Outages can disrupt daily life and create uncertainty, more so on a statewide level. Iowa, which experiences rapidly changing weather conditions coupled with some severe storms, also experiences abrupt power interruptions. This comprehensive guide outlines the essential facets of the Iowa power outage landscape, featuring an interactive map for real-time outage tracking, expert insights into common causes, and tips on how to prepare. Whether you want to understand the landscape of ongoing outages or arm yourself with knowledge for potential future outages, this resource will provide you with the bottom line on which you can build up your understanding to stay informed and resilient.
Understanding Outages in Iowa
Power cuts and infrastructure breaks in Iowa are frequent and can be triggered by various reasons, such as severe storms and extreme weather events like rain accompanied by thunder, snowstorms, or even windy conditions during specific seasons. In fact, such conditions affect power systems, blowing off power lines and, in rare cases, causing outages in some regions, hence resulting in a blackout effect. There are occasions when equipment failures cause glitches in power delivery, such as transformer failures or aged parts of the power grid, from scheduled maintenance acts by utility companies to accidents that occur when someone hits a utility pole. Therefore, being aware of and monitoring these reports concerning outages, which can be queried through respective utility websites and outage maps, is essential. They stay up to date with accurate information concerning disrupted regions.
What Causes Power Outages?
It is a fact that there are generally three main types of power cuts: brief or transient depressions, regular or sustained depressions, and frequent or prolonged ones. Precise sky power cuts are usually the type of power cuts that are temporarily resolved, e.g., by the passage of birds causing soil and other impediments to fall on top of the power lines, which clear soon. Situational (radiation) or Temporary power outages are defined as pending outages that generally last for over an hour and above. Some emergency power outages are caused by domestic power short circuits or exposure to electricity that do not require amputation or necessitate seeking outside medical attention.
Human activities go in combination to cause outages. Excavation work without proper precautions may also result in damage to underground cables, causing a localized interruption. Furthermore, cyberattacks against critical power infrastructure have now emerged as a significant threat and could disrupt service on a regional or even national level. The need is to study these causes to create resilient systems capable of reducing outage frequency and duration.
The Role of Storms in Outages
Storms, such as hurricanes, thunderstorms, and winter storms, are among the primary natural causes of power outages. Power lines are brought down by high winds accompanying these weather events. Heavy rains and floods threaten to damage substations and other electric equipment as well. Lightning is an interesting phenomenon: a strike is momentary, but it can cause power surges that damage infrastructure or trigger trip events. Globally, according to data, most existing power interruptions are due to extreme weather events, with hurricanes alone being responsible for causing power outages affecting millions every year. Ice storms add additional complications in colder climes, contributed by the accumulation of ice over power lines and tree branches —a sure recipe for power lines snapping. Detailed monitoring and forecasting are essential for utility companies to address their storm-related vulnerabilities and maintain a stable supply. Weather tracking technology and grid resilience will help mitigate the effects of these natural disasters.
Emergency Procedures During Outages
Immediate Steps to Take
- Report the outage to the utility provider in the area for their restoration endeavors
- Do not rely on candles as a source of illumination; they are an obvious fire hazard
- Use battery-operated flashlights or lanterns instead
- Unplug electronic devices and appliances to prevent damage from power surges when electricity is restored
Food Safety During Outages
- All perishable products can safely be kept in a refrigerator without power for about 4 hours
- A full freezer may help to maintain the temperature for about 48 hours
- In case a blackout occurs in extreme temperatures, be cautious of the environmental temperatures within the house
Essential Emergency Kit Items
- Mineral water
- Canned foods
- Medications
- Portable power banks
- Battery-operated or hand-crank radio
Accessing Outage Information
If you are looking for information on Power Cuts, the best thing to do is to get in touch with your local power supplier first. Nearly all electricity service providers allow their customers to view the most recent status of outages on their websites, where one can browse outage maps along with expected restoration times, among other helpful details. They also often provide access to this information through their smartphone apps. It is also possible to receive status updates on Outages in the Area through text or email services from the service providers. If there is no reliable connection, you can use the utility company’s hotline phone number to make these inquiries. It is essential to stay informed through local news, especially on the radio, to be prepared for any potential outages that may arise.
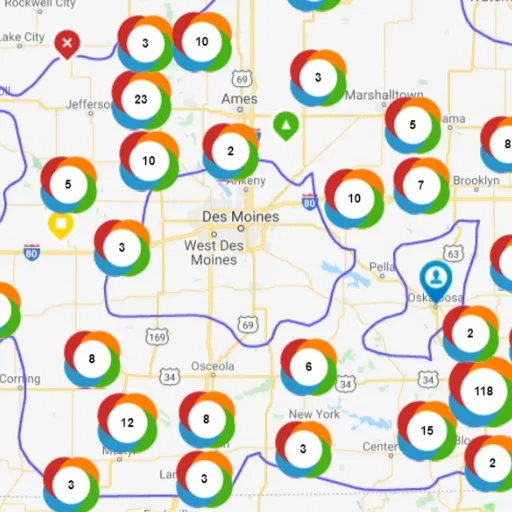
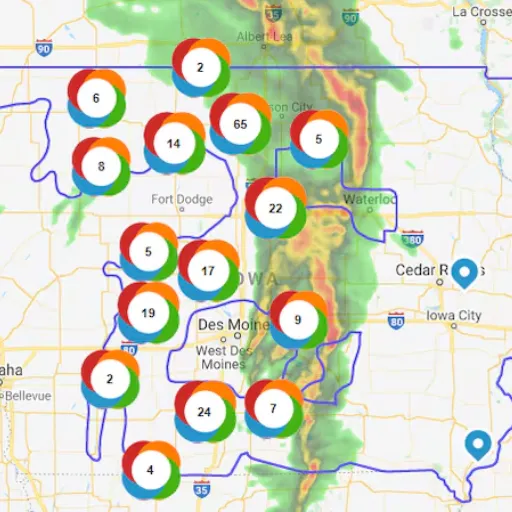
How to Use the Statewide Outage Map?
The Statewide Outage Map is an interactive power outage map that provides a graphical visualization of power failures or strains, covering even the far reaches of the region. The strategy for using the map is discovery, which means that more details can be found on the specific utility provider’s website or their mobile app, such as an older or newer version of the map book. The informal practice of using phone outage mapping involves observing how many households have been affected, which is an example of the situation. It consists of preserving layers of such findings in the most appropriate poses possible.
Combining the map’s information with trustworthy data, including tacit reports on ongoing situations in various territories, one can create a more detailed picture of the extent of the power supply problem and identify potential strategies to address this issue. Many outage maps also display layers of information, allowing one to visualize impacted grids alongside high-risk zones and key alerts. Remember to update the map periodically to stay current with the latest information. This tool is invaluable during emergencies, helping you stay informed and prepared.
Latest Updates on Iowa Power Outages
The most accurate and exhaustive update on power failures in the state of Iowa requires the contribution of digital sources with higher traffic and information. Current data show that in various weather conditions, both commercial centers and remote areas are frequently affected by power outages. Moreover, electricity providers report that they have already begun repairing works and have laid emphasis on critical facilities, such as hospitals, water treatment plants, and emergency services, before moving on to domestic issues. The regions that are most severely affected in the end should experience more frequent power instabilities; hence, it can be deduced that some areas will be the last to reconnect. In that case, managers, planners, and decision-makers require access to the same updates to make well-informed decisions on corrective measures for cases of blackouts and fear, rather than trying to eliminate such outages and instead manage them.
Reporting and Restoring Power

How to Report an Outage
It is essential to contact the relevant services and notify them of the situation in the event of a power failure. You can initially check if the power outage is only applicable to your household. You can investigate whether the problem is due to a shorted conduit or why a fuse in your electrical panel might have blown. If it appears that the power loss is greater than expected, try to contact the relevant utility company using their designated platforms, such as their hotline or the internet. Almost all firms have adopted a trend of mobile applications that allow customers to report power defects, among others, directly.
Vital Information to Provide:
- Your precise address and location
- Visible damage to equipment (power lines, transformers, fallen trees)
- When the problem started
- Any safety hazards you observe
The Process of Restoring Power
To restore power after an outage, it is essential to consider various parameters and prioritize specific activities to ensure a safe and efficient restoration. Typically, the process of reinstating supply adheres to the following rules: the rated and root causes of the outage are identified. It all starts with the utility personnel focusing on the most critical point of the electricity distribution system that serves all end users —the substation. The faulty, previous, or offline substation unit is repaired to minimize power interruption; either the disconnect side is loosened or made fully operable to the other side. After that, the transmission lines are also carefully examined for damage to re-establish the energy supply across the entire system grid.
The initial step in implementing the plan is to secure vital links, after which branch lines or neighborhood lines are addressed. Care is taken, most importantly, in providing efficient supply to special facilities such as hospitals, dispatch centers, and treatment centers for water operations. Then, the restoration crews attempt to quickly remove minor faults, such as disconnecting damaged power lines to residential buildings. Modern devices, Outage Management Systems (OMS), and Geographical Information Systems (GIS) play a significant role in minimizing outages and enhancing response to faults, while ensuring safety measures.
Importance of Community Reporting
Community reporting is essential for modern infrastructure management services, especially during active failures or natural disasters. The citizens’ exceptional response time on issues such as blackouts, water leakages, and the like, highlights the fact that it is difficult to know what is happening unless people manually notify the incidents. These operational complaints or notifications enable service providers to utilize their resources and operations in a way that minimizes downtime and threats. Such cases include the ability to use community members’ information to detect multiple events, identify areas with less social equity, and uncover incidents that were previously unknown yet are now visible to the public. This input at the community level, when applied to modern technology and intelligence probation efforts, establishes a system that ensures the aligned and managed response requirements are met timely and appropriate. Equally important, making it easier for people to share their experiences also serves to bridge the gap between residents and service providers, thereby enhancing the resilience of the entire system.
Staying Prepared for Outages

- Maintain Emergency Supplies
Include a well-stocked emergency kit with non-perishable foods, extra batteries, canned or dried goods, water, and a first aid kit, among other essential items. These are important as they provide the necessary services to those who have been cut off for a long time. - Develop a Communication Plan
Acquire the necessary schematic layout map to familiarize yourself with escape routes and obtain basic contact details, including family, friends, their location map, or work contacts. - Safeguard Electronics and Data
To quickly start a mobile phone and recharge it, if the cell phone has a removable battery, non-rechargeable batteries like Dynathiums or Radium batteries can be used to boost and give the battery a temporary charge. - Stay Updated
One of the possible risks of long-term outages is the loss of equipment or data. Electronic equipment can be protected by cable TV hardwire modems, television receivers, or computer supplies connected to another surge protector and unplugged when in use. - Perform Regular Maintenance
Familiarizing oneself with the targeted area and climatic conditions involves understanding previous climatic conditions, allowing one to adopt a comprehensive approach to handling environmental disasters and become more comfortable.
Taking such measures helps mitigate the effects of outages and increase the level of preparedness to ensure an effective countermeasure.
Emergency Preparedness Tips
Develop a Household Emergency Plan
Draft a detailed emergency plan that addresses various emergencies, including blackouts, earthquakes, and hurricanes. Additionally, consider the map of the area, the location of the emergency meeting spot, and the names of the contacts. Studies have shown that households with emergency plans in place are 42% more likely to respond sooner in the event of a crisis.
Maintain an Emergency Kit
Assemble an emergency kit that contains necessities such as non-perishable food, bottled water (enough for at least one gallon per day per person for at least three days), a flashlight with extra batteries, medicine, a first aid kit, a power bank, and necessary tools. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends stocking up on food and other essential supplies that can last at least 72 hours in the home.
Secure Important Documents
Files and several documents about essential services, together with a compact, waterproof, and fireproof scenario, can be used to store critical information and also protect both documents and hard information. Additionally, as a preventive measure, the documents are supposed to be protected by shielding the electronic content and storing it in a digital backup.
Stay Informed About Local Risks
Look into the environmental hazards available within their area, such as unusually high rates of hurricanes, earthquakes, or water levels in ordinary situations. Moreover, if using professional help come to the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) known for their hazard map while it is for your benefits. This will facilitate safety measures.
Install Backup Power Solutions
When there is no electricity and necessary appliances cannot be used, it is recommended to set up alternative power sources. Different sources of information such as those provided by Energy Information Administration (EIA) have statistics of the data that indicated weather played a role in 96.9% of the power outages in the United States in 2020.
Communication Strategy
Additionally, the centralized contact system is advised to ensure that information is channeled in a unified manner. It will be essential to provide addresses and phone numbers for emergency family members, as the usual communication systems may not be operational.
Plan for Special Needs
Personalize your readiness strategies by incorporating provisions for elderly or disabled relatives, babies, and even pets. For instance, if you suffer from a medical condition, ensure you have sufficient medication. If you have a baby at home, make sure you have enough food. If you have pets, provide them with some food as well. One study by the National Safety Council found that disability-related medical crises are a significant issue in emergency preparedness, considering that they affect 15% of Americans.
Recommended Supplies for Outages
To prepare for unforeseen power blackouts, it is crucial to be well-equipped with both immediate and long-term supplies as a foundation. A large number of essentials should include torches with batteries, which are of utmost importance when one is left with no power supply during the night. For those involved in such a situation, it would be beneficial to stock non-perishable food items, such as canned goods that require manual can openers, as well as prepare freeze-dried food, which can last a long time. The storage of water is equally important, with at least one gallon per day per person for at least three days being the guideline, as advised by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA).
Essential Supplies Checklist:
- Battery-operated flashlights and lanterns
- Extra batteries
- Non-perishable food items
- Manual can opener
- Water (1 gallon per person per day for 3 days minimum)
- Battery or hand-crank radio
- Mobile phone chargers and power banks
- First aid kit and medications
- Portable generators (with proper ventilation)
- Solar chargers for devices
When attempting to reach someone, having a battery or a crank far receiver is vital, especially if the individual needs emergency information. Additionally, mobile phone chargers, also known as power banks, can help ensure the devices continue to work even when there is no power. Some are also arranged for other immediate supplies, such as disaster supplies, alcohol, necessities, some essential medications, a medical kit, and gloves for Infection Control, ensuring gender-sensitive, substantial medical and health services outreach. Extra precautions are also taken for other needs that may arise.
Among the solutions considered are the use of energy such as portable generators and solar chargers, which are effective for critical devices even when there is no electricity, because the equipment is not limited. Cautions should be observed in busy areas, as generators should not be run within closed rooms due to the risk of excessive carbon monoxide buildup. With the above list of materials in hand and periodically checking their storage at home, families can reduce the likelihood of a significant problem hindering their capabilities during disasters, as well as maintain safety measures until everything is back to normal.
Staying Informed During an Outage
Safety and avoiding panic during a blackout are essential tasks. It is necessary to have regular contact with updated information on weather, emergency tests, and the probable presence of electricity soon. Many people consider a battery or hand-powered radio the best option for receiving information that comes in long sound waves when other means of communication fail. Apart from this, people can refer to their phones, where alert apps are often implemented to send information, or mobile bookmarks are created for local government resources. For example, in the case where the internet is up, it would be easy to find the list of outages, the condition of existing paths, and the location of check-ins. It is easy to find, even without a search engine, catalog material concerning this problem. It is wise to develop a set of instructions on how to access information in such instances, which include underscores, such as saving essential contacts and links for availability awareness and decoration.
Resources for Iowa Residents

| Resource | Service | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|
| Iowa Department of Homeland Security and Emergency Management (HSEMD) | Emergency preparedness, response, and recovery resources | www.homelandsecurity.iowa.gov |
| Iowa 2-1-1 Services | Local resources, shelter locations, food banks, mental health support | Dial 2-1-1 or visit www.211iowa.org |
| National Weather Service (NWS) – Iowa Alerts | Severe weather updates and advisories | www.weather.gov |
| Iowa DOT (Department of Transportation) | Road conditions, closures, and travel advisories | www.511ia.org |
| Local County Emergency Management Agencies | Localized emergency response measures | Directory available on HSEMD website |
Where to Find Statewide Outage Information?
To stay current with power interruptions occurring across various regions of a state, several trustworthy avenues can be explored. It is recommended to start from the official websites of the concerned utility, which may be rich in outage maps and news of forthcoming repairs. Moreover, online information about power outages can be provided by the government procurement and finance agency and localized in the preparedness areas of several management resources, thereby ensuring that data indicators and frequent updates correspond to other published records. Lastly, alternative, more sophisticated search configurations can provide some probable answers, such as consolidating all possible data into one, addressing the challenge of determining how much time needs to be spared to review various documents. The dance shown on most makes, without a doubt, demonstrates that one can respect the spectacle and that it does not turn into frustration, regardless of one’s build. Applying these tools facilitates the receipt of the relevant information necessary for effective preparation during the power outages.
Local Utilities and Emergency Contacts
During blackouts, local services and emergency contacts remain vital for knowing the status of the unexpected event. Additionally, several external systems provide data with detailed, updated addresses and phone numbers of all relevant utility operators, emergency management activities, and territorial forces of action. For example, such systems provide the latest operational status in territorial dispatch calls, reports of outages, maps of such outages, as well as information about repair times for cables, all of which help the user make quick decisions. Dependable storage and recovery of any type of data are facilitated by the timely and efficient removal of the shortcomings mentioned above – specifically, the locality and unawareness aspects. These information resources are designed for prompt and easy retrieval of specifics, either locally or nationwide, and, in turn, seek to address as many data needs as possible in the shortest time possible. This is why people can find and ask questions faster, as the friction and steps between points have been eliminated.
Community Support and Assistance Programs
In this day and age, offering help and support services to a particular group of individuals in an event of necessity or even in their normal state is quite important. Another dimension of these programs is the observation, analysis, and delivery of vital demographics and practical information in real-time, thanks to the advanced information systems integrated into them. It also ensures that people with access to toolkits, network resources, and specifics at their disposal seek to comply with the preset so that the target is reached. And beyond that is the fact that improvements should also be made in the necessity to work on them alongside utilization and strategies—Integrating new ways preserves integrity and reduces the time lag for assistance to improve Udem Adriiktrind.
Reference Sources
-
Area angles monitor area stress by responding to line outages
- Key Findings: This study introduces the concept of “area angles” to monitor stress changes in power systems due to line outages. It demonstrates how area angles can quickly identify stress points and potential vulnerabilities in the grid.
-
Impacts of Bad Data on the PMU based Line Outage Detection
- Key Findings: This research demonstrates how false data injection can mask line outages, making them undetectable by traditional monitoring systems. It emphasizes the need for robust data validation mechanisms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How can I report an outage in Iowa?
A: Should you notice there is no power, please get in touch with the local electric cooperative – most of them have a line solely for that. Some cooperatives have alternative means of reporting for further convenience. Be aware that you must equip yourself with the account details and premises details of the fault. The Iowa Association of Electric Cooperatives (IAEC) places a top priority on communication regarding power outages and treats its members as the most critical individuals. The purpose is to reduce the time before the power supply is restored. Therefore, everyone is urged to check the status reports every 15 minutes for new updates.
Q: What causes a storm-related outage in Iowa?
A: Iowa’s power lines can go down after thunderstorm winds have passed, when the poles are corroded due to rain or a thin layer of ice. As a result, extended periods with no power are recorded. In these situations, relief and repair crews from Iowa FDA and various other local electric cooperatives stand ready to render immediate assistance. They will keep track of the weather forecasts and, based on those forecasts, carry out preemptive assessments to ensure that power is restored just as quickly. Even if the weather is bad, follow the news and use data from local power companies to help them make informed decisions and take footage. Such knowledge will help one to avoid any kind of trouble with a blackout, without panic.
Q: How often is the outage information updated for Iowans?
A: Iowans in general catch updated information about outages every quarter of an hour from their nearest electric cooperatives. The word out practically pisses itself a little, but informs on the available service and the ongoing restoration. The existence of worry about the restoration of power encourages the Iowa Association of Electric Cooperatives (IAEC) and cooperatives, especially those serving rural areas, to use different means of communication in connection with the power restoration process. Underground downed homes and wires keep checking these resources, which help the residents update themselves on the latest alerts and update services for outages and their anticipated reconnection times. It also helps them make the right decisions and to know the duration for which they will be and what to do if their electricity is cut off.
Q: What resources are available on the Iowa outage map?
A: Iowa’s power outage map shows people a graphic of what the current situation is in terms of power outages across the state. The software provides a clear view of the specific points in the state where issues exist, the number of customers affected, and also provides a timeframe for the repairs. The electric cooperatives update each other using the map to display real-time operational information, particularly regarding outages. There may as well be features such as incident reporting and assisting relevant organizations and cooperatives involved. Therefore, such system functionalities can be effectively utilized in helping local communities in Iowa, which can easily absorb high levels of outages due to their size.







