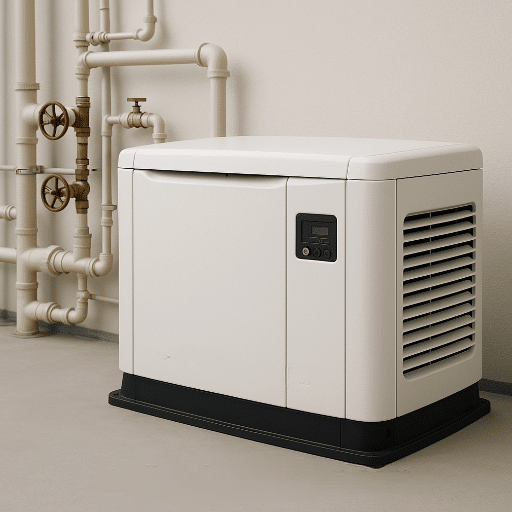
They are devices utilized for converting mechanical energy into electrical energy by means of the electromagnetic induction process operated by generators. They wear an internal combustion engine that runs on fuel, be it gasoline diesel, or natural gas, dreamers. Whenever the known engine turns the rotor within the magnetic field, it starts and optimizes the generation of flow current through the generator windings.
To make this happen, the primary engine will generate the necessary mechanical energy that is then converted into electricity in the secondary of the alternator. The output power is controlled as per the demand of a connected load or system, thus ensuring a balance of efficiency and reliability in the event of a failure or under off-grid conditions. It is vital that proper and regular maintenance of all parts be carried out in order to ensure reliable operation over a long time.
What is a Generator?
A generator is used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy by the principle of electromagnetic induction. The mechanical energy, often derived from an internal combustion engine, steam turbine, or water turbine, causes the rotor within the generator to spin. This rotor, normally equipped with a magnetic field, will rotate in the stator coils and, through induction, make an electrical current. Generators are categorized with respect to capacity, fuel type, and method of generating the electric field. These range in size from miniature power generators used as temporary aid from loads above industrial ones needed by critical infrastructure. Modernized generators have many extra features like automatic voltage regulators (AVRs), inverter designs for a cleaner form of power, or an integrated monitoring system that caters to improving efficiency and reliability. With these technologies in place, the generators have versatile applications, serving as emergency backups and providing continuous power for remote sites.
Types of Generators
| Type of Generator | Fuel Source | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diesel Generator | Diesel fuel | High efficiency, durable, low operational cost | Industrial, hospitals, large-scale backup |
| Gasoline Generator | Gasoline | Portable, less expensive, suitable for light loads | Homes, camping, outdoor events |
| Natural Gas Generator | Natural gas | Clean energy, reliable for continuous supply | Residential, commercial cooling/heating |
| Propane Generator | Propane | Long shelf life, environmentally friendly | Off-grid homes, remote areas |
| Solar Generator | Solar energy | Renewable, quiet, requires sunlight availability | RVs, emergency backup, small-scale devices |
| Hybrid Generator | Multiple sources | Flexible power sourcing, higher sustainability | Remote industries, disaster relief |
| Standby Generator | Various fuels | Automatic operation, permanent installation | Emergency backup for critical infrastructure |
| Portable Generator | Gasoline/diesel | Compact, mobile, cost-effective | Outdoor projects, temporary events |
| Hydrogen Generator | Hydrogen fuel cells | Zero emissions, highly efficient | Future sustainable energy projects |
| Wind-Powered Generator | Wind energy | Renewable, operational in windy regions | Farms, remote installations |
Common Fuel Sources
| Fuel Type | Availability | Environmental Impact | Efficiency | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gasoline | Widely available | High emissions | Moderate | Small generators, transportation |
| Diesel | Widely available | Lower emissions than gasoline | High | Industrial generators, heavy machinery |
| Propane | Moderate availability | Clean-burning | High | Home generators, RVs |
| Natural Gas | Readily available in pipelines | Low emissions | High | Large-scale standby generators |
| Hydrogen | Limited availability | Zero emissions | Very high | Sustainable energy systems |
| Wind | Location-dependent | Renewable, no emissions | Variable | Wind-powered generators |
| Solar (stored energy) | Weather-dependent | Zero emissions | High with storage | Solar-powered systems |
| Biomass | Limited availability | Carbon-neutral | Moderate | Renewable energy projects |
Residential vs Commercial Generators

Residential generators are customarily meant to light homes during any outages and so optimized for smaller energy needs. They are essentially smaller units with less noise and power with the help of natural gas, propane, or diesel. Such systems prefer quick installation, ease of operation, and low cost.
As compared to residential units, commercial generators are built to sustain larger power supplies, which power enormous buildings, industrial plants, or emergency systems. Far more rugged, they are designed for much higher capacities and models that allow for constant trips or commercial abuse. These systems frequently offer fuel types and various configurations in order to cater to varying energy requirements.
The choice between these two partly depends on the scale of the energy requirements and intent of utility, whereas residential models can provide the required electricity for powering essential household appliances and units and must meet those needs only, i.e., commercial models can suffice for enterprises and facilities standardized for way greater and more complex energy requirements.
Key Differences and Similarities
| Feature | Residential Generators | Commercial Generators |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Output Capacity | Low to moderate | High |
| Typical Fuel Types | Gasoline, propane, solar | Diesel, natural gas, custom fuels |
| System Size and Weight | Compact and lightweight | Large and heavy-duty |
| Cost | Affordable for households | Expensive, higher capital cost |
| Installation Complexity | Simple installation process | Requires professional setup |
| Maintenance Requirements | Minimal maintenance | Regular, extensive maintenance |
| Intended Usage Scope | Household energy needs | Large-scale business operations |
| Runtime | Short-to-medium durations | Extended or continuous runtime |
| Power Backup Reliability | Basic reliability | Advanced, redundant solutions |
| Customization Options | Limited customization available | Highly configurable features |
Power Capacity Ranges
Capacity scaling in power systems varies based on system design, application, and scale of operation. For household systems, power capacity varies within a 1-kW to 10-kW spectrum, which can cater to essential appliances and daily energy requirements. Concerning applications for bigger commercial or industrial systems, their capacities revolve around a 50-kW to several-MW range, which provides access to big machinery, large lighting operations, and other high-demand functions. Power utility systems may run into hundreds of MWs or greater to meet the requirements of sectional or national grids. These power capacities are made to cater to a certain need, as dictated by the world’s consumption patterns in much the same way the magnitude of power produced depends on the energy loads in the system, each respect being qualified by the target environment’s characteristics.
Standby vs Portable Generators
Standby and portable generators have different purposes depending on power needs. Their design and installation convenience are also based on what operations will be running. Standby generators are massive electrical system installations that usually come on automatically to power critical equipment from the home to the whole system power below a certain level. Usually, standby generator fueling includes a natural gas or propane supply, which requires maintenance for low fuel consumption. Their capacity can range from 7 kW to several hundred kW and would be perfect for hospitals, data centers, and industries needing an indefinite supply of power.
Portable generators, on the other hand, are a versatile yet compact option that is selectable, from among many other ways, for use in different locales; having an estimated electrical output of 1 kW to 10 kW—enough to support power supply for vital tools, minor kitchen appliances, or small lighting sources; relying on duress at a fuel that is gasoline or diesel (typically) with refueling to be carried out by hand during its operation. Portable generators are mainly used in open-air events, or events at construction sites, or any other form of emergency relief due to impractical fixed power sources.
The cost comparison will lie in better installation and automation in order to opt for permanent system generators over with much cheaper front-end installation and maintenance costs for portables. Nevertheless, such a comparison is an oversimplification between standby and portable generators since standby generators stand out in the dimension of reliability and having this kind of “always-on” operation, whilst portable generators uphold such emphasis in the categories of mobility and flexibility for periodic reason-based power requests.
Commercial Generator Installation

Commercial generator installation refers to the setup and hookup of a generator, providing backup or primary power for businesses. Embedded in the installation procedure is the need for a choice of the right generator size as per the facility’s power needs, the transformation of the unit to operate in synchronization with the existing electrical systems, and compliance with all legal and safety manuals. With that out of the way comes the installation of the generator, allowing all security measures to be duly put in place. For a secure installation, ensure that the experienced operator does all the work, making sure all of his works abide by industrial standards of safety and efficient production.
Installation Process Overview
A few significant steps go into installing a generator so it works properly and remains safe. Site inspections are performed for the appropriate positioning of the unit, checking ventilation, power supply, and local building code needs. After site preparation, the unit is to be properly placed or fastened to the site so as to remain level and stable and, hence, prevent operational problems and threats. The placement of this unit is the start of the electrical work, which hooks up the primary system from other power supplies, usually through an automatic transfer switch that allows for an easy switch between these sources for uninterrupted flow during a loss of power.
Actually, testing down-build and regular maintenance is tried and completed for checking the standard of operation, voltage accuracy, and the compatibility of the load capacity levels. While better installation trends of the day are often based on energy efficiency and the specific realization of the components in the form of features such as surge protection, as well as various order names that improve the system’s performance. Doing this will result in good operation of said equipment in adverse conditions and will maintain its longevity.
Requirements for Installation
To Guarantee safety, operation, and standard compliance always is by strictly following that there are certain rules set up for the installation of the series of electrical systems. First of all, all components have to be industry standards that are certification either by organizations like UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or some IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission). This will ensure the compatibility of the components and the operational safety under various load conditions. The design should also have the defect tolerance and redundancy aspects to be taken care of, especially for low-risk buildings like hospitals and data centers where system failures can cause very high hazard levels to human life or property.
It is important to determine the proper rating of the transformers, breakers, and conductors because the distribution system could be overloaded or any of its components underused, thus gravely endangering the installation. It is also a must to evaluate the ambient conditions of the installation where temperature, humidity, and other factors have to be taken into account. In addition to this, if any harsh conditions such as high humidity or corrosive environment are likely, the installation should take into consideration such conditions too. When the solar PV system is placed either on the slab or on the rooftop, the installation should also consider the module orientation, shading analysis, and inverter efficiency for getting the maximum output. Moreover, it is crucial to meet both the local and national building codes because they aims to secure the installations and they make sure that an installation is granted a compliance certificate for inspection today as well as in the future.
Cost Implications
The monetary aspect of meshing sophisticated systems, such as renewable energy solutions or state-of-the-art construction materials, has multiple layers. The initial investment costs are mostly high because of the sophisticated technology or the specialized labour, only to be smoothed by the lifetime savings on running costs and power efficiency. Those solar panels’ economic cost would thus comprise some expenses coming from the procurement of the panels, mounting systems, inverters, and professional installation services.
Per federal tax incentives and state incentives the federal government may offer, solar system costs for residential applications lie in the range of $15,000 to $25,000, varying according to system size and market conditions. Further, upfront investment in materials, whether low-maintenance composites or assemblies with energy-efficient thermal insulation capability, has long-term rewards in terms of easy maintenance and reduced energy bills during the life of the structure. So as to take an accurate view of the ownership cost, ongoing maintenance and warranty terms must be considered along with replacement parts. Being cost-effective and sustainable simultaneously could be guaranteed by policymakers by taking both immediate expenses and long-term savings into account.
Benefits of Home and Commercial Generators

Home and commercial generators yield a reliable power supply in times of sudden interruption due to storms, blackouts, or even other disasters, so they can keep running for required use and serve to provide electronic communication, warmth, preservation of food–in the case of household use–or prevent financial disasters by way of incorporation-protection of equipment and keeping downtime to a minimum. Conveniently designed to use efficient fuel and maintenance practices, today’s generator puts forth superior reliability, resulting in cost-effectiveness. Acquiring a generator in one’s dwelling or workplace would safeguard outputs, peace, and well-being.
Advantages of Residential Generators
1. Uninterrupted Power Supply
The treatment of power failures has been made continuously available by support generators, such that arguably essential household equipment, including fridges, heaters, and medical equipment, can continue to function during the said emergency times. This solidifies industry reports depicting that an average American household goes without power for 8 hours annually.
2. Protection of Perishable Goods
Having electricity flowing can prevent any misfortune connected with spoiled food and costly wastage, mainly for freezers and refrigerators. A consistent supply of electricity, provided by a generator, can consequently mean saving hundreds of dollars per year on food security.
3. Enhanced Safety and Security
An assured power supply assists in forced maintenance, critical from the homeowner’s perspective to security-related systems they have- ablution cameras and alarms that work to deter any incidents. They could double up in areas with the neighborhood having more wrath and harsh weather conditions.
4. Comfort and Convenience
Generators ensure that heating and cooling systems continue to run, thereby ensuring that comfort may be maintained throughout serious climatic conditions. For instance, bowel temperatures indoors may soar by 20°F or more through air conditioning during a heat wave, exposing babies to the threat of joan.
5. Low Maintenance and Longevity
Residential generators are designed to require little maintenance and run highly efficiently. They can run up to 10,000 hours provided regular services if the advanced inverter options are utilized.
6. Economic Savings During Outages
Generators keep high costs at bay by minimizing disturbances that can force one to live in hotels, spoil food, or ruin electronics when power is so famously restored through distribution grids.
Benefits of Commercial Generators
1. Uninterrupted Operations
Commercial generators supply power throughout outages, meaning continuity of operations for businesses. Industries that frequently need electric supply, such as healthcare facilities, data centers, and manufacturing plants, where the electric supply must always be on, are especially in need of power so that the lights and machines keep running. It contributes immensely to models showing the each yearly cost in outages of about $150 billion for U. S. businesses, taking into account the fact that backup plant must be reliable.
2. Protection of Sensitive Equipment
To financial recompense damage resulting from abrupt power failures or voltage fluctuations, several businesses rely on sophisticated and sensitive machinery. Commercial generators are vital for standardizing power supply, which is crucial for boundaries in almost all sensitive equipment, e.g., servers, medical apparatus, and industrial machinery.
3. Improved Safety and Security
Power failures could result in certain safety hazards, such as alarm systems, video surveillance systems, and lighting in critical spaces getting out of order. This is being addressed by business generators, whereby many security systems operating during such a time remarkably reduce the possibility of burglary, vandalism, or other incidents during blackouts.
4. Customizability for Industry Needs
Currently available commercial generators are eventually modified so as to match the specific power supply requirements of different industries. Hospitals, for instance, require graceful transitions between grid power and backup systems, or else patient care is interrupted, while retail-powered businesses give priority to lighting systems and transaction apparatus. Load-sharing capabilities and scalable options allow as much flexibility as possible, which can ebb with differing energy needs.
5. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Reduce fuel consumption by using efficient technology and lowering operational costs. Next-generation generator models in compliance with stringent emissions standards guarantee clean power even with lower environmental impact. For instance, generators compatible with the stringent Tier 4 standards demonstrated nitrogen oxide emissions reduced by over 90%.
6. Durability and Long Lifespan
Commercial generators are intended for extended use under challenging conditions. Depending on the style, well-kept generators can remain fully functional for 20 or 30 years or longer. Namely, diesel-powered generators have a good reputation for operation and in handling heavy loads over a long period.
Maintenance and Service Requirements

- Scheduled Inspections: Do visual health check-ups for signs of fatigue wear, damage, or clean leakage; includes belts, pipes, filters, and fluid level check.
- Oil and Filter Changes: Oil change and oil filter replacement shall be made per prescribed schedules of the manufacturer, typically ranging between 250 and 500 hours or annually, whichever is earlier.
- Battery Maintenance: Whenever its operation is in doubt, the battery needs to be checked and tested regularly so as to make sure it has received proper charging. Battery contacts also need their cleaning and, where necessary, maintenance.
- Fuel System Care: For diesel engines, regular checking is highly recommended for fuel lines and the fuel tank to prevent leaks and contaminants. Either alter the fuel by removing old fuel and adding fresh from time to time or put some stabilizer in the fuel to stop the degradation of the same.
- Cooling System Checks: Check the level of coolant and ensure that the radiator and the cooling system remain primed and proper; replace with due coolants as per the manufacturer’s set standards or time.
- Load Testing: Occasionally, perform load bank testing in order to ascertain the capability of the generator to handle the rated load and run it on full load conditions without breaking down.
Routine Maintenance for Home Generators
Regular maintenance will ensure the effective operation of home generators during times of utmost priority. Homeowners should clearly follow these essential rules:
- Oil and Filter Maintenance
In the same way, the beneficial performance of the generator and its longevity will be unavoidably affected by not performing the manufacturer’s recommended oil and oil filter replacement on the generator periodically, normally based on the hours of generator use. Synthetic oils are excellent for use in harsh weather conditions as they protect the engine against wear and thus prolong its working life. - Battery Inspections and Care
Generator startup may be hampered by poor condition and failure to hold a full charge. Checking battery terminals for rust and testing voltage levels with a multimeter are tips to follow. It is wise to replace the batteries every 2-3 years, or according to the manufacturer’s advice. A trickle charger certainly, will keep your battery up during long idle periods, thus maintaining battery life.
- Air Filter Replacement
The lodging of air filters with dust or debris may choke the engine and reduce performance. After monitoring yearly intervals, clean or replace the filters if five years. The clean filter ensures the most fuel versatility and ensures that the generator is operated in a reliable manner. - Fuel System Management
Make sure that fuel stored in the tank is at a sufficient liquid level for running medium-capacity generators. Systematically inspect fuel lines for any fluids that indicate leaks, cracks, or damage. Additives or stabilizers must be used to prevent breakdown (especially gasoline) while fuels are stored. - Testing Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS)
Transfer switches serve a major purpose in transferring power from the utility grid to the generator during an emergency. Its essentials ensure functioning in such a way that the automatic transfer switch detects a power breakdown and immediately sends a signal to the genset to begin working. Regular inspection and cleaning of electrical contacts are mandatory. - Emergency Simulation Drills
To check for issues in the mechanical and electrical systems while under loaded conditions, purposefully simulate a power failure by shutting down main utility service and observing real-time operation of the generator to confirm its overall reliability.
These preventative maintenance measures benefit the homeowners in reliability, sustainability, and life assurance of having their home generator work even in extended power outages. Referring to the operator manual will offer model-specific guidelines and advice to be followed by only a qualified service technician.
Service Needs for Commercial Generators
Commercial generators are well-maintained, always in operation, and avoid costly stoppages during critical times. These run at most loads-thus the need for more robust maintenance protocols than needed on a residential model. Basic skills include regular scrutiny of the fuel system, as even the smallest amount of contamination might damage it, and regular oil/coolant testing for signs of wear or contamination on inner levels. Furthermore, frequent testing of the battery is also very necessary: most of the time, the generator is about to fail with a battery that is no good.
Also, the mending and cleaning of air filters must not be forgotten because clogged filters are unaware of their motive for clogging under respective conditions, and if not resolved, these may reduce the heat efficiency of the system. Load bank tests of the generator are important, so as to confirm whether it is capable of tolerating the specified load without sacrificing performance. Tracking of engine parameters may be performed by some advanced diagnostic systems to diagnose any error in the form of electronics.
Reference Sources
- Electric generators and motors: An overview
Read more on IEEE Xplore - Electricity generation using small wind turbines for home or farm use
Read the PDF - Feasibility analysis of a renewable hybrid energy system with producer gas generator fulfilling remote household electricity demand in Southern Norway
Read more on ScienceDirect
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between residential and commercial generator options?
At their core, comparative residential and commercial offerings are differentiated primarily by size, placement, and intended function. For instance, residential units are laid out to cover a residence or to handle chosen circuits. In contrast, commercial ones generate power for a commercial building or location with heightened power requirements. The commercial gen sets usually use larger fuel tanks and have significant maintenance charges when compared to the home backup ones. Well, once you need to work around to give yourself a generator that will produce the kind of energy you are interested in, and keeping track of that energy is not an easy task.
How does a standby generator compare for home vs commercial use?
The standby generator can be installed permanently, harnessed together with an automatic transfer switch to help in the complete powering of your home/facility, the instant power goes out. Standby units are generally quieter than old commercial generators and run safely within residential noise regulations. When opting for generators, choose between portable or standby, based on the generator requirement, residential backup power requirement, or the power required in a commercial setting.
How should I prepare for an outage when choosing between home and commercial systems?
Calculating the watts for determining the crucial loads and the circuit types one seeks for backup to secure their business or home at a certain level are primary concerns when planning for outages. The right generator size, venting, or an automatic transfer switch, as minimum code requirements, are needed to make sure that your generator works and abides by its purpose. Meeting local codes, select from the best out of the available generators for peace of mind for both homes and businesses.







