The generator has been cranking, but it failed to start, resulting in numerous frustrating downtime scenarios, especially when power is crucial. Frequently, this problem occurs, and knowing answers to the primary causes will accelerate remedies. From fuel-related problems to electrical issues, a wide range of factors could have been responsible. This article will cover the typical reasons why your generator cranks without starting and provide practical troubleshooting methods to diagnose and resolve the problem effectively. From being a veteran technician to a newbie in generator ownership, this guide will provide you with the necessary insight to get the equipment back into working condition.
Understanding the Issue of Generator Cranking
Fuel-Related Issues
A tank running low or being empty is among the most frequently cited reasons for generators theoretically cranking but not starting. Fill the tank with fresh, clean fuel and inspect the fuel lines to ensure that nothing is obstructing the flow.
Battery Problems
A low battery or a dead battery can prevent the generator from gaining ignition. Test the battery voltage and verify that the connections are secure and the battery is fully charged.
Clogged Air Filters
A free flow of air is necessary for the generator to start; hence, a dirty or clogged air filter may impede airflow and prevent the unit from starting. Check the air filter and change it if necessary.
Spark Plug Failure
Considering that an inefficient or dirty spark plug could affect ignition, remove the spark plug and inspect it for damage or wear. Replace it if necessary.
Carburetor Malfunction
Over time, gunk and residues of old fuel accumulate in the dirtiness of the carburetor, preventing it from mixing fuel and air correctly. Cleaning or repairing the carburetor is usually worth it.
What Does It Mean When a Generator Cranks?
Essentially, the term ‘cranking’ refers to the mechanism of turning the engine over without allowing it to run on its own. This initial half-crank period begins when the starter motor engages and turns the engine’s flywheel, creating conditions for ignition. Not surprisingly, the word ‘crank’ is used when the starting system and battery are functioning, but it rarely guarantees ignition or smooth running of the generator. Common causes of a generator cranking but not starting include the absence of fuel, air, and spark–all vital elements for an ignition to occur. Thorough troubleshooting of these components, such as fuel, spark plug, and carburetor, is required to identify and remedy the actual problem.
Common Symptoms of a Diesel Generator Cranking Issue
Unusual Exhaust Smoke
Some excessive or discolored exhaust smoke during cranking often indicates trouble. White smoke is typically caused by unburnt fuel resulting from poor compression or cold conditions, while black smoke can indicate either an overly rich mixture or air restriction.
Extended Cranking Time Without Starting
If the generator cranks for too long, it indicates that there is insufficient fuel delivery, inadequate compression, or a problem with the ignition timing system. Such symptoms require a thorough inspection of the fuel injectors, filters, and timing mechanism.
Erratic Engine Noise
Irregular or uneven engine sounds during cranking suggest a mechanical fault, such as stationary internal components or valve clearance, that has not been rectified. Usually, such irregularities become visible by way of further mechanical diagnostics.
Insufficient Fuel Pressure
If low or irregular fuel pressure exists in the system, that could affect proper fuel atomization; hence, it could range from a clogged fuel filter to a faulty fuel pump or air leak in the fuel system.
Electrical Component Malfunction
Other generator cranking issues may come from faulty electrical components, such as a weak starter motor, a discharged battery, or faulty sensors. These components must be thoroughly tested by using appropriate diagnostic tools.
Differences Between Diesel and Gas Generator Cranking Problems
| Key Point | Diesel Generators | Gas Generators |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Type | Diesel fuel | Gasoline or natural gas |
| Combustion Process | Compression ignition | Spark ignition |
| Startup in Cold Weather | Challenging due to fuel gelling | Easier with proper maintenance |
| Fuel System Issues | Prone to clogging, injector problems | Sensitive to vapor lock or carburetor issues |
| Maintenance Intervals | Longer, designed for heavy-duty operation | Shorter, lighter-duty use |
| Operating Efficiency | Higher fuel efficiency | Lower fuel efficiency compared to diesel |
| Initial Cost | Higher due to robust design | Lower, affordable for smaller applications |
| Durability and Lifespan | Longer lifespan under heavy loads | Shorter lifespan in high-demand applications |
| Noise Levels | Generally louder during operation | Typically quieter |
| Environmental Considerations | Higher emissions without after-treatment | Cleaner burning, fewer emissions |
Common Reasons for Generator Cranking but Not Starting
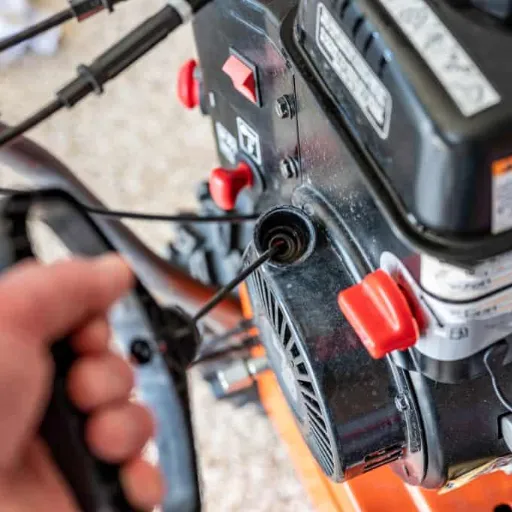

Insufficient Fuel Supply
A very simple and most frequent problem is merely a low or empty fuel tank. Additionally, obstructed fuel lines or clogged filters can impede the system’s ability to deliver fuel properly to the engine.
Dead or Weak Battery
If the battery does not have enough charge or is defective, the generator will crank but will not start. Ensure that the battery terminals are securely attached and that the battery is fully charged.
Faulty Spark Plug (in Gasoline Generators)
A defective or dirty spark plug can inhibit installation and prevent the vehicle from starting. Check the spark plug and replace it if necessary.
Air Filter Blockage
An air filter clogged with dirt or mud may block sufficient airflow for the engine to start correctly. Filtering the air or replacing it will do the trick.
Starter Motor Issues
Other mechanical malfunctions might occur in the starter and its electrical circuits, allowing him to crank but never ignite successfully.
Improper Oil Levels
Many generators have safeguards in place to prevent starting if the oil level is below the required operating level. Check and fill the oil if needed.
Fuel Issues: Diesel and Gas Considerations
Fuel Quality and Contamination
Fuel quality dictates the generator’s performance. At least diesel fuel is highly susceptible to contamination with water, microbial growth, or oxidation, which can lead to particle formation. On the contrary, gasoline tends to age, especially when exposed to air and humidity. The gum deposits can block fuel delivery. The use of fuel stabilizers periodically and proper sealing of tanks can help decrease the risk.
Fuel Line Blockages
Any sediment, debris, or air locks in fuel lines interrupt a steady supply of fuel to the engine. For a diesel generator, air entering the fuel lines, typically due to loose connections, causes the fuel system to lose its prime, thereby preventing the engine from starting. All these call for regular inspection and purging of fuel lines as part of the maintenance process.
Fuel Filter Maintenance
A blocked fuel filter slows the flow of fuel to the engine, whether it is gas or diesel. A fine layer of sediment accumulates on the filter over time, reducing its efficiency. Replacing the filters at the recommended intervals by the generator’s manufacturer ensures a good flow of fuel to the engine, which is essential for the generator’s optimum performance.
Cold Weather Considerations
For a diesel generator, a low temperature can cause fuel to gel: a consequence of the paraffin wax in the diesel solidifying and blocking the fuel system. Using winter-grade diesel or additives designed to prevent gelling lays down a smooth track for cold-weather start-up problems. Gasoline generators, on the other hand, may experience vapor lock in high temperatures, which blocks fuel vapor flow to the carburetor. Adequate storage of fuel and adherence to the directives for cold-weather operation will be beneficial.
Sufficient Fuel Supply
Both diesel and gasoline generators require sufficient fuel to power the engine. Using up fuel can not only halt operation but also cause an issue whereby air tries to enter the fuel system in diesel generators, and then needs to be bled to restore proper functioning. Hence, monitoring fuel levels continuously presents itself as a proactive approach to addressing these operational issues.
Electrical System Failures
Failure in the electrical system of generators is mainly attributed to alternators, circuit breakers, or wiring connections. Alternators transform mechanical energy into electrical energy, and any malfunction in these can greatly hamper power generation. Worn-out or damaged bearings, faulty windings, or a malfunction in the voltage regulator cause most alternator failures. Circuit breakers primarily protect systems against overloads or short circuits, but they may also experience faults due to tripping, aging, or wear caused by frequent triggering. Loose connections or corroded wiring are other common issues that can cause intermittent power supply or complete failure. Testing these components regularly alongside a preventive maintenance schedule would ensure that the chances of electrical failure remain minimal and allow for a long service life of the generator.
Mechanical Problems in Generac and Other Brands
Mechanical failures in generators, such as those by Generac, are generally attributed to typical wear and tear within the components or the lack of regular maintenance, while some are due to design flaws. In general, misalignment of engine components, defective bearings, and worn-out belts are common issues that lead to poor performance or a total breakdown of the unit. Regarding Generac units in particular, there have been reports of valve misadjustments and excessive carbon buildup on the cylinder head, which may result from prolonged periods of operation without proper maintenance.
A multitude of brands have also encountered cooling system failures. Heat dissipation inefficiencies due to a clogged radiator, malfunctioning cooling fans, or a lack of coolant may cause situations that induce high stress on critical engine components. Another common cause is lubrication issues, particularly in older units, where there could be oil leaks or very low oil pressure. The problems will escalate into extensive internal damage, necessitating expensive repairs if left unattended.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
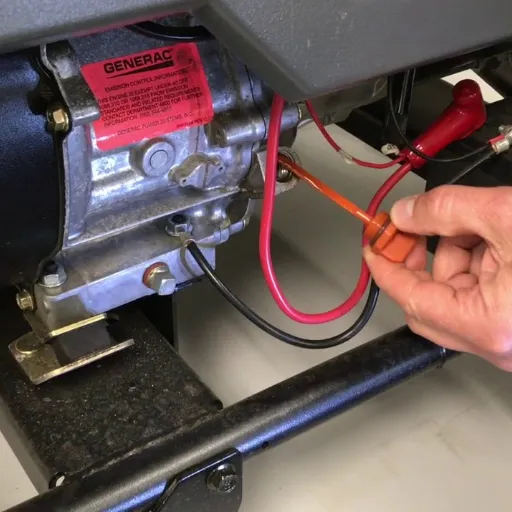

Inspect the Cooling System
First, inspect the radiator, coolant level, and cooling fans. They should be free of any debris in the radiator area, and the coolant level should be within the recommended range specified by the manufacturer. If it is found that the cooling fans are not functioning, an analysis of the fan motor and electrical connections is warranted.
Assess the Thermostat Functionality
Check the thermostat. A stuck open or closed thermostat will restrict coolant flow, resulting in overheating. Replace it with a new one.
Check for Oil Leaks or Low Oil Levels
Look for any signs of oil leakage close to the gaskets and sealing surfaces. Additionally, ensure the engine has sufficient oil and top it up if the level falls below the recommended mark. Otherwise, repair any leaks to prevent further lubrication issues.
Examine Hoses and Belts
Inspect any hoses and belts connected to the engine and cooling system for signs of wear, cracking, or looseness, and replace any that are faulty to ensure proper system operation.
Monitor Operating Temperature
Once all possible problems have been resolved, start the engine and monitor its operating temperature using a trusted gauge or the onboard diagnostic method. Look for consistent readings within the normal range, which will confirm that the problem has been addressed.
Initial Checks: What to Inspect First
Check Coolant Levels
Start by inspecting the coolant reservoir to ensure the fluid level is correct. Low coolant levels cause overheating and inefficiency of the cooling system. It is recommended to always check the coolant level at the suggested mark. If it is found to be otherwise, fill it with the correct type and mixture of coolant as recommended in the vehicle manual.
Inspect the Radiator and Cap
Check the radiator for noticeable points of corrosion, damage, or leaks. The radiator cap should be tested to determine if it can hold the specified pressure, as failure to do so can contribute to coolant loss and, consequently, overheating-related problems.
Assess the Water Pump Functionality
Considering that the water pump will significantly affect the circulation of coolant through the engine. Leaking, unusual sounds, or wobbling movements are signs that the pump is malfunctioning and requires immediate repair.
Evaluate the Thermostat
Failure of the thermostat will cause unpredictable temperature variation inside the engine. If temperature readings during engine operation show any irregularity, the thermostat should be replaced.
Inspect Cooling Fans
Cooling fans should switch on when necessary to maintain the engine temperature within safe limits. Either check the condition of the fan blades or verify if the fan motors can run, and all electrical connections from the power source to the fan motors are intact. A dead cooling fan probably would lead to the radiator failing to dissipate heat properly.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
Evaluate the Thermostat Housing and Seals
Any leakage from the thermostat housing allows coolant to spill out of the system, making it less efficient at regulating the engine’s temperature. Inspect the housing for cracks, warping, or corrosion; also, check the seals or gaskets for any signs of wear or damage. Replace compromised components in order to maintain the integrity of the system, thus avoiding any possibility of overheating occurring.
Analyze Coolant Flow Using Infrared Thermometers
Measure the temperature differentials in the radiator and coolant hoses using an infrared thermometer. Corresponding irregularities in such measurements are clues to blockages, restricted flow, or inefficient heat transfer. Once temperature irregularities have been identified, specific measures can be taken to rectify the problem, such as flushing the system or replacing the blockages.
Conduct a Cooling System Pressure Test
Pressurizing the system allows you, using a pressure tester attached to the radiator cap, to secure and verify the integrity of all components comprising the system, including hoses, rubber seals, the radiator itself, and the engine block, by identifying potential leaks. Watch for drops in pressure as this may uncover hidden weaknesses or compromised seals.
Verify Coolant Sensor Accuracy
A faulty coolant temperature sensor provides incorrect inputs to the vehicle’s ECU, affecting optimal engine performance. Using an onboard diagnostic tool (OBD-II scanner), compare the live sensor data to the expected temperature readings and replace the sensor if inconsistencies arise.
Inspect Water Pump Functionality
The water pump failure means improper coolant circulation, trying to create localized overheating. Look for signs of leaking, unusual noises, or wear of bearings in the pump. Check for tension and alignment of the drive belt supporting the pump as well to ensure it is operational.
Preventative Maintenance Tips for Generators

- Perform Regular Inspections: Check for any visible signs of damage or leaks in or around the generator. Fuel, oil, and coolant levels should also be checked because low levels can cause system failures.
- Run the Generator Periodically: Start the generator under load at least once a month to keep it in good condition and to prevent fuel system problems caused by inactivity.
- Replace Filters and Fluids as Scheduled: Change oil and the filters for fuel, air, and coolant in time according to the manufacturer’s manual. This will ensure optimal operation and avert any contamination.
- Inspect and Maintain the Battery: Make sure the battery is fully charged and properly connected. Clean the terminals if any corrosion is found on them to ensure a constant electrical performance.
- Test the Transfer Switch: Verify the proper functioning of the automatic transfer switch and ensure a seamless power transfer during an outage.
- Keep the Area Clean and Clear: Clear debris, dust, and any obstruction on, around, and beneath the generator to allow free ventilation and reduce fire hazards.
Regular Maintenance Checks to Prevent Cranking Issues
Inspect the Starter Motor and Wiring
Conduct a detailed inspection of traits showing wear, damage, or corrosion on a starter motor and associated wiring. Loose or faulty connections could stop a generator from cranking properly, so ensure all are secure and working as they should.
Examine Fuel Quality and Delivery System
Starting trouble can be caused by poor fuel and obstruction in the fuel delivery system. Change fuel with decent regularity, as stale fuel can ruin engine performance. Then, inspect the fuel lines, filters, and injectors to ensure a consistent and clean fuel flow.
Check Spark Plugs
Defective or worn sexual plugs can delay ignition. Follow the maintenance schedule for cleaning and replacing plugs to assure fast and smooth starts and engine operation.
Test the Battery Voltage and Condition
Check your battery voltage using a multimeter, and ensure it complies with the recommended specifications. Replace any battery that has reduced capacity or a battery that has physical damage. This is to prevent potential issues in the delivery of power.
Review Engine Oil Levels and Quality
When oil is low or degraded, it will deny proper operation to the internal components, thus causing problems in cranking. Always check the oil level and top it up or change it as per the manufacturer’s guidelines for the generator.
Validate the Air Intake System
A blocked air inlet, caused by either clogged filters or debris, obstructs the generator’s ability to start. Regularly inspect and clean the air filters to maintain an unobstructed air path for combustion.
Best Practices for Fuel Storage and Quality
Use High-Quality Fuel
Always use the specified fuel by the manufacturer for your generator, which usually includes restrictions on sulfur content and octane rating. Unworthy fuel will cause poor combustion, deposit of carbon, and wear of the engine as time progresses.
Implement Fuel Stabilization
If you intend to store fuel for an extended period, use a fuel stabilizer that has been approved for this purpose. Such stabilizers reduce oxidation as well as the creation of varnish or gum, which may clog fuel lines and reduce fuel flow.
Store Fuel in Suitable Containers
Use hermetically sealed containers that are corrosion-resistant and made of certified materials, such as steel and HDPE. Avoid containers that may deteriorate with time and introduce particles into fuel.
Regularly Rotate Stored Fuel
Fuel should be stored for less than its recommended period, which may vary depending on the type (diesel or gasoline) and the stabilizers added. The best practice is to rotate fuel every 6 to 12 months for optimal results, while also reducing the likelihood of microbes growing in diesel fuel.
Monitor for Contaminants
Moisture, dirt, and microbial contamination hamper fuel quality. Employ filtration systems designed expressly for the generator to eliminate particulate matter. Periodically, inspect the tanks for any water accumulation or microbial sludge.
Maintain an Optimal Storage Environment
Store the fuel in a manner that ensures it remains dry, calm, and protected from direct sunlight and heat sources, thereby minimizing evaporation and condensation. Ventilation must be appropriate to reduce the accumulation of explosive fumes.
Recommended Tools and Solutions

Fuel Stabilizers
Use a reputable brand of fuel stabilizer to inhibit oxidation and fuel degradation during storage. Such products can considerably augment the lifetime of fuel when used as directed by the manufacturer.
Advanced Filtration Systems
The installation of multi-stage filtration systems, capable of removing water, microbial contaminants, and fine particles, remains strongly recommended. Filters should be changed regularly to prevent clogging and maintain optimal flow rates.
Tank Monitoring Systems
Digital tank monitoring systems can be installed to monitor fuel levels, temperature, and water intrusions. The system provides real-time data with alerts, allowing it to effectively prevent a situation from worsening.
Desiccant Breathers
Desiccant breathers should be installed at fuel tank vents to curb moisture ingress. These devices provide excellent protection against condensation, thus maintaining a consistent fuel quality.
Professional Fuel Testing Kits
Testing kits for quick and accurate analysis of stored fuel’s chemical stability and the presence of contaminants should be used periodically for inspection, at least to ensure they are up to operational standards.
Essential Tools for Troubleshooting Your Generator
Infrared Thermometers
Infrared thermometers enable operators to measure temperatures remotely, thereby avoiding contact with hot exhaust manifolds, bearings, electrical connections, and other high-temperature components. This can help identify overheating components that have shown signs of distress due to temperature, serving as an indicator of operational safety and ultimately ensuring equipment longevity.
Multimeters
Having digital multimeters is great for troubleshooting electrical issues, such as voltage irregularities, grounding problems, and circuit continuity. Make sure the meter you choose is capable of True RMS readings, which means it provides an accurate voltage measurement in environments where non-linear loads are present.
Fuel Contamination Detectors
Fuel Dryness Detectors help quickly detect water or particulate contamination in a generator fuel system. Early detection of these problems can prevent damage to the injectors and provide for proper combustion.
Load Bank Testing Equipment
Portable load banks simulate actual operating conditions by applying a load on the generator. This tool is used to check generator performance under variable load and verify its output according to the specification.
Engine Diagnostic Scanners
The advanced engine diagnosis scanner interfaces with the generator control module to retrieve error codes, monitor engine performance, and provide information on suspected malfunctions. This will make troubleshooting much easier and faster by providing actionable data.
Oscilloscopes
Oscilloscopes are certainly valuable for in-depth electrical diagnostics. They enable the detailed visual inspection of waveform patterns in generator outputs, assisting in the detection of voltage distortion, frequency variation, or harmonic imbalance.
Top Products for Generator Maintenance
- Briggs & Stratton Power Products Maintenance Kit: This package is specifically designed to keep portable generators running at optimal levels. It consists of premium air filters, fuel stabilizers, and spark plugs for optimal engine protection and performance.
- Hose Clamp Pliers for Fuel Line Repairs: Precision-grade hose clamp pliers help clamp fuel lines during maintenance. These tools also help minimize leaks and provide an airtight seal in instances when air could enter the fuel line.
- Fluke 376 FC True-RMS Clamp Meter with iFlex: Widely known for its accuracy and versatility, clamp meters give you advanced diagnostic capability on electrical issues in generators- it measures AC/DC, voltage, resistance- on top of wireless data logging for direct data analysis.
- Onan Generator Oil Change Kit: Suitable for Onan brand generators, this oil change kit includes oil with an SAE rating, oil filters, and detailed instructions for proper lubrication and extended generator service life.
- Kohler Genuine Maintenance Kit: The maintenance kit is designed explicitly for Kohler generators and contains factory-recommended parts, including pre-cleaners, spark plugs, and oil filters. It ensures the parts are compatible and conform to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Infrared Thermometer with Laser Accuracy: Infrared thermometers are non-invasive diagnostic devices that monitor generator temperatures. They detect heat abnormalities in real-time and characterize precise temperature data to identify overheating components.
Using the best-rated products will help any generator maintenance professional increase efficiency, extend generator life, and ensure that generators perform well in demanding conditions.
Reference Sources
-
A Novel Engine Start Mechanism for an Electrified Powertrain
- Summary: This study evaluates a novel planetary starter mechanism designed for hybrid electric vehicles. The research focuses on improving the efficiency and reliability of engine cranking during flying start maneuvers.
-
Optimizing Engine Start Systems with Application to Sailing
- Summary: This paper introduces two innovative mechatronic starter systems aimed at improving engine start quality. The research emphasizes faster and quieter starts, with a focus on applications in sailing and other specialized environments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Why is my diesel generator cranking but not starting?
A: Diesel generator cranking may carry a good number of underlying causes. One common issue could be the glow plugs not working properly; if the engine cannot get warm enough, combustion will not occur. Check water or debris contamination in the fuel systems; it can impact starting. Ensure that fuel is reaching the injection pump and that there is no clogging in the gas line. If the generator cranks but doesn’t start after all this, you might just have to bleed the fuel system and release the air trapped within.
Q: How can I troubleshoot a gas generator that cranks but won’t start?
A: A multitude of steps involve dealing with the inspection of a gas generator cranking but refusing to start. Ensure the gas tank is full and that fresh fuel is being used. Ensure the fuel is flowing smoothly and that the fuel shutoff valve is in the position of being open. Check the plug wire for damage and inspect the oil level, as low oil may prevent your generator from starting. If it still does not, inspect the filter housing for blockages and ensure the start button is functioning properly. If your generator displays error codes, then it is time to check those.
Q: What are common failures in a generator that cranks but does not start?
A: Since the generator cranks but won’t start, there are the usual culprits: fuel- and electrical-system-related problems. Fuel contaminants can keep the engine from starting, so always check for clean fuel. Getting into conflicts with the solenoid and starter can make the cranking process fail to start. Then, another issue could be inadequate maintenance; keeping up with oil checks and changes will solve a large majority of the starting problems. If the generator starts sometimes, check the wiring and connectors for any loose or damaged components. Lastly, valve adjustments may be necessary if there are issues with engine compression.
Q: What could be causing my Generac generator to crank but not start?
A: If the Generac generator is cranking and failing to start, several reasons could be responsible for it. Firstly, ensure that gasoline is freely flowing from the tank to the engine, as any blockage will prevent the engine from starting. Check the generator engine for any indications of inadequate servicing, such as dirty filters and old oil. Check that the fuel shut-off valve is open and that the gas tank is full. If your model has glow plugs, check if they are functioning correctly, as they are vital for cold starting in a diesel engine. Finally, verify the electrical connections to ensure they are all properly connected and functioning.







